Abstract
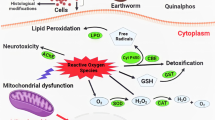
Cycloxaprid (CYC) is a novel neonicotinoid insecticide with high activity against resistant pests but is safe for mammals. The toxic effects of CYC on earthworms (Eisenia fetida) were studied in this paper. The 14-day exposure results showed that CYC is potentially toxic to earthworms, with a 14d-LC50 of 10.21 mg/kg dry soil, and that it induced tissue damage to the epidermis, gut, and neurochord at sublethal doses. During a 21-day exposure, CYC induced oxidative stress in earthworms, and both enzyme activities of catalase (CAT) and superoxide dismutase (SOD) were impacted. In addition, expression of the genes Cat and Sod were down- and upregulated, respectively. The activity of the enzyme acetylcholinesterase (AChE) was increased at day 7 but decreased at day 21 after CYC exposure, while expression of the signal transduction-related genes was significantly regulated. Our study shows for the first time that negative impacts could be induced by CYC on earthworms under both acute and chronic exposure through oxidative stress and gene regulation. The present study provides a database for assessing the environmental risk to non-target organisms resulting from the use of CYC.






Similar content being viewed by others
References
Azevedo-Pereira HM, Lemos MF, Soares AM (2011) Effects of imidacloprid exposure on Chironomus riparius Meigen larvae: linking acetylcholinesterase activity to behaviour. Ecotox Environ SA 74:1210–1215
Capowiez Y, Rault M, Costagliola G, Mazzia C (2005) Lethal and sublethal effects of imidacloprid on two earthworm species (Aporrectodea nocturna and Allolobophora icterica). Biol Fertil Soils 41:135–143
Capowiez Y, Bastardie F, Costagliola G (2006) Sublethal effects of imidacloprid on the burrowing behaviour of two earthworm species: modifications of the 3D burrow systems in artificial cores and consequences on gas diffusion in soil. Soil Biol Biochem 38:285–293
Casida JE (2011) Neonicotinoid metabolism: compounds, substituents, pathways, enzymes, organisms, and relevance. J Agric Food Chem 59:2923–2931
Chang X, Yuan Y, Zhang T, Wang D, Du X, Wu X, Chen H, Chen Y, Jiao Y, Teng H (2015) The toxicity and detoxifying mechanism of cycloxaprid and buprofezin in controlling Sogatella furcifera (Homoptera: Delphacidae). J Insect Sci 15(1):98
China National Standardization Management Committee (2014) Earthworm acute toxicity test (T 31270.15-2014"/T 31270.15-2014). The guidelines on environmental safety assessment for chemical pesticies. Part 15. CNAM, Beijing, China
Cui L, Sun L, Yang D, Yan X, Yuan H (2012) Effects of cycloxaprid, a novel cis-nitromethylene neonicotinoid insecticide, on the feeding behaviour of Sitobion avenae. Pest Manag Sci 68:1484–1491
Cui L, Qi HL, Yang DB, Yuan HZ, Rui CH (2016) Cycloxaprid: a novel cis-nitromethylene neonicotinoid insecticide to control imidacloprid-resistant cotton aphid (Aphis gossypii). Pestic Biochem Physiol 132:96–101
Decourtye A, Devillers J (2010): Insect Ninotinic acetylcholine receptors. In: Thany SH (Editor), Advances in experimental medicine and biology, France, 85–95
Dittbrenner N, Schmitt H, Capowiez Y, Triebskorn R (2011) Sensitivity of Eisenia fetida in comparison to Aporrectodea caliginosa and Lumbricus terrestris after imidacloprid exposure. Body mass change and histopathology. J Soils Sediments 11:1000–1010
Dondero F, Negri A, Boatti L, Marsano F, Mignone F, Viarengo A (2010) Transcriptomic and proteomic effects of a neonicotinoid insecticide mixture in the marine mussel (Mytilus galloprovincialis, Lam.) Sci Total Environ 408:3775–3786
Elbert A, Haas M, Springer B, Thielert W, Nauen R (2008) Applied aspects of neonicotinoid uses in crop protection. Pest Manag Sci 64:1099–1105
Englert D, Bundschuh M, Schulz R (2012) Thiacloprid affects trophic interaction between gammarids and mayflies. Environ Pollut 167:41–46
Federico A, Cardaioli E, Pozzo P, Formichi P, Gallus G, Radi E (2012) Mitochondria, oxidative stress and neurodegenetation. J Neurol Sci 322:254–262
Feng L, Zhang L, Zhang Y, Zhang P, Jiang H (2015) Inhibition and recovery of biomarkers of earthworm Eisenia fetida after exposure to thiacloprid. Environ Sci Pollut Res 22:9475–9482
Han W, Tian Y, Shen X (2018) Human exposure to neoicotinoid insecticides and the evaluation of their potential toxicity: an overview. Chemosphere 192:59–65
Kapoor U, Srivastava MK, Srivastava LP (2011) Toxicological impact of technical imidacloprid on ovarian morphology, hormones and antioxidant enzymes in female rats. Food Chem Toxicol : Int J Published Br Ind Biol Res Assoc 49:3086–3089
Laurino D, Porporato M, Patetta A, Manino A (2011) Toxicity of neonicotinoid insecticides to honey bees: laboratoty tests. B Insectol 64:107–113
Liu S, Zhou Q, Chen C (2012) Antioxidant enzyme activities and lipid peroxidation in earthworm Eisenia fetida exposed to 1,3,4,6,7,8-hexahydro-4,6,6,7,8,8-hexamethyl-cyclopenta-gamma-2-benzopyran. Environ Toxicol 27:472–479
Liu X, Xu X, Li C, Zhang H, Fu Q, Shao X, Ye Q, Li Z (2015a) Degradation of chiral neonicotinoid insecticide cycloxaprid in flooded and anoxic soil. Chemosphere 119:334–341
Liu X, Xu X, Zhang H, Li C, Shao X, Ye Q, Li Z (2015b) Bioavailability and release of nonextractable (bound) residues of chiral cycloxaprid using geophagous earthworm Metaphire guillelmi in rice paddy soil. Sci Total Environ 526:243–250
Mu XY, Wang K, Chai TT, Zhu LZ, Yang Y, Zhang J, Pang S, Wang CJ, Li XF (2015) Sex specific response in cholesterol level in zebrafish (Danio rerio) after long-term exposure of difenoconazole. Environ Pollut 197:278–286
Muangphra P, Tharapoom K, Euawong N, Namchote S, Gooneratne R (2016) Chronic toxicity of commercial chlorpyrifos to earthworm Pheretima peguana. Environ Toxicol 31:1450–1459
OECD (1984) Earthworm, acute toxicity tests. Guideling for testing chemicals. No.207. OECD, Paris, France
OECD (2004) Earthworm reproduction tests. Guideling for testing chemicals. No.222. OECD, Paris, France
Qi SZ, Wand D, Zhu L, Teng M, Wang C, Xue X, Wu L (2018) Neonicotinoid insecticde imidacloprid, guadipyr, and cycoxaprid induce acute oxidative stress in Daphnia magna. Ecotox Environ SA 148:352–358
Qi SZ, Wang C, Chen XF, Qin ZH, Li XF, Wang CJ (2013) Toxicity assessments with Daphnia magna of guadipyr, a new neonicotinoid insecticide and studies of its effect on acetylcholinesterase (AChE), glutathione S-transferase (GST), catalase (CAT) and chitobiase activities. Ecotox Environ SA 98:339–344
Sanchez-Bayo F (2014) The trouble with neonicotinoids: chronic exposure to widely used insecticides kills bees and many other invertebrates. Science 346:806–807
Sanchez-Bayo F, Goulson D, Pennacchio F, Nazzi F, Goka K, Desneux N (2016) Are bee diseases linked to pesticides?—a brief review. Environ Int 89-90:7–11
Sanchez-Hernandez JC, Narvaez C, Sabat P, Martinez Mocillo S (2014) Integrated biomarker analysis of chlorpyrifos metabolism and toxicity in the earthworm Aporrectodea caliginosa. Sci Total Environ 490:445–455
Sawasdee B, Kohler HR (2009) Embryo toxicity of pesticides and heavy metals to the ramshorn snail, Marisa cornuarietis (Prosobranchia). Chemosphere 75:1539–1547
Shao X, Xia S, Durkin KA, Casida JE (2013) Insect nicotinic receptor interactions in vivo with neonicotinoid, organophosphorus, and methylcarbamate insecticides and a synergist. P Natl Acad Sci USA 110(43):17273–17277
Shi Z, Tang Z, Wang C (2017) A brief review and evaluation of earthworm biomarkes in soil pollution assessment. Environ Sci Pollut Res 24:13284–13294
Song Y, Zhu LS, Wang J, Wang JH, Liu W, Xie H (2009) DNA damage and effects on antioxidative enzymes in earthworm (Eisenia foetida) induced by atrazine. Soil Biol Biochem 41:905–909
Su WC, Zhou YH, Ma YQ, Wang L, Zhang Z, Rui CH, Duan HX, Qin ZH (2012) N’-nitro-2-hydrocarbylidenehydrazinecarboximidamides: design, synthesis, crystal structure, insecticidal activity, and structure-activity relationships. J Agric Food Chem 60:5028–5034
Wang K, Mu XY, Qi SZ, Chai TT, Pang S, Yang Y, Wang CJ, Jiang JZ (2015a) Toxicity of a neonicotinoid insecticide, guadipyr, in earthworm (Eisenia fetida). Ecotoxicol Environ SA 114:17–22
Wang K, Pang S, Mu XY, Qi SZ, Li DZ, Cui F, Wang CJ (2015b) Biological response of earthworm, Eisenia fetida, to five neonicotinoid insecticides. Chemosphere 132:120–126
Wang Y, Cang T, Zhao X, Yu R, Chen L, Wu C, Wang Q (2012) Comparative acute toxicity of twenty-four insecticides to earthworm, Eisenia fetida. Ecotoxicol Environ SA 79:122–128
Xu R, Luo M, Xia R, Meng X, Xu X, Xu Z, Cheng J, Shao X, Li H, Li Z (2014a) Seven-membered azabridged neonicotinoids: synthesis, crystal structure, insecticidal assay, and molecular docking studies. J Agric Food Chem 62:11070–11079
Xu R, Xia R, Luo M, Xu X, Cheng J, Shao X, Li Z (2014b) Design, synthesis, crystal structures, and insecticidal activities of eight-membered azabridge neonicotinoid analogues. J Agric Food Chem 62:381–390
Zhang J, Xiong K, Chen A, Li F (2017) Toxicity of a novel neonicotinoid insecticide paichongding to earthworm Eisenia fetida. Soil Sediment Contam 26(3):235–246
Zhang L, Ji F, Li M, Cui Y, Wu B (2014) Short-term effects of Dechlorane plus on the earthworm Eisenia fetida determined by a systems biology approach. J Hazard Mater 273:239–246
Zhang Q, Zhang G, Yin P, Lv Y, Yuan S, Chen J, Wei B, Wang C (2015) Toxicological effects of soil contaminated with spirotetramat to the earthworm Eisenia fetida. Chemosphere 139:138–145
Acknowledgements
This work was mainly funded by the China Post-doctoral Science Foundation (No.2015M570178) and kindly supported by Dr. Wenting Zhao by the Young Teacher Science Fund of Da Bei Nong Group (15ZK002) and Young Teacher Science Fund of Beijng University of Agriculture (2017516006). We thank Dr. Shao Xusheng in East China University of Science and Technology for kindly providing CYC.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Additional information
Responsible editor: Philippe Garrigues
Electronic supplementary material
ESM 1
(DOCX 106 kb)
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Qi, S., Wang, D., Zhu, L. et al. Effects of a novel neonicotinoid insecticide cycloxaprid on earthworm, Eisenia fetida. Environ Sci Pollut Res 25, 14138–14147 (2018). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11356-018-1624-z
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11356-018-1624-z