Abstract
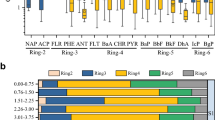
Environmental pollution due to primitive e-waste dismantling activities has been intensively investigated over the last decade in the south-eastern coastal region of China. In the present study, we investigated the distribution and composition of polycyclic aromatic hydrocarbons (PAHs) in soils and plants around e-waste recycling sites in Longtang, Guangdong province, South China. The results indicated that PAH concentrations in rhizosphere soil and non-rhizosphere soil were in the range of 133 to 626 ng/g and 60 to 816 ng/g, respectively, while PAH levels in plant tissue were 96 to 388 ng/g in shoots and 143 to 605 ng/g in roots. PAHs were enriched in rhizosphere soils in comparison with non-rhizosphere soils. The concentrations of PAHs in plant tissues varied greatly among plant cultivars, indicating that the uptake of PAHs by plants is species-dependent. Different profiles of PAHs in the soil and the corresponding plant tissue implied that PAH uptake and translocation by plants were selective.The total daily intakes of PAHs and carcinogenic PAHs through vegetables at the e-waste recycling site were estimated to be 99 and 22 ng/kg/day, respectively, suggesting that potential health risks associated with the consumption of contaminated vegetables should not be ignored.


Similar content being viewed by others
References
Becerra-Castro C, Kidd PS, Rodriguez-Garrido B, Monterroso C, Santos-Ucha P, Prieto-Fernandez A (2013) Phytoremediation of hexachlorocyclohexane (HCH)-contaminated soils using Cytisus striatus and bacterial inoculants in soils with distinct organic matter content. Environ Pollut 178:202–210
Burken JG, Schnoor JL (1997) Uptake and metabolism of atrazine by poplar trees. Environ Sci Technol 31:1399–1406
Cai QY, Mo CH, Li YH, Zeng QY, Katsoyiannis A, Wu QT, Ferard JF (2007) Occurrence and assessment of polycyclic aromatic hydrocarbons in soils from vegetable fields of the Pearl River Delta, South China. Chemosphere 68:159–168
Cao SP, Ni HG, Qin PH, Zeng H (2010) Occurrence and human non-dietary exposure of polycyclic aromatic hydrocarbons in soils from Shenzhen, China. J Environ Monitor 12:1445–1450
Chen LG, Ran Y, Xing BS, Mai BX, He JH, Wei XG, Fu JM, Sheng GY (2005) Contents and sources of polycyclic aromatic hydrocarbons and organochlorine pesticides in vegetable soils of Guangzhou, China. Chemosphere 60:879–890
Chen SJ, Tian M, Zheng J, Zhu ZC, Luo Y, Luo XJ, Mai BX (2014) Elevated levels of polychlorinated biphenyls in plants, air, and soils at an E-waste site in southern China and enantioselective biotransformation of chiral PCBs in plants. Environ Sci Technol 48:3847–3855
Chen ZX, Ni HG, Jing X, Chang WJ, Sun JL, Zeng H (2015) Plant uptake, translocation, and return of polycyclic aromatic hydrocarbons via fine root branch orders in a subtropical forest ecosystem. Chemosphere 131:192–200
Desalme D, Binet P, Chiapusio G (2013) Challenges in tracing the fate and effects of atmospheric polycyclic aromatic hydrocarbon deposition in vascular plants. Environ Sci Technol 47:3967–3981
Duan HB, Li JH, Liu YC, Yamazaki N, Jiang W (2011) Characterization and inventory of PCDD/Fs and PBDD/Fs emissions from the incineration of waste printed circuit board. Environ Sci Technol 45:6322–6328
Gao YZ, Ren LL, Ling WT, Gong SS, Sun BQ, Zhang Y (2010) Desorption of phenanthrene and pyrene in soils by root exudates. Bioresour Technol 101:1159–1165
Gerhardt KE, Huang XD, Glick BR, Greenberg BM (2009) Phytoremediation and rhizoremediation of organic soil contaminants: potential and challenges. Plant Sci 176:20–30
Haritash AK, Kaushik CP (2009) Biodegradation aspects of polycyclic aromatic hydrocarbons (PAHs): a review. J Hazard Mater 169:1–15
Horiguchi H, Oguma E, Sasaki S, Miyamoto K, Ikeda Y, Machida M, Kayama F (2005) Environmental exposure to cadmium at a level insufficient to induce renal tubular dysfunction does not affect bone density among female Japanese farmers. Environ Res 97:83–92
Hsu FC, Marxmiller RL, Yang AYS (1990) Study of root uptake and xylem translocation of cinmethylin and related-compounds in detopped soybean roots using a pressure chamber technique. Plant Physiol 93:1573–1578
Huang HL, Zhang SZ, Christie P, Wang S, Xie M (2010) Behavior of decabromodiphenyl ether (BDE-209) in the soil-plant system: uptake, translocation, and metabolism in plants and dissipation in soil. Environ Sci Technol 44:663–667
Huang DY, Liu CP, Li FB, Liu TX, Liu CS, Tao L, Wang Y (2014) Profiles, sources, and transport of polycyclic aromatic hydrocarbons in soils affected by electronic waste recycling in Longtang, south China. Environ Monit Assess 186:3351–3364
Javorska H, Tlustos P, Kaliszova R (2009) Degradation of polychlorinated biphenyls in the rhizosphere of rape, Brassica Napus L. B Environ Contam Tox 82:727–731
Joner EJ, Leyval C (2003) Rhizosphere gradients of polycyclic aromatic hydrocarbon (PAH) dissipation in two industrial soils and the impact of arbuscular mycorrhiza. Environ Sci Technol 37:2371–2375
Kaimi E, Mukaidani T, Miyoshi S, Tamaki M (2006) Ryegrass enhancement of biodegradation in diesel-contaminated soil. Environ Exp Bot 55:110–119
Labunska I, Harrad S, Wang MJ, Santillo D, Johnston P (2014) Human dietary exposure to PBDEs around E-waste recycling sites in eastern China. Environ Sci Technol 48:5555–5564
Leung A, Cai ZW, Wong MH (2006) Environmental contamination from electronic waste recycling at Guiyu, southeast China. J Mater Cycles Waste Manage 8:21–33
Leung AOW, Luksemburg WJ, Wong AS, Wong MH (2007) Spatial distribution of polybrominated diphenyl ethers and polychlorinated dibenzo-p-dioxins and dibenzofurans in soil and combusted residue at Guiyu, an electronic waste recycling site in southeast China. Environ Sci Technol 41:2730–2737
Liao CY, Lv JG, Fu JJ, Zhao ZS, Liu F, Xue QZ, Jiang GB (2012) Occurrence and profiles of polycyclic aromatic hydrocarbons (PAHs), polychlorinated biphenyls (PCBs) and organochlorine pesticides (OCPs) in soils from a typical e-waste recycling area in Southeast China. Int J Environ Health Res 22:317–330
Limmer MA, Burken JG (2014) Plant translocation of organic compounds: molecular and physicochemical predictors. Environ Sci Tech Let 1:156–161
Lin DH, Zhu LZ, He W, Tu YT (2006) Tea plant uptake and translocation of polycyclic aromatic hydrocarbons from water and around air. J Agric Food Chem 54:3658–3662
Luo CL, Liu CP, Wang Y, Liu XA, Li FB, Zhang G, Li XD (2011) Heavy metal contamination in soils and vegetables near an e-waste processing site, south China. J Hazard Mater 186:481–490
Martorell I, Perello G, Marti-Cid R, Castell V, Llobet JM, Domingo JL (2010) Polycyclic aromatic hydrocarbons (PAH) in foods and estimated PAH intake by the population of Catalonia, Spain: temporal trend. Environ Int 36:424–432
Mattina MJI, Iannucci-Berger W, Eitzer BD, White JC (2004) Rhizotron study of Cucurbitaceae: transport of soil-bound chlordane and heavy metal contaminants differs with genera. Environ Chem 1:86–89
Montiel-Rozas MM, Madejon E, Madejon P (2016) Effect of heavy metals and organic matter on root exudates (low molecular weight organic acids) of herbaceous species: an assessment in sand and soil conditions under different levels of contamination. Environ Pollut 216:273–281
Mueller KE, Mueller-Spitz SR, Henry HF, Vonderheide AP, Soman RS, Kinkle BK, Shann JR (2006) Fate of pentabrominated diphenyl ethers in soil: abiotic sorption, plant uptake, and the impact of interspecific plant interactions. Environ Sci Technol 40:6662–6667
Nisbet ICT, Lagoy PK (1992) Toxic equivalency factors (Tefs) for polycyclic aromatic-hydrocarbons (Pahs). Regul Toxicol Pharmacol 16:290–300
Ravindra K, Sokhi R, Van Grieken R (2008) Atmospheric polycyclic aromatic hydrocarbons: source attribution, emission factors and regulation. Atmos Environ 42:2895–2921
Smith KEC, Jones KC (2000) Particles and vegetation: implications for the transfer of particle-bound organic contaminants to vegetation. Sci Total Environ 246:207–236
Sui H, Li L, Zhu XZ, Chen DY, Wu GZ (2016) Modeling the adsorption of PAH mixture in silica nanopores by molecular dynamic simulation combined with machine learning. Chemosphere 144:1950–1959
Szoboszlay M, Lambers J, Chappell J, Kupper JV, Moe LA, McNear DH (2015) Comparison of root system architecture and rhizosphere microbial communities of Balsas teosinte and domesticated corn cultivars. Soil Biol Biochem 80:34–44
Tao YQ, Zhang SZ, Zhu YG, Christie P (2009) Uptake and acropetal translocation of polycyclic aromatic hydrocarbons by wheat (Triticum aestivum L.) grown in field-contaminated soil. Environ Sci Technol 43:3556–3560
Tian M, Chen SJ, Wang J, Luo Y, Luo XJ, Mai BX (2012) Plant uptake of atmospheric brominated flame retardants at an E-waste site in southern China. Environ Sci Technol 46:2708–2714
Trapp S (2000) Modelling uptake into roots and subsequent translocation of neutral and ionisable organic compounds. Pest Manag Sci 56:767–778
Wang WT, Simonich SLM, Xue MA, Zhao JY, Zhang N, Wang R, Cao J, Tao S (2010) Concentrations, sources and spatial distribution of polycyclic aromatic hydrocarbons in soils from Beijing, Tianjin and surrounding areas, North China. Environ Pollut 158:1245–1251
Wang Y, Luo CL, Li J, Yin H, Li XD, Zhang G (2011a) Characterization and risk assessment of polychlorinated biphenyls in soils and vegetations near an electronic waste recycling site, South China. Chemosphere 85:344–350
Wang Y, Luo CL, Li J, Yin H, Li XD, Zhang G (2011b) Characterization of PBDEs in soils and vegetations near an e-waste recycling site in South China. Environ Pollut 159:2443–2448
Wang Y, Tian ZJ, Zhu HL, Cheng ZN, Kang ML, Luo CL, Li J, Zhang G (2012) Polycyclic aromatic hydrocarbons (PAHs) in soils and vegetation near an e-waste recycling site in South China: concentration, distribution, source, and risk assessment. Sci Total Environ 439:187–193
Wang SR, Li HS, Lin CX (2013) Physiological, biochemical and growth responses of Italian ryegrass to butachlor exposure. Pestic Biochem Phys 106:21–27
Wang Y, Luo CL, Li J, Yin H, Zhang G (2014) Influence of plants on the distribution and composition of PBDEs in soils of an e-waste dismantling area: evidence of the effect of the rhizosphere and selective bioaccumulation. Environ Pollut 186:104–109
Wang SR, Wang Y, Lei WR, Sun YT, Wang YJ, Luo CL, Zhang G (2015a) Simultaneous enhanced removal of Cu, PCBs, and PBDEs by corn from e-waste-contaminated soil using the biodegradable chelant EDDS. Environ Sci Pollut Res 22:18203–18210
Wang Y, Wang SR, Xu Y, Luo CL, Li J, Zhang G (2015b) Characterization of the exchange of PBDEs in a subtropical paddy field of China: a significant inputs of PBDEs via air-foliage exchange. Environ Pollut 205:1–7
Wang SR, Wang Y, Luo CL, Li J, Yin H, Zhang G (2016a) Plant selective uptake of halogenated flame retardants at an e-waste recycling site in southern China. Environ Pollut 214:705–712
Wang SR, Wang Y, Song MK, Luo CL, Li J, Zhang G (2016b) Distributions and compositions of old and emerging flame retardants in the rhizosphere and non-rhizosphere soil in an e-waste contaminated area of South China. Environ Pollut 208:619–625
Warezak T, Wlodarczyk-Makula M, Sadecka Z (2016) Accumulation of PAHs in plants from vertical flow-constructed wetland. Desalin Water Treat 57:1273–1285
Welsh GL, Mueller KE, Soman RS, Vonderheide AP, Shann JR (2009) Accessibility of polybrominated diphenyl ether congeners in aging soil. J Environ Monit 11:1658–1663
White JC, Mattina MJI, Eitzer BD, Iannucci-Berger W (2002) Tracking chlordane compositional and chiral profiles in soil and vegetation. Chemosphere 47:639–646
Wild SR, Jones KC (1994) The significance of polynuclear aromatic-hydrocarbons applied to agricultural soils in sewage sludges in the UK. Waste Manag Re 12:49–59
Yoon E, Park K, Lee H, Yang JH, Lee C (2007) Estimation of excess cancer risk on time-weighted lifetime average daily intake of PAHs from food ingestion. Hum Ecol Risk Assess 13:669–680
Zhang YX, Tao S (2009) Global atmospheric emission inventory of polycyclic aromatic hydrocarbons (PAHs) for 2004. Atmos Environ 43:812–819
Zhang HB, Luo YM, Wong MH, Zhao QG, Zhang GL (2006) Distributions and concentrations of PAHs in Hong Kong soils. Environ Pollut 141:107–114
Zhang T, Huang YR, Chen SJ, Liu AM, Xu PJ, Li N, Qi L, Ren Y, Zhou ZG, Mai BX (2012) PCDD/Fs, PBDD/Fs, and PBDEs in the air of an e-waste recycling area (Taizhou) in China: current levels, composition profiles, and potential cancer risks. J Environ Monitor 14:3156–3163
Acknowledgments
This study was supported by the National Natural Science Foundation of China (Nos. 41322008, 41673111, and 41603072), the Joint Funds of the National Natural Science Foundation of China and the Natural Science Foundation of Guangdong Province, China (No. U15012345) and the China Postdoctoral Science Foundation (2016M602552).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding authors
Additional information
Responsible editor: Zhihong Xu
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Wang, Y., He, J., Wang, S. et al. Characterisation and risk assessment of polycyclic aromatic hydrocarbons (PAHs) in soils and plants around e-waste dismantling sites in southern China. Environ Sci Pollut Res 24, 22173–22182 (2017). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11356-017-9830-7
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11356-017-9830-7