Abstract
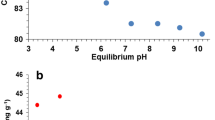
This study is aiming to investigate tetravalent manganese feroxyhyte (TMFx) adsorption efficiency in removing heavy metals. The motivation of this study was the fact that TMFx is a highly negatively charged nanostructure material and that the metals Cd, Hg, and Ni were characterized as priority pollutants for drinking water. TMFx was evaluated through batch and continuous flow experiments in National Sanitation Foundation (NSF) water matrix which simulated the physicochemical characteristics of natural water. Water’s pH significantly influences Cd and Ni adsorption efficiency which gradually increases when pH value rises from 5 to 9, while the corresponding one for Hg remains almost constant. Thermodynamic data showed a spontaneous and an exothermic nature weak-chemisorption (ΔΗ° = −17.5 ± 2 kJ/mol) of Cd, Ni, and Hg by TMFx. The determined ranking of adsorption affinity and selectivity (Cd > Ni > Hg) seems to be governed by the metals’ speciation, as well as by hydration free energy, which is influenced, however, by their atomic radius. The lower adsorption capacity and selectivity of TMFx for Hg should be attributed both to uncharged species and to higher atomic radius. The similar Cd and Ni speciation in the NSF water matrix leads to the conclusion that the better affinity, selectivity, and adsorption kinetic of Cd versus Ni should be attributed to the lower hydration free energy of Cd which is in turn related to its higher atomic radius. The faster adsorption kinetic (Hg > Cd > Ni) of Hg may be attributed to the lower radius of its anhydrate species. Furthermore, TMFx showed high removal efficiency under continuous flow application in an adsorption bed setup. The determined uptake capacity (q RL) at equilibrium-breakthrough concentration equal to the drinking water regulation limit (RL) of each metal were q 1 = 2.5 μg Hg/mg TMFx, q 5 = 5.2 μg Cd/mg TMFx, and q 20 = 7.1 μg Ni/mg TMFx. Leaching tests of spent TMFx samples from the rapid small-scale column tests (RSSCTs) could be treated either as inert wastes after Cd and Ni adsorption or as non-hazardous waste after Hg adsorption.









Similar content being viewed by others
References
Amaro-Estrada JI, Maron L, Ramírez-Solis A (2013) Aqueous solvation of Hg(OH)2: energetic and dynamical density functional theory studies of the Hg(OH)2-(H2O)n (n = 1-24) structures. J Phys Chem A 117:9069–9075. doi:10.1021/jp405500f
Azizian S (2004) Kinetic models of sorption: a theoretical analysis. J Colloid Interface Sci 276:47–52. doi:10.1016/j.jcis.2004.03.048
Carro L, Barriada JL, Herrero R, Sastre de Vicente ME (2011) Adsorptive behaviour of mercury on algal biomass: competition with divalent cations and organic compounds. J Hazard Mater 192:284–291
Charerntanyarak L (1999) Heavy metals removal by chemical coagulation and precipitation. In: Water Science and Technology. pp 135–138
Chiarle S, Ratto M, Rovatti M (2000) Mercury removal from water by ion exchange resins adsorption. Water Res 34:2971–2978. doi:10.1016/S0043-1354(00)00044-0
Directive 98/8/EC of the European Parliament and of the Council of 16 February 1998 concerning the placing of biocidal products on the market
Dong L, Zhu Z, Ma H, Qiu Y, Zhao J (2010) Simultaneous adsorption of lead and cadmium on MnO2-loaded resin. J Environ Sci 22:225–229. doi:10.1016/S1001-0742(09)60097-8
Engates KE, Shipley HJ (2011) Adsorption of Pb, Cd, Cu, Zn, and Ni to titanium dioxide nanoparticles: effect of particle size, solid concentration, and exhaustion. Environ Sci Pollut Res 18:386–395. doi:10.1007/s11356-010-0382-3
European Commission (2001) Decision No. 2455/2001/EC of the European Parliament and of the Council of 20 November 2001 establishing the list of priority substances in the field of water policy and amending Directive 2000/60/EC. Off J Eur Union L 331:1–5. http://eur-lex.europa.eu/pri/en/oj/ dat/2003/l_285/l_28520031101en00330037.pdf
European Committee for Standardization (2002) ΕΝ 12457-2: characterisation of waste—leaching—compliance test for leaching of granular waste materials and sludges—part 2: one stage batch test at liquid to solid ratio of 10 L/kg for materials with particle size below 4 mm (without or with size reduction). European Standard, Brussels
Fernandez-Luqueno F, Lopez-Valdez F, Gamero-Melo P, Luna-Suarez S, Aguilera-Gonzalez EN, Martinez AI, García-Guillermo MDS, Hernandez-Martinez G, Herrera-Mendoza R, Alvarez-Garza MA, Perez-Velazquez IR (2013) Heavy metal pollution in drinking water—a global risk for human health: a review. Afr J Environ Sci Technol 7:567–584
Fu F, Wang Q (2011) Removal of heavy metal ions from wastewaters: a review. J Environ Manag 92:407–418
Gusain D, Singh PK, Sharma YC (2016) Kinetic and equilibrium modeling of adsorption of cadmium on nano crystalline zirconia using response surface methodology. Environ Nanotechnol Monit Manag 6:99–107. doi:10.1016/j.enmm.2016.07.002
Hakami O, Zhang Y, Banks CJ (2012) Thiol-functionalised mesoporous silica-coated magnetite nanoparticles for high efficiency removal and recovery of Hg from water. Water Res 46:3913–3922. doi:10.1016/j.watres.2012.04.032
Herrero R, Lodeiro P, Rey-Castro C, Vilarino T, Sastre de Vicente ME (2005) Removal of inorganic mercury from aqueous solutions by biomass of the marine macroalga Cystoseira baccata. Water Res 39:3199–3210
Hua M, Zhang S, Pan B, Zhang W, Lv L, Zhang Q (2012) Heavy metal removal from water/wastewater by nanosized metal oxides: a review. J Hazard Mater 211–212:317–331
Kang SY, Lee JU, Moon SH, Kim KW (2004) Competitive adsorption characteristics of Co2+, Ni2+, and Cr3+ by IRN-77 cation exchange resin in synthesized wastewater. Chemosphere 56:141–147. doi:10.1016/j.chemosphere.2004.02.004
Karami H (2013) Heavy metal removal from water by magnetite nanorods. Chem Eng J 219:209–216. doi:10.1016/j.cej.2013.01.022
Kokkinos E, Simeonidis K, Pinakidou F, Katsikini M, Mitrakas M (2017) Optimization of tetravalent manganese feroxyhyte’s negative charge density: a high-performing mercury adsorbent from drinking water. Sci Total Environ 574:482–489. doi:10.1016/j.scitotenv.2016.09.068
Kyzas GZ, Kostoglou M (2014) Green adsorbents for wastewaters: a critical review. Materials (Basel) 7:333–364
Li X, Zeng GM, Huang JH, Zhang C, Fang YY, Qu YH, Luo F, Lin D, Liu HL (2009) Recovery and reuse of surfactant SDS from a MEUF retentate containing Cd2+ or Zn2+ by ultrafiltration. J Memb Sci 337:92–97. doi:10.1016/j.memsci.2009.03.030
Liu HY, Fang CH, Fang Y, Zhou YQ, Ge HW, Zhu FY, Sun PC, Miao JT (2016) Characterizing Ni(II) hydration in aqueous solution using DFT and EXAFS. J Mol Model:2–10
Mahmoud ME, Nabil GM, Mahmoud SME (2015) High performance nano-zirconium silicate adsorbent for efficient removal of copper (II), cadmium (II) and lead (II). J Environ Chem Eng 3:1320–1328. doi:10.1016/j.jece.2014.11.027
Mitrakas MG, Bakaloulis AK, Gkinis KT (2012) Studies on arsenic adsorption by the use of aluminum anodizing sludge. Desalin Water Treat 39:235–247
Persson I (2010) Hydrated metal ions in aqueous solution: how regular are their structures? Pure Appl Chem 82:1901–1917. doi:10.1351/PAC-CON-09-10-22
Ramesh A, Lee DJ, Wong JWC (2005) Thermodynamic parameters for adsorption equilibrium of heavy metals and dyes from wastewater with low-cost adsorbents. J Colloid Interface Sci 291:588–592. doi:10.1016/j.jcis.2005.04.084
Randall SR, Sherman DM, Ragnarsdottir KV, Collins CR (1999) The mechanism of cadmium surface complexation on iron oxyhydroxide minerals. Geochim Cosmochim Acta 63:2971–2987. doi:10.1016/S0016-7037(99)00263-X
Ruckenstein E, Vaidyanathan AS, Youngquist GR (1971) Sorption by solids with bidisperse pore structures. Chem Eng Sci 26:1305–1318. doi:10.1016/0009-2509(71)80051-9
Ruthven DM (1984) Principles of adsorption and adsorption processes. Wiley & Sons, New York
Samper E, Rodríguez M, De la Rubia MA, Prats D (2009) Removal of metal ions at low concentration by micellar-enhanced ultrafiltration (MEUF) using sodium dodecyl sulfate (SDS) and linear alkylbenzene sulfonate (LAS). Sep Purif Technol 65:337–342. doi:10.1016/j.seppur.2008.11.013
Shipley HJ, Engates KE, Grover VA (2013) Removal of Pb(II), Cd(II), Cu(II), and Zn(II) by hematite nanoparticles: effect of sorbent concentration, pH, temperature, and exhaustion. Environ Sci Pollut Res 20:1727–1736. doi:10.1007/s11356-012-0984-z
Smith SD, Edwards M (2005) The influence of silica and calcium on arsenate sorption to oxide surfaces. J Water Supply Res Technol AQUA 54:201–211
Tansel B (2012) Significance of thermodynamic and physical characteristics on permeation of ions during membrane separation: hydrated radius, hydration free energy and viscous effects. Sep Purif Technol 86:119–126. doi:10.1016/j.seppur.2011.10.033
Tian HZ, Zhu CY, Gao JJ, Cheng K, Hao JM, Wang K, Hua SB, Wang Y, Zhou JR (2015) Quantitative assessment of atmospheric emissions of toxic heavy metals from anthropogenic sources in China: historical trend, spatial distribution, uncertainties, and control policies. Atmos Chem Phys 15:10127–10147. doi:10.5194/acp-15-10127-2015
Tien C (1994) Adsorption calculation and modeling. Butterworth-Heinemann, Boston
Tresintsi S, Mitrakas M, Simeonidis K, Kostoglou M (2015) Kinetic modeling of AS(III) and AS(V) adsorption by a novel tetravalent manganese feroxyhyte. J Colloid Interface Sci 460:1–7. doi:10.1016/j.jcis.2015.07.075
Ulewicz M, Walkowiak W, Bartsch RA (2006) Ion flotation of zinc(II) and cadmium(II) with proton-ionizable lariat ethers—effect of cavity size. Sep Purif Technol 48:264–269. doi:10.1016/j.seppur.2005.07.037
Yadanaparthi SKR, Graybill D, von Wandruszka R (2009) Adsorbents for the removal of arsenic, cadmium, and lead from contaminated waters. J Hazard Mater 171:1–15
Yu JG, Yue BY, Wu XW, Liu Q, Jiao FP, Jiang XY, Chen XQ (2016) Removal of mercury by adsorption: a review. Environ Sci Pollut Res 23:5056–5076. doi:10.1007/s11356-015-5880-x
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Additional information
Responsible editor: Philippe Garrigues
Electronic supplementary material
ESM 1
(DOCX 158 kb).
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Kokkinos, E., Soukakos, K., Kostoglou, M. et al. Cadmium, mercury, and nickel adsorption by tetravalent manganese feroxyhyte: selectivity, kinetic modeling, and thermodynamic study. Environ Sci Pollut Res 25, 12263–12273 (2018). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11356-017-9738-2
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11356-017-9738-2