Abstract
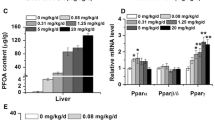
Perfluorooctane sulfonate (PFOS), an artificial fluorosurfactant and global contaminant, is used widely in various consumer products. In this study, we investigated the function of estrogen receptor β (ERβ) in PFOS-induced bile acid and cholesterol metabolism disorders and gut microbiome using ERβ knockout mice that were exposed to PFOS by gavage. Our results showed that a daily dose of 5 mg PFOS/kg significantly induced hydropic degeneration and vacuolation in hepatic cells, reduced bile acid, and cholesterol levels in liver tissue, and influenced the abundance and composition of gut microbiota. Notably, ERβ deficiency not only ameliorated morphological alterations of hepatocytes but also relieved disorders in bile acids and cholesterol metabolism caused by PFOS. Furthermore, the changes in the gut microbiome by PFOS were also modulated. The relative transcript abundance of key genes involved in bile acid and cholesterol metabolism exhibited similar changes. In HepG2 cells, PFOS increased ERβ expression, which could be blocked by adding PHTPP (a selective antagonist of ERβ). Our study thus provides new evidence that ERβ mediates PFOS-induced hepatotoxicity.





Similar content being viewed by others
References
Arumugam M et al (2011) Enterotypes of the human gut microbiome. Nature 473:174–180
Baldan A, Bojanic DD, Edwards PA (2009) The ABCs of sterol transport. J Lipid Res 50(Suppl):S80–S85
Bean LA, Ianov L, Foster TC (2014) Estrogen receptors, the hippocampus, and memory. Neuroscientist 20:534–545
Berthiaume J, Wallace KB (2002) Perfluorooctanoate, perflourooctanesulfonate, and N-ethyl perfluorooctanesulfonamido ethanol; peroxisome proliferation and mitochondrial biogenesis. Toxicol Lett 129:23–32
Buck RC, Franklin J, Berger U, Conder JM, Cousins IT, de Voogt P, Jensen AA, Kannan K, Mabury SA, van Leeuwen SP (2011) Perfluoroalkyl and polyfluoroalkyl substances in the environment: terminology, classification, and origins. Integr Environ Assess Manag 7:513–541
Chang ET, Adami HO, Boffetta P, Cole P, Starr TB, Mandel JS (2014) A critical review of perfluorooctanoate and perfluorooctanesulfonate exposure and cancer risk in humans. Crit Rev Toxicol 44(Suppl 1):1–81
Cheng Y, Cui Y, Chen HM, Xie WP (2011) Thyroid disruption effects of environmental level perfluorooctane sulfonates (PFOS) in Xenopus laevis. Ecotoxicology 20:2069–2078
Chiang JY (2009) Bile acids: regulation of synthesis. J Lipid Res 50:1955–1966
Degirolamo C, Rainaldi S, Bovenga F, Murzilli S, Moschetta A (2014) Microbiota modification with probiotics induces hepatic bile acid synthesis via downregulation of the Fxr-Fgf15 axis in mice. Cell Rep 7:12–18
Dellafiora L, Mena P, Cozzini P, Brighenti F, Del Rio D (2013) Modelling the possible bioactivity of ellagitannin-derived metabolites. In silico tools to evaluate their potential xenoestrogenic behavior. Food Funct 4:1442–1451
Dong GH, Zhang YH, Zheng L, Liu W, Jin YH, He QC (2009) Chronic effects of perfluorooctanesulfonate exposure on immunotoxicity in adult male C57BL/6 mice. Arch Toxicol 83:805–815
Du G, Hu J, Huang H, Qin Y, Han X, Wu D, Song L, Xia Y, Wang X (2013) Perfluorooctane sulfonate (PFOS) affects hormone receptor activity, steroidogenesis, and expression of endocrine-related genes in vitro and in vivo. Environ Toxicol Chem 32:353–360
Eriksen KT, Sorensen M, McLaughlin JK, Lipworth L, Tjonneland A, Overvad K, Raaschou-Nielsen O (2009) Perfluorooctanoate and perfluorooctanesulfonate plasma levels and risk of cancer in the general Danish population. J Natl Cancer Inst 101:605–609
Fang C, Wu X, Huang Q, Liao Y, Liu L, Qiu L, Shen H, Dong S (2012) PFOS elicits transcriptional responses of the ER, AHR and PPAR pathways in Oryzias melastigma in a stage-specific manner. Aquat Toxicol 106-107:9–19
Fiorucci S, Distrutti E (2015) Bile acid-activated receptors, intestinal microbiota, and the treatment of metabolic disorders. Trends Mol Med 21:702–714
Fletcher T, Galloway TS, Melzer D, Holcroft P, Cipelli R, Pilling LC, Mondal D, Luster M, Harries LW (2013) Associations between PFOA, PFOS and changes in the expression of genes involved in cholesterol metabolism in humans. Environ Int 57-58:2–10
Foryst-Ludwig A, Clemenz M, Hohmann S, Hartge M, Sprang C, Frost N, Krikov M, Bhanot S, Barros R, Morani A, Gustafsson JA, Unger T, Kintscher U (2008) Metabolic actions of estrogen receptor beta (ERbeta) are mediated by a negative cross-talk with PPARgamma. PLoS Genet 4:e1000108
Fuentes S, Vicens P, Colomina MT, Domingo JL (2007) Behavioral effects in adult mice exposed to perfluorooctane sulfonate (PFOS). Toxicology 242:123–129
Gao H, Falt S, Sandelin A, Gustafsson JA, Dahlman-Wright K (2008) Genome-wide identification of estrogen receptor alpha-binding sites in mouse liver. Mol Endocrinol 22:10–22
Goffredo M, Mass K, Parks EJ, Wagner DA, McClure EA, Graf J, Savoye M, Pierpont B, Cline G, Santoro N (2016) Role of gut microbiota and short chain fatty acids in modulating energy harvest and fat partitioning in youth. J Clin Endocrinol Metab 101:4367–4376
Harada KH, Yang HR, Moon CS, Hung NN, Hitomi T, Inoue K, Niisoe T, Watanabe T, Kamiyama S, Takenaka K, Kim MY, Watanabe K, Takasuga T, Koizumi A (2010) Levels of perfluorooctane sulfonate and perfluorooctanoic acid in female serum samples from Japan in 2008, Korea in 1994-2008 and Vietnam in 2007-2008. Chemosphere 79:314–319
Humblet O, Diaz-Ramirez LG, Balmes JR, Pinney SM, Hiatt RA (2014) Perfluoroalkyl chemicals and asthma among children 12-19 years of age: NHANES (1999-2008). Environ Health Perspect 122:1129–1133
Hylemon PB, Zhou H, Pandak WM, Ren S, Gil G, Dent P (2009) Bile acids as regulatory molecules. J Lipid Res 50:1509–1520
Inagaki T, Choi M, Moschetta A, Peng L, Cummins CL, McDonald JG, Luo G, Jones SA, Goodwin B, Richardson JA, Gerard RD, Repa JJ, Mangelsdorf DJ, Kliewer SA (2005) Fibroblast growth factor 15 functions as an enterohepatic signal to regulate bile acid homeostasis. Cell Metab 2:217–225
Ingelido AM, Marra V, Abballe A, Valentini S, Iacovella N, Barbieri P, Porpora MG, Domenico A, De Felip E (2010) Perfluorooctanesulfonate and perfluorooctanoic acid exposures of the Italian general population. Chemosphere 80:1125–1130
Joyce SA, MacSharry J, Casey PG, Kinsella M, Murphy EF, Shanahan F, Hill C, Gahan CG (2014) Regulation of host weight gain and lipid metabolism by bacterial bile acid modification in the gut. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A 111:7421–7426
Kato K, Wong LY, Jia LT, Kuklenyik Z, Calafat AM (2011) Trends in exposure to polyfluoroalkyl chemicals in the U.S. population: 1999-2008. Environ Sci Technol 45:8037–8045
Khalid AB, Krum SA (2016) Estrogen receptors alpha and beta in bone. Bone 87:130–135
Kim HS, Jun Kwack S, Sik Han E, Seok Kang T, Hee Kim S, Young Han S (2011) Induction of apoptosis and CYP4A1 expression in Sprague-Dawley rats exposed to low doses of perfluorooctane sulfonate. J Toxicol Sci 36:201–210
Kjeldsen LS, Bonefeld-Jorgensen EC (2013) Perfluorinated compounds affect the function of sex hormone receptors. Environ Sci Pollut Res Int 20:8031–8044
Kleiner DE, Brunt EM, Van Natta M, Behling C, Contos MJ, Cummings OW, Ferrell LD, Liu YC, Torbenson MS, Unalp-Arida A, Yeh M, McCullough AJ, Sanyal AJ (2005) Design and validation of a histological scoring system for nonalcoholic fatty liver disease. Hepatology 41:1313–1321
Krege JH, Hodgin JB, Couse JF, Enmark E, Warner M, Mahler JF, Sar M, Korach KS, Gustafsson JA, Smithies O (1998) Generation and reproductive phenotypes of mice lacking estrogen receptor beta. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A 95:15677–15682
Lau C, Butenhoff JL, Rogers JM (2004) The developmental toxicity of perfluoroalkyl acids and their derivatives. Toxicol Appl Pharmacol 198:231–241
Lopez-Doval S, Salgado R, Pereiro N, Moyano R, Lafuente A (2014) Perfluorooctane sulfonate effects on the reproductive axis in adult male rats. Environ Res 134:158–168
Mariussen E (2012) Neurotoxic effects of perfluoroalkylated compounds: mechanisms of action and environmental relevance. Arch Toxicol 86:1349–1367
Menazza S, Murphy E (2016) The expanding complexity of estrogen receptor signaling in the cardiovascular system. Circ Res 118:994–1007
Miele L, Giorgio V, Alberelli MA, De Candia E, Gasbarrini A, Grieco A (2015) Impact of gut microbiota on obesity, diabetes, and cardiovascular disease risk. Curr Cardiol Rep 17:120
Nilsson S, Gustafsson JA (2002) Biological role of estrogen and estrogen receptors. Crit Rev Biochem Mol Biol 37:1–28
Org E, Mehrabian M, Lusis AJ (2015) Unraveling the environmental and genetic interactions in atherosclerosis: central role of the gut microbiota. Atherosclerosis 241:387–399
Pennisi E (2010) Body’s hardworking microbes get some overdue respect. Science 330:1619
Qazi MR, Nelson BD, Depierre JW, Abedi-Valugerdi M (2010) 28-Day dietary exposure of mice to a low total dose (7 mg/kg) of perfluorooctanesulfonate (PFOS) alters neither the cellular compositions of the thymus and spleen nor humoral immune responses: does the route of administration play a pivotal role in PFOS-induced immunotoxicity? Toxicology 267:132–139
Rabot S, Membrez M, Bruneau A, Gerard P, Harach T, Moser M, Raymond F, Mansourian R, Chou CJ (2010) Germ-free C57BL/6J mice are resistant to high-fat-diet-induced insulin resistance and have altered cholesterol metabolism. FASEB J 24:4948–4959
Sayin SI, Wahlstrom A, Felin J, Jantti S, Marschall HU, Bamberg K, Angelin B, Hyotylainen T, Oresic M, Backhed F (2013) Gut microbiota regulates bile acid metabolism by reducing the levels of tauro-beta-muricholic acid, a naturally occurring FXR antagonist. Cell Metab 17:225–235
Seacat AM, Thomford PJ, Hansen KJ, Clemen LA, Eldridge SR, Elcombe CR, Butenhoff JL (2003) Sub-chronic dietary toxicity of potassium perfluorooctanesulfonate in rats. Toxicology 183:117–131
Shim GJ, Wang L, Andersson S, Nagy N, Kis LL, Zhang Q, Makela S, Warner M, Gustafsson JA (2003) Disruption of the estrogen receptor beta gene in mice causes myeloproliferative disease resembling chronic myeloid leukemia with lymphoid blast crisis. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A 100:6694–6699
Snedeker SM, Hay AG (2012) Do interactions between gut ecology and environmental chemicals contribute to obesity and diabetes? Environ Health Perspect 120:332–339
Tai N, Wong FS, Wen L (2015) The role of gut microbiota in the development of type 1, type 2 diabetes mellitus and obesity. Rev Endocr Metab Disord 16:55–65
Wan YJ, Li YY, Xia W, Chen J, Lv ZQ, Zeng HC, Zhang L, Yang WJ, Chen T, Lin Y, Wei J, Xu SQ (2010) Alterations in tumor biomarker GSTP gene methylation patterns induced by prenatal exposure to PFOS. Toxicology 274:57–64
Wan HT, Zhao YG, Wei X, Hui KY, Giesy JP, Wong CK (2012) PFOS-induced hepatic steatosis, the mechanistic actions on beta-oxidation and lipid transport. Biochim Biophys Acta 1820:1092–1101
Wang L, Wang Y, Liang Y, Li J, Liu Y, Zhang J, Zhang A, Fu J, Jiang G (2014) PFOS induced lipid metabolism disturbances in BALB/c mice through inhibition of low density lipoproteins excretion. Sci Rep 4:4582
Xu C, Liu Q, Huan F, Qu J, Liu W, Gu A, Wang Y, Jiang Z (2015) Changes in gut microbiota may be early signs of liver toxicity induced by epoxiconazole in rats. Chemotherapy 60:135–142
Yan L, Xu C, Liu Q, Gu A, Jiang ZY (2015) Altered profile of gut microbiota after subchronic exposure to neochamaejasmin A in rats. Environ Toxicol Pharmacol 39:927–933
Zhang W, Lin Z, Hu M, Wang X, Lian Q, Lin K, Dong Q, Huang C (2011) Perfluorinated chemicals in blood of residents in Wenzhou, China. Ecotoxicol Environ Saf 74:1787–1793
Acknowledgements
This work was supported by the National Natural Science Foundation of China (Grant Nos. 81172694 and 81270537), the Outstanding Youth Fund of Jiangsu Province (SBK2014010296), the Research Project of Chinese Ministry of Education (213015A), the Priority Academic Program Development of Jiangsu Higher Education Institutions (PAPD), and Jiangsu Province’s QingLan project (JX2161015124).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Contributions
The authors’ contributions are as follows: Q.L. and C.X. conducted data analyses, and Z.Y.J. and A.H.G. were involved in the design of the study and interpretation of the results and critically reviewed the manuscript. All authors have approved the final manuscript.
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
All procedures performed in studies involving animals were in strict accordance with the ethical standards of the Animal Ethical Committee, Nanjing Medical University, China. This article does not contain any studies with human participants performed by any of the authors.
Conflict of interest
The authors declare that they have no competing interests.
Additional information
Responsible editor: Philippe Garrigues
Electronic supplementary material
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Xu, C., Jiang, ZY., Liu, Q. et al. Estrogen receptor beta mediates hepatotoxicity induced by perfluorooctane sulfonate in mouse. Environ Sci Pollut Res 24, 13414–13423 (2017). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11356-017-8943-3
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11356-017-8943-3