Abstract
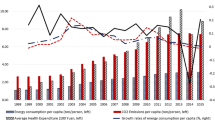
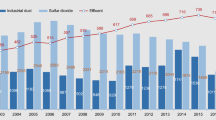
Based on the panel data model, data on environmental expenditures, the air quality index, economic aggregates, industrial structures, etc., of seven seriously polluted cities in China, from the period 2007–2015, were collected, and this paper estimates the general relationship between environmental expenditures and the air quality index. Besides, the impact of the fuel tax policy on air quality as well as on the relationship between environmental expenditure and the air quality index is tested using the method of regression discontinuity. We find that there is a long-term equilibrium relationship between environmental expenditure and air quality index as well as a 0.0507% positive effect of the former on the latter. Second, for Beijing, Taiyuan, Chongqing, and Lanzhou, a 1% increase in environmental expenditure leads to 0.0773, 0.0125, 0.0965, and 0.0912% decreases in the air quality index, respectively; however, for Shijiazhuang, Ji’nan, and Urumqi, effect of environmental expenditure on air quality is insignificant. Third, both economic growth and optimization of the industrial structure can lead to an improvement of air quality. Fourth, since the implementation of the fuel tax policy in 2009, the air quality of the sample cities has improved, and the pulling effect of environmental expenditure on the air quality index has decreased from 0.0507 to 0.0048%. Our findings cannot only clarify the effect of environmental expenditures on air quality but can also objectively judge the effectiveness of environmental policies of China to a certain extent. It may benefit Chinese government to effectively govern air pollution with fiscal tools in conjunction with economic and environmental characteristics.




Similar content being viewed by others
References
Almond D, Chen Y, Greenstone M, Li H (2009) Winter heating or clean air? Unintended impacts of China’s Huai River policy. Am Econ Rev 99(2):184–190. https://doi.org/10.1257/aer.99.2.184
Antoci A, Galeotti M, Russu P (2007) Undesirable economic growth via agents’ self-protection against environmental degradation. J Franklin Insti 344(5):377–390. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jfranklin.2006.02.037
Barro RJ (1990) Government spending in a simple endogenous growth model. J Polit Econ 98:103–126
Bovenberg AL, Smulders SA (1995) Environmental quality and pollution-augmenting technological change in a two-sector endogenous growth model. J Public Econ 57(3):369–391. https://doi.org/10.1016/0047-2727(95)80002-Q
Brock WA, Taylor MS (2010) The green solow model. J Econ Growth 15(2):127–153
Chen Y, Ebenstein A, Greenstone M, Li H (2013) Evidence on the impact of sustained exposure to air pollution on life expectancy from China’s Huai River policy. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A 110(32):12936–12941. https://doi.org/10.1073/pnas.1300018110
Cao J, Wang X, Zhong X-H (2014) Did driving restrictions improve air quality in Beijing? Chin Econ Q 13:1091–1126 (in Chinese)
Dong X-B, Yin J-J, Wen Y-B (2012) Environmental quality, government regulation and economic growth: an extended endogenous framework. Dissertation, Shandong University (in Chinese)
Gao M, Huang Q-H (2015) Further inspection towards the relationship between environmental protection investment and industrial pollution reduction threshold effect analysis based on governing investment structure. Econ Manag 37:167–177 (in Chinese)
Grimaud A, Rouge L (2005) Polluting non-renewable resources, innovation and growth: welfare and environmental policy. Resour Energy Econ 27(2):109–129. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.reseneeco.2004.06.004
Grossman G, Krueger A (1992) Environmental impacts of a North American Free Trade Agreement. Social Science Electron Publ 8:223–250
Gupta S, Miranda K, Parry I (1995) Public expenditure policy and the environment: a review and synthesis. World Dev 23(3):515–528. https://doi.org/10.1016/0305-750X(94)00139-P
Gao Y-T, She F, Wang S et al (2011) Assessment on air quality in Lanzhou and its relation with meteorological conditions. J Arid Land Res Environ 25:100–105 (in Chinese)
Heyes A (2000) A proposal for the greening of textbook macro: ‘IS-LM-EE’. Ecol Econ 32:1–7
He M-Y, Du J (2015) Study on the relationship between economic growth and air pollution in China: based on the study of key environmental protection cities and regional heterogeneity. Price Theor Prac 10:108–110 (in Chinese)
He J, Wang Z (2015) Government expenditure structure, tax revenue and resident consumption under endogenous growth-analysis based on provincial panel data. J Dalian Univ Technol (Soc Sci Ed) 4:53–58 (in Chinese)
Huang Q-Z, Zhang L, Wang Z-Z (2016) Study of environmental protection investment impact of Silk Road Economic Belt. Chin Popul Resour Environ 26:89–99 (in Chinese)
Lawn P (2003) Environmental macroeconomics: extending the IS-LM model to include an “environmental equilibrium” curve. Aust Econ Pap 42(1):118–134. https://doi.org/10.1111/1467-8454.00190
Lee DS (2008) Randomized experiments from non-random selection in U.S. House elections. J Econ 142(2):675–697. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jeconom.2007.05.004
Liu S-J (2012) Research on regional environmental investment and economic sustainable development: based on the comparative analysis of regional panel data in China. Enterpr Econ 1:136–140 (in Chinese)
Li P (2015a) Is there an inverted U curve relationship between industrial structure adjustment and environmental pollution? Inq Into Econ Issues 12:56–67 (in Chinese)
Li P (2015b) Does industrial restructuring worsen China’s environmental pollution? Inq Into Econ Issues 6:150–156 (in Chinese)
Li L (2016) Environmental benefit spillover and energy saving and environmental protection expenditure of local government: an empirical analysis based on spatial lag model. Modern Business Trade Industry 17:143–145 (in Chinese)
Lin Q, Chen G, Du W, Niu H (2012) Spillover effect of environmental investment: evidence from panel data at provincial level in China. Front Environ Sci Eng 6(3):412–420. https://doi.org/10.1007/s11783-012-0392-0
Lu H-Y, Du Y-X, Qi Y (2015) Fiscal expenditures in China and consumption-generated pollution: theoretical model and empirical test. Chin Popul Res Environ 10:61–70 (in Chinese)
López R, Galinato GI, Islam A (2011) Fiscal spending and the environment: theory and empirics. J Environ Econ Manag 62(2):180–198. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jeem.2011.03.001
Liu Y, Huang J-Z (2013) Environmental effect of Liaoning’s industrial structure evolution. Res Ind 2:110–116 (in Chinese)
Lei G-Q, Huang X-H, Hui X-P (2015) The impact of transfer payments on urban and rural income gap: based on fuzzy RD analysis of China’s Midwestern counties data. Finance Trade Econ 36:35–48 (in Chinese)
Lee DS, Lemieux T (2010) Regression discontinuity designs in economics. J Econ Lit 48(2):281–355. https://doi.org/10.1257/jel.48.2.281
Li L, Qi P (2011) The impact of China’s investment increase in fixed assets on ecological environment: an empirical analysis. Energy Procedia 5:501–507. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.egypro.2011.03.087
Li Q, Song J-P, Zhang J-H et al (2013) Dynamics in the effect of China’s urbanization on air quality. Acta Sci Circumst 33:2402–2411 (in Chinese)
Li W-J, Zheng M-N (2016) Governance mechanism of air pollution and its effects: evidence from Chinese prefecture-level cities. Chin Ind Econ 4:93–109 (in Chinese)
Liu Y-B, Yang X-M (2011) “End effect” of resources and environment in the process of urbanization based on endogenous economic growth theory. J Chin Popul Res Environ 21:24–30 (in Chinese)
Moon Y, Sonn Y (1996) Productive energy consumption and economic growth: an endogenous growth model and its empirical application. Resour Energy Econ 18(2):189–200. https://doi.org/10.1016/0928-7655(96)00006-1
Panayotou T (1993) Empirical tests and policy analysis of environmental degradation at different stages of economic development. Ilo Working Papers 4:1–45
Qi W, Huang H-J, Wang S-W (2015) Traffic restrictions effect on air quality: data integration analysis for Lanzhou City. Stat Inf Forum 30:74–81 (in Chinese)
Stokey NL (1998) Are there limits to growth? Int Econ Rev 39(1):1–31. https://doi.org/10.2307/2527228
Sim NCS (2006) Environmental Keynesian macroeconomics: some further discussion. Ecol Econ 59(4):401–405. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ecolecon.2005.11.006
Wang Y-F (2011) Analysis on the impact of public financial environmental protection on environmental pollution. Publ Finance Res 2:38–42 (in Chinese)
Wan J-X (2015) Performance analysis of China's fiscal budget expenditure on economic growth, resource consumption and environmental protection. Publ Finance Res 3:6–10 (in Chinese)
Wang M, Huang Y (2015) China’s environmental pollution and economic growth. Chin Econ Q 14:557–578 (in Chinese)
Wu J, Jia L, Shi L et al (2012) The development of American environmental finance and its enlightenment to China. Environ Prot 20:74–76 (in Chinese)
Xiong B, Chen W-J, Pan L et al (2016) Fiscal policy, local governments competition and air pollution control quality. J Chin Univ Geosci (Soc Sci Ed) 16:20–33 (in Chinese)
Xi P-H, Liang R-B (2015a) Urban air quality and environmental migration: an empirical study based on fuzzy breakpoint model. Econ Sci 37:30–43 (in Chinese)
Xi P-H, Liang R-B (2015b) Can air pollution influence the local environmental protection expenditure: based on the multiple-cutoffs regression discontinuity design. Stat Res 32:76–83 (in Chinese)
Xi J-C, Sun Z (2017) Whether the rise in labor costs pushed the industry to upgrade: the empirical evidence based on China’s industry with a regression-discontinuity. J Shanxi Univ Finance Econ 39:39–53 (in Chinese)
Xu S-C, He Z-X, Wei X-P (2010) Resource consumption and sustainable development of economic sustainable growth under pollution control. Chin J Manag Sci 13:20–30 (in Chinese)
Xu Y-D, Zhang J, Zhu J-M (2015) The effect evaluation of the energy: saving emission reduction policies. Based Diff Chin Air Qual Index J Hei he Univ 4:56–60 (in Chinese)
Yuan Y-J, Kong F-B (2015) Local fiscal expenditures on environmental protection, corporate environmental investment and industrial technology upgrading in China. China Soft Science 5:139–148 (in Chinese)
Yang Y, Shen Z-H, Zheng T-L et al (2016) Influence major factors analysis of comprehensive air quality in the cities in China. Acta Sci Nat Univ Pekin 6:1102–1108 (in Chinese)
Yu C-L, Yang H-Z (2016) Impact of Chinese local government fiscal expenditure on environment pollution under the fiscal decentralization: empirical analysis based on panel data from 287 cities. Publ Finance Res 7:46–58 (in Chinese)
Zhang C, Zhu Q-L, Yu T-S (2011) Relationship between environmental pollution and economic development. Stat Res 28:59–67 (in Chinese)
Zhang P-D, Zhu S, Zhu Y-C (2012) Spillover effect of environmental investment. J Beijing Normal Univ 3:126–133 (in Chinese)
Zheng Z-N, Liu D-S (2003) Estimating energy-capital-labor substitution parameters of nested production functions for China. Proceedings of international conference on energy and the environment, May 22–24, Shanghai, China
Zou Q, Chen X, Lv J-N (2014) Research on the coordinated development of economic growth and environment in China: analysis based on endogenous growth model and EKC hypothesis. J Central Univ Finance Econ 1:89–96 (in Chinese)
Acknowledgments
The authors are grateful for the financial support provided by the Key Program of National Statistical Science Research of China under Grant No. 2016LZ13, the Ministry of Education of Humanities and Social Science project of China under Grant No. 16YJAZH015, and the National Natural Science Foundation of China under Grant No.71203219.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Ethics declarations
Conflict of interest
The authors declare that they have no conflicts of interest.
Additional information
Responsible editor: Philippe Garrigues
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
He, L., Wu, M., Wang, D. et al. A study of the influence of regional environmental expenditure on air quality in China: the effectiveness of environmental policy. Environ Sci Pollut Res 25, 7454–7468 (2018). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11356-017-1033-8
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11356-017-1033-8