Abstract
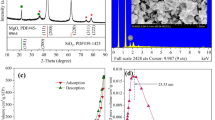
Magnesium-enriched magnesium slag particles (MSPs) can be used as an adsorption substrate as well as the magnesium source for struvite precipitation. In this study, an HCl treatment was used to enhance MSPs for phosphorus removal. After soaking in 1 mol/L HCl, an 11.27% decrease in median diameter (D50) and a 6.73% increase in specific surface area were observed when compared with the original MSPs. The improvement of the MSP surface properties resulted in 188.96 mg/kg increase in the PO4 3− adsorption capacity. Irrespective of HCl treatment, the phosphorus adsorption process followed the Dubinin–Radushkevich (D–R) model much more accurately than the Langmuir and Freundlich equations with correlation coefficients higher than 0.94. The adsorption free energy obtained through the D–R model revealed a 9.75% decrease after HCl treatment. Sequential fraction extraction results indicated that 96% of the Mg2+ released from the HCl-treated MSPs came from acid-soluble magnesium (exchangeable and carbonate-bound). Mg2+ obtained from HCl-treated solutions provided a reliable magnesium source for struvite precipitation. The PO4 3− removal rate can reach 53.63% with the optimal pH value of 10.0 and molar ratio of NH4 + to PO4 3− of 1:1. Struvite precipitation and adsorption can simultaneously occur in HCl-treated MSP solution. It contributed 63.19% to the overall PO4 3− removal and is a major contributor compared with adsorption. Thus, HCl treatment greatly enhanced the potential of MSPs for phosphorus removal due to an improved adsorption capacity and is a reliable Mg2+ source for struvite precipitation.







Similar content being viewed by others
References
APHA (1998) Standard methods for the examination of water and wastewater, 20th edn. American Public Health Association/American Water Works Association/ Water Environment Federation, Washington DC, USA
Argun ME, Dursun S, Ozdemir C, Karatas M (2007) Heavy metal adsorption by modified oak sawdust: thermodynamics and kinetics. J Hazard Mater 141(1):77–85. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jhazmat.2006.06.095
Barbosa SG, Peixoto L, Meulman B, Alves MM, Pereira MA (2016) A design of experiments to assess phosphorous removal and crystal properties in struvite precipitation of source separated urine using different Mg sources. Chem Eng J 298:146–153. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.cej.2016.03.148
Barnes NJ, Bowers AR (2017) A probabilistic approach to modeling struvite precipitation with uncertain equilibrium parameters. Chem Eng Sci 161:178–186. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ces.2016.12.026
Bi W, Li Y, Hu Y (2014) Recovery of phosphorus and nitrogen from alkaline hydrolysis supernatant of excess sludge by magnesium ammonium phosphate. Bioresour Technol 166:1–8. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.biortech.2014.04.092
Chen J, Yan L, Yu H, Li S, Qin L, Liu G, Li Y, Du B (2016) Efficient removal of phosphate by facile prepared magnetic diatomite and illite clay from aqueous solution. Chem Eng J 287:162–172. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.cej.2015.11.028
Chen T, Huang X, Pan M, Jin S, Peng S, Fallgren PH (2009) Treatment of coking wastewater by using manganese and magnesium ores. J Hazard Mater 2009(168):843–849
Chitrakar R, Tezuka S, Sonoda A, Sakane K, Ooi K, Hirotsu T (2006) Phosphate adsorption on synthetic goethite and akaganeite. J Colloid Interface Sci 298(2):602–608. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jcis.2005.12.054
Chubar NI, Kanibolotskyy VA, Strelko VV, Gallios GG, Samanidou VF, Shaposhnikova TO, Milgrandt VG, Zhuravlev IZ (2005) Adsorption of phosphate ions on novel inorganic ion exchangers. Colloids Surf A Physicochem Eng Asp 255(1-3):55–63. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.colsurfa.2004.12.015
Cordell D, Drangert JO, White S (2009) The story of phosphorus: global food security and food for thought. J Glob Environ Chang 19(2):292–305. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.gloenvcha.2008.10.009
Crutchik D, Garrido JM (2016) Kinetics of the reversible reaction of struvite crystallization. Chemosphere 154:567–572. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.chemosphere.2016.03.134
Etter B, Tilley E, Khadka R, Udert KM (2011) Low-cost struvite production using source-separated urine in Nepal. Water Res 45(2):852–862. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.watres.2010.10.007
Güneyisi E, Gesoğlu M, Algin Z, Yazici H (2014) Effect of surface treatment methods on the properties of self-compacting concrete with recycled aggregates. Constr Build Mater 64:172–183. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.conbuildmat.2014.04.090
Han C, Wang Z, Yang W, Wu Q, Yang H, Xue X (2016) Effects of pH on phosphorus removal capacities of basic oxygen furnace slag. Ecol Eng 89:1–6. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ecoleng.2016.01.004
Huang H, Guo G, Zhang P, Zhang D, Liu J, Tang S (2017) Feasibility of physicochemical recovery of nutrients from swine wastewater: evaluation of three kinds of magnesium sources. J Taiwan Inst Chem Eng 70:209–218. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jtice.2016.10.051
Kundu S, Gupta AK (2006) Adsorptive removal of As (III) from aqueous solution using iron oxide coated cement (IOCC): evaluation of kinetic, equilibrium and thermodynamic models. Sep Purif Technol 51(2):165–172. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.seppur.2006.01.007
Le Corre KS, Valsami-Jones E, Hobbs P, Jefferson B, Parsons SA (2007) Agglomeration of struvite crystals. Water Res 41(2):419–425. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.watres.2006.10.025
Lee SI, Weon SY, Lee CW, Koopman B (2003) Removal of nitrogen and phosphate from wastewater by addition of bittern. Chemosphere 51(4):265–271. https://doi.org/10.1016/S0045-6535(02)00807-X
Li Q, Xu XT, Cui H, Pang JF, Wei ZB, Sun ZQ, Zhai JP (2012) Comparison of two adsorbents for the removal of pentavalent arsenic from aqueous solutions. J Environ Manag 98:98–106. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jenvman.2011.12.018
Mijangos F, Kamel M, Lesmes G, Muraviev DN (2004) Synthesis of struvite by ion exchange isothermal supersaturation technique. React Funct Polym 60:151–161. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.reactfunctpolym.2004.02.019
Muster TH, Douglas GB, Sherman N, Seeber A, Wright N, Güzükara Y (2013) Towards effective phosphorus recycling from wastewater: quantity and quality. Chemosphere 91(5):676–684. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.chemosphere.2013.01.057
Okano K, Yamamoto Y, Takano H, Aketo T, Honda K, Ohtake H (2016) A simple technology for phosphorus recovery using acid-treated concrete sludge. Sep Purif Technol 165:173–178. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.seppur.2016.03.054
Onyango MS, Kuchar D, Kubota M, Matsuda H (2007) Adsorptive removal of phosphate ions from aqueous solution using synthetic zeolite. Ind Eng Chem Res 46(3):894–900. https://doi.org/10.1021/ie060742m
Park J-H, Kim S-H, Delaune RD, Kang B-H, Kang S-W, Cho J-S, Ok YS, Seo D-C (2016) Enhancement of phosphorus removal with near-neutral pH utilizing steel and ferronickel slags for application of constructed wetlands. Ecol Eng 95:612–621. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ecoleng.2016.06.052
Rahman MM, Liu YH, Kwag JH, Ra CS (2011) Recovery of struvite from animal wastewater and its nutrient leaching loss in soil. J Hazard Mater 186(2-3):2026–2030. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jhazmat.2010.12.103
Rahman MM, Salleh MAM, Rashid U, Ahsan A, Hossain MM, Ra CS (2014) Production of slow release crystal fertilizer from wastewaters through struvitecrystallization-a review. Arab J Chem 7(1):139–155. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.arabjc.2013.10.007
Saidou H, Korchef A, Ben Moussa S, Ben Amor M (2009) Struvite precipitation by the dissolved CO2 degasification technique: impact of the airflow rate and pH. Chemosphere 74(2):338–343. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.chemosphere.2008.09.081
Song YH, Qiu GL, Yuan P, Cui XY, Peng JF, Zeng P, Duan L, Xiang LC, Qian F (2011) Nutrients removal and recovery from anaerobically digested swine wastewater by struvite crystallization without chemical additions. J Hazard Mater 190(1-3):140–149. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jhazmat.2011.03.015
Tang XQ, Wu M, Li R, Wang ZH (2017) Prospect of recovering phosphorus in magnesium slag packed wetland filter. Environ Sci Pollut Res 24(29):22808–22815. https://doi.org/10.1007/s11356-017-8398-6
Tang XQ, Huang SL (2007) Mechanisms of pollutant removal in constructed wetlands and their applications both at home and abroad. Technol Water Treatment 33:9–13 (in Chinese)
Triger A, Pic JS, Cabassud C (2012) Determination of struvite crystallization mechanisms in urine using turbidity measurement. Water Res 46(18):6084–6094. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.watres.2012.08.030
Ure, A.M., Quevauviller, Ph., Muntau, H., Griepink, B., 1992. B. EUR report. CEC Brussels, 14763, 1992:85
Wang SG, Zhang B, Wang ZH (2005) Study on P-recover as guano from wastewater treatment plant. Environ Eng 23:78–80 (in Chinese)
Wang SR, Jin XC, Zhao HC, Zhou XN, Wu FC (2007) Effect of organic matter on the sorption of dissolved organic and inorganic phosphorus in lake sediments. Colloids Surf A Physicochem Eng Asp 297(1-3):154–162. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.colsurfa.2006.10.040
Xue YJ, Hou HB, Zhu SJ (2009) Characteristics and mechanisms of phosphate adsorption onto basic oxygen furnace slag. J Hazard Mater 162(2-3):973–980. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jhazmat.2008.05.131
Yang K, Yan L, Yang Y, Yu S, Shan R, Yu H, Zhu B, Du B (2014) Adsorptive removal of phosphate by Mg–Al and Zn–Al layered double hydroxides: kinetics, isotherms and mechanisms. Sep Purif Technol 124:36–42. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.seppur.2013.12.042
Ye Z, Shen Y, Ye X, Zhang Z, Chen S, Shi J (2014) Phosphorus recovery from wastewater by struvite crystallization: property of aggregates. J Environ Sci 26(5):991–1000. https://doi.org/10.1016/S1001-0742(13)60536-7
Yuan JH (2003) Characteristics and development strategies of phosphorite resources in China. Express Information Mining Industry 12:4–9 (in Chinese)
Zhang Z, Zhu M, Zhang Y, Hendrix YS, Li J, Zhang D (2017) Ignition and combustion characteristics of single particles of Zhundong lignite: effect of water and acid washing. P Combust Inst 36:2139–2146. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.proci.2016.07.072
Zhou K, Barjenbruch M, Kabbe C, Inial G, Remy C (2016) Phosphorus recovery from municipal and fertilizer wastewater: China’s potential and perspective. J Environ Sci 52:151–159. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jes.2016.04.010
Zhou Q, Wang XZ, Liu JY, Zhang L (2012) Phosphorus removal from wastewater using nano-particulates of hydrated ferric oxide doped activated carbon fiber prepared by sol-gel method. Chemical Engineering J 200–202:619–626
Acknowledgements
This study was supported by the National Natural Science Foundation of China (Grants 51379017 and 51409009) and the Central Public-interest Scientific Institution Basal Research Fund (Grants CKSF2017047/SH and CKSF2016025/SH).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Additional information
Responsible editor: Guilherme L. Dotto
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Tang, X., Li, R., Wu, M. et al. Enhanced phosphorus removal using acid-treated magnesium slag particles. Environ Sci Pollut Res 25, 3860–3871 (2018). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11356-017-0781-9
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11356-017-0781-9