Abstract
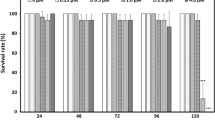
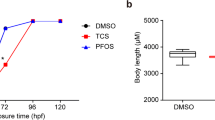
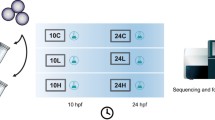
All-trans retinoic acid (atRA) and 9-cis retinoic acid (9cRA) are two natural derivatives of vitamin A that contribute to the normal vertebrate development by affecting gene expression through the retinoic acid signalling pathway. We show transcriptomic effects of the ectopic addition of atRA or 9cRA to zebrafish embryos at the posthatching embryonic stage. Exposure for 24 or 72 h to sublethal concentrations of both isomers resulted in characteristic transcriptome changes, in which many proliferation and development-related genes became underexpressed, whereas genes related to retinoid metabolism and some metabolic functions became overrepresented. While short and long exposures elicit essentially the same set of genes, atRA specifically induced expression of a specific subset of proteases, likely acting at the extracellular level, and of elements of the response to xenobiotics. These results reflect the well-known antiproliferative activity of retinoids, and they suggest a dysregulation of the developmental process at final stages of embryogenesis. They also indicate a potential role of endopeptidases as markers of developmental alterations, as well as their possible control by the retinoic signalling pathway. We propose to monitor mRNA levels of cyp16a, cyp16b, and cyp16c in zebrafish embryos as a bioassay for retinoid disruption.





Similar content being viewed by others
References
Altucci L, Gronemeyer H (2001) The promise of retinoids to fight against cancer. Nat Rev Cancer 1(3):181–193. https://doi.org/10.1038/35106036
Blomhoff R, Blomhoff HK (2006) Overview of retinoid metabolism and function. J Neurobiol 66(7):606–630. https://doi.org/10.1002/neu.20242
Carbon S, Ireland A, Mungall C, Shu S, Marshall B, Lewis S, Hub A, Web Presence Working Group (2009) AmiGO: online access to ontology and annotation data. Bioinformatics 25(2):288–289. https://doi.org/10.1093/bioinformatics/btn615
Chen Y, Pollet N, Niehrs C, Pieler T (2001) Increased XRALDH2 activity has a posteriorizing effect on the central nervous system of Xenopus embryos. Mech Dev 101(1-2):91–103. https://doi.org/10.1016/S0925-4773(00)00558-X
Costaridis P, Horton C, Zeitlinger J, Holder N, Maden M (1996) Endogenous retinoids in the zebrafish embryo and adult. Dev Dyn 205(1):41–51. https://doi.org/10.1002/(SICI)1097-0177(199601)205:1<41::AID-AJA4>3.0.CO;2-5
Dawson MI, Xia Z (2012) The retinoid X receptors and their ligands. Biochim Biophys Acta Mol Cell Biol Lipids 1821(1):21–56. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.bbalip.2011.09.014
Dobbs-McAuliffe B, Zhao Q, Linney E (2004) Feedback mechanisms regulate retinoic acid production and degradation in the zebrafish embryo. Mech Dev 121(4):339–350. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.mod.2004.02.008
Dolle P (2009) Developmental expression of retinoic acid receptors (RARs). Nucl Recept Signal 7:e006. https://doi.org/10.1621/nrs.07006
European Comission (2010) Directive 2010/63/EU on the protection of animals used for scientific purposes. Official Journal of the European Union, L276/33. 2010. http://eur-lex.europa.eu/LexUriServ/LexUriServ.do?uri=OJ:L:2010:276:0033:0079:en:PDF
EFSA (2005) Opinion of the scientific panel on animal health and welfare on a request from the commission related to the aspects of the biology and welfare of animals used for experimental and other scientific purposes (EFSA-Q-2004-105). EFSA J 292:1–46
Eichele G, Thaller C (1987) Characterization of concentration gradients of a morphogenetically active retinoid in the chick limb bud. J Cell Biol 105(4):1917–1923. https://doi.org/10.1083/jcb.105.4.1917
Farres M, Platikanov S, Tsakovski S, Tauler R (2015) Comparison of the variable importance in projection (VIP) and of the selectivity ratio (SR) methods for variable selection and interpretation. J Chemom 29(10):528–536. https://doi.org/10.1002/cem.2736
Francis GA, Fayard E, Picard F, Auwerx J (2003) Nuclear receptors and the control of metabolism. Annu Rev Physiol 65(1):261–311. https://doi.org/10.1146/annurev.physiol.65.092101.142528
Guerrera MC, De Pasquale F, Muglia U, Caruso G (2015) Digestive enzymatic activity during ontogenetic development in zebrafish (Danio rerio). J Exp Zool B Mol Dev Evol 324(8):699–706. https://doi.org/10.1002/jez.b.22658
Hallare A, Nagel K, Kohler HR, Triebskorn R (2006) Comparative embryotoxicity and proteotoxicity of three carrier solvents to zebrafish (Danio rerio) embryos. Ecotoxicol Environ Saf 63(3):378–388. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ecoenv.2005.07.006
Heyman RA, Mangelsdorf DJ, Dyck JA, Stein RB, Eichele G, Evans RM, Thaller C (1992) 9-cis retinoic acid is a high affinity ligand for the retinoid X receptor. Cell 68(2):397–406. https://doi.org/10.1016/0092-8674(92)90479-V
Hu P, Tian M, Bao J, Xing G, Gu X, Gao X, Linney E, Zhao Q (2008) Retinoid regulation of the zebrafish cyp26a1 promoter. Dev Dyn 237(12):3798–3808. https://doi.org/10.1002/dvdy.21801
Huang DW, Sherman BT, Lempicki RA (2009) Systematic and integrative analysis of large gene lists using DAVID bioinformatics resources. Nat Protoc 4:44–57
Jimenez MJG, Balbin M, Alvarez J, Komori T, Bianco P, Holmbeck K, Birkedal-Hansen H, Lopez JM, Lopez-Otin C (2001) A regulatory cascade involving retinoic acid, Cbfa1, and matrix metalloproteinases is coupled to the development of a process of perichondrial invasion and osteogenic differentiation during bone formation. J Cell Biol 155(7):1333–1344. https://doi.org/10.1083/jcb.200106147
Kane MA (2012) Analysis, occurrence, and function of 9-cis-retinoic acid. Biochim Biophys Acta Mol Cell Biol Lipids 1821(1):10–20. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.bbalip.2011.09.012
Kohle C, Bock KW (2007) Coordinate regulation of phase I and II xenobiotic metabolisms by the Ah receptor and Nrf2. Biochem Pharmacol 73(12):1853–1862. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.bcp.2007.01.009
Kosian PA, Makynen EA, Ankley GT, Degitz SJ (2003) Uptake and metabolism of all-trans retinoic acid by three native north American ranids. Toxicol Sci 74(1):147–156. https://doi.org/10.1093/toxsci/kfg100
Lammer E, Carr GJ, Wendler K, Rawlings JM, Belanger SE, Braunbeck T (2009) Is the fish embryo toxicity test (FET) with the zebrafish (Danio rerio) a potential alternative for the fish acute toxicity test? Comp Biochem Physiol C Toxicol Pharmacol 149(2):196–209. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.cbpc.2008.11.006
Lefebvre P, Benomar Y, Staels B (2010) Retinoid X receptors: common heterodimerization partners with distinct functions. Trends Endocrinol Metab 21(11):676–683. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.tem.2010.06.009
Li N, Jiang WW, Ma M, Wang DH, Wang ZJ (2016) Chlorination by-products of bisphenol a enhanced retinoid X receptor disrupting effects. J Hazard Mater 320:289–295. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jhazmat.2016.08.033
Lima D, Castro LFC, Coelho I, Lacerda R, Gesto M, Soares J, Andre A, Capela R, Torres T, Carvalho AP et al (2015) Effects of tributyltin and other retinoid receptor agonists in reproductive-related endpoints in the zebrafish (Danio rerio). J Toxicol Environ Health A 78(12):747–760. https://doi.org/10.1080/15287394.2015.1028301
Mark M, Ghyselinck NB, Chambon P (2006) Function of retinoid nuclear receptors: lessons from genetic and pharmacological dissections of the retinoic acid signaling pathway during mouse embryogenesis. Annu Rev Pharmacol Toxicol 46(1):451–480. https://doi.org/10.1146/annurev.pharmtox.46.120604.141156
Morais S, Knoll-Gellida A, Andre M, Barthe C, Babin PJ (2007) Conserved expression of alternative splicing variants of peroxisomal acyl-CoA oxidase 1 in vertebrates and developmental and nutritional regulation in fish. Physiol Genomics 28(3):239–252. https://doi.org/10.1152/physiolgenomics.00136.2006
Nagel R (2002) DarT: the embryo test with the Zebrafish Danio rerio—a general model in ecotoxicology and toxicology. ALTEX 19:38–48
Niederreither K, Dolle P (2008) Retinoic acid in development: towards an integrated view. Nat Rev Genet 9(7):541–553. https://doi.org/10.1038/nrg2340
Oliveira E, Casado M, Faria M, Soares AMVM, Maria Navas J, Barata C, Pina B (2013) Transcriptomic response of zebrafish embryos to polyaminoamine (PAMAM) dendrimers. Nanotoxicology 8:92–99. https://doi.org/10.3109/17435390.2013.858376
Pelayo S, Oliveira E, Thienpont B, Babin PJ, Raldua D, Andre M, Pina B (2012) Triiodothyronine-induced changes in the zebrafish transcriptome during the eleutheroembryonic stage: implications for bisphenol a developmental toxicity. Aquat Toxicol 110–111:114–122. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.aquatox.2011.12.016
Pfaffl MW (2001) A new mathematical model for relative quantification in real-time RT-PCR. Nucleic Acids Res 29(9):45e–445. https://doi.org/10.1093/nar/29.9.e45
Pfaffl MW, Horgan GW, Dempfle L (2002) Relative expression software tool (REST©) for group-wise comparison and statistical analysis of relative expression results in real-time PCR. Nucleic Acids Res 30:e36, 9, 36e, 336. https://doi.org/10.1093/nar/30.9.e36
Pina B, Barata C (2011) A genomic and ecotoxicological perspective of DNA array studies in aquatic environmental risk assessment. Aquat Toxicol 105(3-4):40–49. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.aquatox.2011.06.006
Raldua D, Piña B (2014) In vivo zebrafish assays for analyzing drug toxicity. Expert Opin Drug Metab Toxicol 10(5):685–697. https://doi.org/10.1517/17425255.2014.896339
Raldua D, Thienpont B, Babin PJ (2012) Zebrafish eleutheroembryos as an alternative system for screening chemicals disrupting the mammalian thyroid gland morphogenesis and function. Reprod Toxicol 33(2):188–197. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.reprotox.2011.09.001
Rhinn M, Dolle P (2012) Retinoic acid signalling during development. Development 139(5):843–858. https://doi.org/10.1242/dev.065938
Ritchie ME, Phipson B, Wu D, Hu Y, Law CW, Shi W, Smyth GK (2015) Limma powers differential expression analyses for RNA-sequencing and microarray studies. Nucleic Acids Res 43(7):e47. https://doi.org/10.1093/nar/gkv007
Scholz S (2013) Zebrafish embryos as an alternative model for screening of drug-induced organ toxicity. Arch Toxicol 87(5):767–769. https://doi.org/10.1007/s00204-013-1044-2
Spoorendonk KM, Peterson-Maduro J, Renn J, Trowe T, Kranenbarg S, Winkler C, Schulte-Merker S (2008) Retinoic acid and Cyp26b1 are critical regulators of osteogenesis in the axial skeleton. Development 135(22):3765–3774. https://doi.org/10.1242/dev.024034
Strahle U, Scholz S, Geisler R, Greiner P, Hollert H, Rastegar S, Schumacher A, Selderslaghs I, Weiss C, Witters H et al (2012) Zebrafish embryos as an alternative to animal experiments—a commentary on the definition of the onset of protected life stages in animal welfare regulations. Reprod Toxicol 33(2):128–132. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.reprotox.2011.06.121
Szondy Z, Reichert U, Bernardon JM, Michel S, Toth R, Ancian P, Ajzner E, Fesus L (1997) Induction of apoptosis by retinoids and retinoic acid receptor gamma-selective compounds in mouse thymocytes through a novel apoptosis pathway. Mol Pharmacol 51(6):972–982
Tabb MM, Blumberg B (2006) New modes of action for endocrine-disrupting chemicals. Mol Endocrinol 20(3):475–482. https://doi.org/10.1210/me.2004-0513
Tanumihardjo SA, Russe RM, Stephensen CB, Gannon BM, Craft NE, Haskell MJ, Lietz G, Schulze K, Raiten DJ (2016) Biomarkers of nutrition for development (BOND)-vitamin a review. J Nutr 146:1816–1848
Theodosiou M, Laudet V, Schubert M (2010) From carrot to clinic: an overview of the retinoic acid signaling pathway. Cell Mol Life Sci 67(9):1423–1445. https://doi.org/10.1007/s00018-010-0268-z
Urbach J, Rando RR (1994) Isomerization of all-trans-retinoic acid to 9-cis-retinoic acid. Biochem J 299(2):459–465. https://doi.org/10.1042/bj2990459
Wolf G (2006) Is 9-cis-retinoic acid the endogenous ligand for the retinoic acid-X receptor? Nutr Rev 64(12):532–538. https://doi.org/10.1111/j.1753-4887.2006.tb00186.x
Zhang XK, Liu Y, Lee MO (1996) Retinoid receptors in human lung cancer and breast cancer. Mutat Res 350(1):267–277. https://doi.org/10.1016/0027-5107(95)00102-6
Zhao J, Zhu XW, Xu T, Yin DQ (2015) Structure-dependent activities of polybrominated diphenyl ethers and hydroxylated metabolites on zebrafish retinoic acid receptor. Environ Sci Pollut Res 22(3):1723–1730. https://doi.org/10.1007/s11356-014-3364-z
Funding
This work was supported by the Spanish Research Project CTM2014-51985. LNM was supported by a Beatriu de Pinos postdoctoral fellow (2013BP-B-00088) awarded by the Secretary for Universities and Research of the Ministry of Economy and Knowledge of the Government of Catalonia and the Cofound programme of the Marie Curie Actions of the 7th R&D Framework Programme of the European Union.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Additional information
Responsible editor: Thomas Braunbeck
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Navarro-Martín, L., Oliveira, E., Casado, M. et al. Dysregulatory effects of retinoic acid isomers in late zebrafish embryos. Environ Sci Pollut Res 25, 3849–3859 (2018). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11356-017-0732-5
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11356-017-0732-5