Abstract
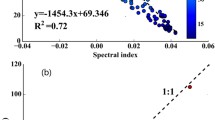
Chlorophyll-a (Chla) is an important indicator of water quality and eutrophication status. Monitoring Chla concentration (C Chla ) and understanding the interactions between C Chla and related environmental factors (hydrological and meteorological conditions, nutrients enrichment, etc.) are necessary for assessing and managing water quality and eutrophication. An acceptable Landsat 8 OLI-based empirical algorithm for C Chla has been developed and validated, with a mean absolute percentage error of 14.05% and a root mean square error of 1.10 μg L−1. A time series of remotely estimated C Chla was developed from 2013 to 2015 and examined the relationship of C Chla to inflow rate, rainfall, temperature, and sunshine duration. Spatially, C Chla values in the riverine zone were higher than in the transition and lacustrine zones. Temporally, mean C Chla value were ranked as spring > summer > autumn > winter. A significant positive correlation [Pearson correlation coefficient (r) = 0.88, p < 0.001] was observed between the inflow rate and mean C Chla in the northwest segment of the Xin’anjiang Reservoir. However, no significant relation was observed between mean C Chla and meteorological conditions. Mean (± standard deviation) value for the ratio of total nitrogen concentration to total phosphorus concentration in our in situ dataset is 75.75 ± 55.72. This result supports that phosphorus is the restrictive factor to algal growth in Xin’anjiang Reservoir. In addition, the response of nutrients to Chla has spatial variabilities. Current results show the potential of Landsat 8 OLI data for estimating Chla in slight turbid reservoir and indicate that external pollution loading is an important driving force for the Chla spatiotemporal variability.












Similar content being viewed by others
References
Alcântara E, Bernardo N, Rodrigues T et al (2017) Modeling the spatio-temporal dissolved organic carbon concentration in Barra Bonita reservoir using OLI/Landsat-8 images. Model Earth Syst Environ 3:11
Chen J, Quan W (2012) Using Landsat/TM imagery to estimate nitrogen and phosphorus concentration in Taihu Lake, China. IEEE J Stars 5:273–280
Chen J, Zhu WN, Tian YQ et al (2017) Estimation of colored dissolved organic matter from Landsat-8 imagery for complex inland water: case study of Lake Huron. IEEE T Geosci Remote 55:2201–2212
Concha JA, Schott JR (2016) Retrieval of color producing agents in Case 2 waters using Landsat 8. Remote Sens Environ 185:95–107
Gitelson AA, Dall'Olmo G, Moses W et al (2008) A simple semi-analytical model for remote estimation of chlorophyll-a in turbid waters: validation. Remote Sens Environ 112:3582–3593
Gitelson AA, Gao BC, Li RR et al (2011) Estimation of chlorophyll-a concentration in productive turbid waters using a Hyperspectral Imager for the Coastal Ocean—the Azov Sea case study. Environ Res Lett 6:024023
Gordon HR, Clark DK, Mueller JL et al (1980) Phytoplankton pigments from the nimbus-7 coastal zone color scanner: comparisons with surface measurements. Science 2010:63–66
Grosse J, Bombar D, Doan HN et al (2010) The Mekong River plume fuels nitrogen fixation and determines phytoplankton species distribution in the South China Sea during low and high discharge season. Limnol Oceanogr 55:1668–1680
Han L, Jordan KJ (2005) Estimating and mapping chlorophyll-a concentration in Pensacola Bay, Florida using Landsat ETM+ data. Int J Remote Sens 26:5245–5254
Hu Y, Liu LY, Liu LL et al (2014) A Landsat-5 atmospheric correction based on MODIS atmosphere products and 6S model. IEEE J Stars 7:1609–1615
Huang C, Wang X, Yang H et al (2014) Satellite data regarding the eutrophication response to human activities in the plateau lake Dianchi in China from 1974 to 2009. Sci Total Environ 485-486:1–11
Huang C, Guo Y, Yang H et al (2015a) Using remote sensing to track variation in phosphorus and its interaction with chlorophyll-a and suspended sediment. IEEE J Stars 8:4171–4180
Huang C, Shi K, Yang H et al (2015b) Satellite observation of hourly dynamic characteristics of algae with Geostationary Ocean Color Imager (GOCI) data in Lake Taihu. Remote Sens Environ 159:278–287
Iluz D, Yacobi YZ, Gitelson A (2003) Adaptation of an algorithm for chlorophyll-a estimation by optical data in the oligotrophic Gulf of Eilat. Int J Remote Sens 24:1157–1163
Jia X, Luo W, Wu X et al (2017) Historical record of nutrients inputs into the Xin’an Reservoir and its potential environmental implication. Environ Sci Pollut Res 24:20330–20341
Ke Y, Im J, Lee J et al (2015) Characteristics of Landsat 8 OLI-derived NDVI by comparison with multiple satellite sensors and in-situ observations. Remote Sens Environ 164:298–313
Keiner LE, Yan XH (1998) A neural network model for estimating sea surface chlorophyll and sediments from Thematic Mapper imagery. Remote Sens Environ 66:153–165
Le C, Li Y, Zha Y et al (2009) A four-band semi-analytical model for estimating chlorophyll a in highly turbid lakes: the case of Taihu Lake, China. Remote Sens Environ 113:1175–1182
Le C, Hu C, English D et al (2013a) Towards a long-term chlorophyll-a data record in a turbid estuary using MODIS observations. Prog Oceanogr 109:90–103
Le C, Hu C, English D et al (2013b) Climate-driven chlorophyll-a changes in a turbid estuary: observations from satellites and implications for management. Remote Sens Environ 130:11–24
Le C, Lehrter JC, Hu C et al (2014) Spatiotemporal chlorophyll-a dynamics on the Louisiana continental shelf derived from a dual satellite imagery algorithm. J Geophys Res Oceans 119:7449–7462
Lee Z, Ahn Y-H, Mobely C et al (2010) Removal of surface-reflected light for the measurement of remote-sensing reflectance from an above-surface platform. Opt Express 18:26313–26324
Lee Z, Shang S, Qi L et al (2016) A semi-analytical scheme to estimate Secchi-disk depth from Landsat-8 measurements. Remote Sens Environ 177:101–106
Li Y, Zhang Y, Shi K et al (2017) Monitoring spatiotemporal variations in nutrients in a large drinking water reservoir and their relationships with hydrological and meteorological conditions based on Landsat 8 imagery. Sci Total Environ 599-600:1705–1717
Liro M (2015) Gravel-bed channel changes upstream of a reservoir: the case of the Dunajec River upstream of the Czorsztyn Reservoir, southern Poland. Geomorphology 228:694–702
Lymburner L, Botha E, Hestir E et al (2016) Landsat 8: providing continuity and increased precision for measuring multi-decadal time series of total suspended matter. Remote Sens Environ 185:108–118
Matthews MW, Bernard S, Winter K (2010) Remote sensing of cyanobacteria-dominant algal blooms and water quality parameters in Zeekoevlei, a small hypertrophic lake, using MERIS. Remote Sens Environ 114:2070–2087
Michalak AM, Anderson EJ, Beletsky D et al (2013) Record-setting algal bloom in Lake Erie caused by agricultural and meteorological trends consistent with expected future conditions. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A 110:6448–6452
Mobley CD (1999) Estimation of the remote-sensing reflectance from above-surface measurements. Appl Opt 38:7442–7455
Moses WJ, Gitelson AA, Berdnikov S et al (2009) Estimation of chlorophyll-a concentration in case II waters using MODIS and MERIS data—successes and challenges. Environ Res Lett 4:045005
Murphy J, Riley JP (1962) A modified single solution method for the determination of phosphate in natural waters. Anal Chim Acta 27:31–36
Nilsson C, Reidy CA, Dynesius M et al (2005) Fragmentation and flow regulation of the world’s large river systems. Science 308:405–408
Ogashawara I, Li L, Moreno-Madriñán MJ (2016) Slope algorithm to map algal blooms in inland waters for Landsat 8/Operational Land Imager images. J Appl Remote Sens 11:012005
Olmanson LG, Bauer ME, Brezonik PL (2008) A 20-year Landsat water clarity census of Minnesota’s 10,000 lakes. Remote Sens Environ 112:4086–4097
Paerl HW (1996) A comparison of cyanobacterial bloom dynamics in freshwater, estuarine and marine environments. Phycologia 35:25–35
Pahlevan N, Lee Z, Wei J et al (2014) On-orbit radiometric characterization of OLI (Landsat-8) for applications in aquatic remote sensing. Remote Sens Environ 154:272–284
Palmer SCJ, Kutser T, Hunter PD (2015) Remote sensing of inland waters: challenges, progress and future directions. Remote Sens Environ 157:1–8
Prathumratana L, Sthiannopkao S, Kim KW (2008) The relationship of climatic and hydrological parameters to surface water quality in the lower Mekong River. Environ Int 34:860–866
Qin B, Zhu G, Gao G et al (2010) A drinking water crisis in Lake Taihu, China: linkage to climatic variability and lake management. Environ Manag 45:105–112
Roy DP, Wulder MA, Loveland TR et al (2014) Landsat-8: science and product vision for terrestrial global change research. Remote Sens Environ 145:154–172
Shi K, Zhang Y, Zhou Y et al (2017) Long-term MODIS observations of cyanobacterial dynamics in Lake Taihu: responses to nutrient enrichment and meteorological factors. Sci Rep 7:40326
Simis SGH, Peters SWM, Gons HJ (2005) Remote sensing of the cyanobacterial pigment phycocyanin in turbid inland water. Limnol Oceanogr 50:237–245
Smith VH (1982) The nitrogen and phosphorus dependence of algal biomass in lakes: an empirical and theoretical analysis. Limnol Oceanogr 27:1101–1111
Smith VH (2006) Responses of estuarine and coastal marine phytoplankton to nitrogen and phosphorus enrichment. Limnol Oceanogr 51:377–384
Song K, Li L, Tedesco LP et al (2012a) Hyperspectral determination of eutrophication for a water supply source via genetic algorithm–partial least squares (GA–PLS) modeling. Sci Total Environ 426:220–232
Song K, Li L, Wang Z et al (2012b) Retrieval of total suspended matter (TSM) and chlorophyll-a (Chl-a) concentration from remote-sensing data for drinking water resources. Environ Monit Assess 184:1449–1470
Sullivan TJ, Snyder KU, Gilbert E et al (2005) Assessment of water quality in association with land use in the Tillamook Bay Watershed, Oregon, USA. Water Air Soil Poll 161:3–23
Sun D, Hu C, Qiu Z et al (2014) Influence of a red band-based water classification approach on chlorophyll algorithms for optically complex estuaries. Remote Sens Environ 155:289–302
Sun D, Hu C, Qiu Z et al (2015) Estimating phycocyanin pigment concentration in productive inland waters using Landsat measurements: a case study in Lake Dianchi. Opt Express 23:3055–3074
Tang D, Kawamura H, Lee M et al (2003) Seasonal and spatial distribution of chlorophyll-a concentrations and water conditions in the Gulf of Tonkin, South China Sea. Remote Sens Environ 85:475–483
Tett P, Droop MR, Heaney SI (1985) The Redfield Ratio and phytoplankton growth rate. J Mar Biol Assoc UK 65:487–504
Urbanski JA, Wochna A, Bubak I et al (2016) Application of Landsat 8 imagery to regional-scale assessment of lake water quality. Int J Appl Earth Obs 51:28–36
Volpe V, Silvestri S, Marani M (2011) Remote sensing retrieval of suspended sediment concentration in shallow waters. Remote Sens Environ 115:44–54
Wang Y, Xia H, Fu J et al (2004) Water quality change in reservoirs of Shenzhen, China: detection using LANDSAT/TM data. Sci Total Environ 328:195–206
Watanabe F, Alcântara E, Rodrigues T et al (2015) Estimation of chlorophyll-a concentration and the trophic state of the Barra Bonita Hydroelectric Reservoir using OLI/Landsat-8 images. Int J Env Res Pub He 12:10391
Wu C, Wu J, Qi J et al (2010) Empirical estimation of total phosphorus concentration in the mainstream of the Qiantang River in China using Landsat TM data. Int J Remote Sens 31:2309–2324
Wu Z, Zhang Y, Zhou Y et al (2015) Seasonal-spatial distribution and long-term variation of transparency in Xin’anjiang Reservoir: implications for reservoir management. Int J Env Res Pub He 12:9492–9507
Wynne TT, Stumpf RP, Tomlinson MC et al (2010) Characterizing a cyanobacterial bloom in Western Lake Erie using satellite imagery and meteorological data. Limnol Oceanogr 55:2025–2036
Xiao H, Krauss M, Floehr T et al (2016) Effect-directed analysis of aryl hydrocarbon receptor agonists in sediments from the Three Gorges Reservoir, China. Environ Sci Technol 50:11319–11328
Zhang M, Duan H, Shi X et al (2012) Contributions of meteorology to the phenology of cyanobacterial blooms: implications for future climate change. Water Res 46:442–452
Zhang Y, Ma R, Duan H et al (2014b) A spectral decomposition algorithm for estimating chlorophyll-a concentrations in Lake Taihu, China. Remote Sens 6:5090–5106
Zhang Y, Shi K, Liu X et al (2014a) Lake topography and wind waves determining seasonal-spatial dynamics of total suspended matter in turbid Lake Taihu, China: assessment using long-term high-resolution MERIS data. PLoS One 9:e98055
Zhang Y, Ma R, Zhang M et al (2015a) Fourteen-year record (2000–2013) of the spatial and temporal dynamics of floating algae blooms in Lake Chaohu, observed from time series of MODIS images. Remote Sens 7:10523–10542
Zhang Y, Wu Z, Liu M et al (2015b) Dissolved oxygen stratification and response to thermal structure and long-term climate change in a large and deep subtropical reservoir (Lake Qiandaohu, China). Water Res 75:249–258
Zhang Y, Shi K, Zhou Y et al (2016b) Monitoring the river plume induced by heavy rainfall events in large, shallow, Lake Taihu using MODIS 250m imagery. Remote Sens Environ 173:109–121
Zhang Y, Zhang Y, Shi K et al (2016a) A Landsat 8 OLI-based, semianalytical model for estimating the total suspended matter concentration in the slightly turbid Xin’anjiang Reservoir (China). IEEE J Stars 9:398–413
Zhou Q, Zhang Y, Lin D et al (2016b) The relationships of meteorological factors and nutrient levels with phytoplankton biomass in a shallow eutrophic lake dominated by cyanobacteria, Lake Dianchi from 1991 to 2013. Environ Sci Pollut Res 23:15616–15626
Zhou Y, Zhang Y, Jeppesen E et al (2016a) Inflow rate-driven changes in the composition and dynamics of chromophoric dissolved organic matter in a large drinking water lake. Water Res 100:211–221
Acknowledgements
This study was jointly funded by the National Natural Science Foundation of China (grants 41325001, 41621002, and 41501374) and the Zhejiang Provincial Natural Science Foundation of China (LQ16D010001). The authors would like to thank Zhixu Wu, Mingliang Liu, Gang Liu, Yan Yin, and Yang Bai for their participation in the field samples collection and experimental analysis. We are grateful to the two anonymous reviewers and the editor Philippe Garrigues for their constructive comments and suggestions to improve the quality of this work.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Additional information
Responsible editor: Philippe Garrigues
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Li, Y., Zhang, Y., Shi, K. et al. Spatiotemporal dynamics of chlorophyll-a in a large reservoir as derived from Landsat 8 OLI data: understanding its driving and restrictive factors. Environ Sci Pollut Res 25, 1359–1374 (2018). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11356-017-0536-7
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11356-017-0536-7