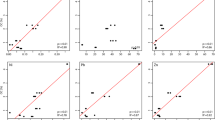
Abstract
Household wastes may constitute a vector of environmental contamination when buried, in particular through degradation and production of leachates containing significant trace metal (TM) concentrations that may constitute a serious risk to biota. The objectives of this study were to assess the bioavailability and transfer potential of various TMs present in water and sediments in a reservoir receiving landfill leachates. An active biomonitoring approach was adopted consisting of exposing naive laboratory organisms in cages deployed in the field. Aquatic insects such as Chironomus riparius larvae are good candidates since they represent key organisms in the trophic functioning of aquatic ecosystems. The results show that water, suspended particles, and sediments were significantly contaminated by various TMs (As, Cd, Cu, Ni, Pb, and Zn). Their contribution to the transfer of TMs depends, however, on the specific element considered, e.g., Cd in sediments or Pb in both suspended particles and sediments. The internal fate of TMs was investigated according to their fractionation between an insoluble and a cytosolic fraction. This approach revealed different detoxification strategies capable of preventing the induction of deleterious effects at the individual scale. However, the accumulation of several TMs in C. riparius larvae tissues may also represent a significant load potentially transferable to higher trophic levels.





Similar content being viewed by others
References
Amiard JC, Amiard-Triquet C, Barka S, Pellerin J, Rainbow PS (2006) Metallothioneins in aquatic invertebrates: their role in metal detoxification and their use as biomarkers. Aquat Toxicol 76:160–202
Arambourou H, Gismondi E, Branchu P, Beisel JN (2013) Biochemical and morphological responses in Chironomus riparius (Diptera, Chironomidae) larvae exposed to lead-spiked sediment. Environ Toxicol Chem 32:2558–2564
Ben Salem Z, Capelli N, Grisey E, Baurand PE, Ayadi H, Aleya L (2014a) First evidence of fish genotoxicity induced by heavy metals from landfill leachates: the advantage of using the RAPD-PCR technique. Ecotoxicol Environ Safe 101:90–96
Ben Salem Z, Capelli N, Laffray X, Grisey E, Ayadi H, Aleya L (2014b) Seasonal variation of heavy metals in water, sediment and roach tissues in a landfill draining system pond (Etueffont, France). Ecol Eng 69:25–37
Ben Salem Z, Xavier X Laffray, Al-Ashoor A, Ayadi H, Aleya L (2016) Metals and metalloid bioconcentrations in the tissues of Typha latifolia grown in four interconnected ponds of a domestic landfill site. J Environ Sci: in press. doi:10.1016/j.jes.2015.10.039
Bervoets L, Meregalli G, de Cooman W, Goddeeris B, Blust R (2004) Cages midge larvae (Chironomus riparius) for the assessment of metal bioaccumulation from sediments in situ. Environ Toxicol Chem 23:443–454
Bervoets L, de Jonge M, Blust R (2016) Identification of threshold body burdens of metals for the protection of the aquatic ecological status using two benthic invertebrates. Environ Pollut 210:76–84
Bichet V, Grisey E, Aleya L (2016) Spatial characterization of leachate plume using electrical resistivity tomography in a landfill composed of old and new cells (Belfort, France). Eng Geol 211:61–73
Butt TE, Gouda HM, Baloch MI, Paul P, Javadi AA, Alam A (2014) Literature review of baseline study for risk analysis—the landfill leachate case. Environ Int 63:149–162
Casado-Martinez MC, Duncan E, Smith BD, Maher WA, Rainbow PS (2012) Arsenic toxicity in a sediment-dwelling polychaete: detoxification and arsenic metabolism. Ecotoxicology 21:576–590
Chowdhury F, Gulshan J, Hossain SS (2015) A comparison of semi-parametric and non-parametric methods for estimating mean time to event for randomly left censored data. J Mod App Stat Meth 14: Article 17
de Deckere E, De Cooman W, Leloup V, Meire P, Schmitt C, von der Ohe PC (2011) Development of sediment quality guidelines for freshwater ecosystems. J Soils Sediments 11:504–517
de Jonge M, Lofts S, Bervoets B, Blust R (2014) Relating metal exposure and chemical speciation to trace metal accumulation in aquatic insects under natural field conditions. Sci Tot Environ 496:11–21
Dumas J, Hare L (2008) The internal distribution of nickel and thallium in two freshwater invertebrates and its relevance to trophic transfer. Environ Sci Technol 42:5144–5149
Ettler V, Matura M, Mihaljevič M, Bezdička P (2006) Metal speciation and attenuation in stream waters and sediments contaminated by landfill leachate. Environ Geol 49:610–619
Ettler V, Mihaljevič M, Matura M, Skalová M, Šebek O, Bezdička P (2008) Temporal variation of trace elements in waters polluted by municipal solid waste landfill leachate. Bull Environ Contam Toxicol 80:274–279
Faria MS, Lopes RJ, Malcato J, Nogueira AJA, Doares AMVM (2008) In situ bioassays with Chironomus riparius larvae to biomonitor metal pollution in rivers and to evaluate the efficiency of restoration measures in mine areas. Environ Pollut 151:213–221
Ferrari BJD, Vignati DAL, Dominik J (2014) Bioaccumulation kinetics and effects of sediment-bound contaminants on chironomids in deep waters: new insights using a low-disturbance in situ system. Environ Technol 35:456–469
Gibbons RD, Morris JWF, Prucha CP, Caldwell MD, Staley BF (2014) Longitudinal data analysis in support of functional stability concepts for leachate management at closed municipal landfills. Waste Manag 34:1674–1682
Gimbert F, de Vaufleury A, Douay F, Scheifler R, Coeurdassier M, Badot PM (2006) Modelling chronic exposure to contaminated soil. A toxicokinetic approach with terrestrial snail Helix aspersa. Environ Int 32:866–875
Gimbert F, Geffard A, Guedron S, Dominik J, Ferrari BJD (2016) Mercury tissue residue approach in Chironomus riparius: involvement of toxicokinetics and comparison of subcellular fractionation methods. Aquatic Toxicol 171:1–8
Grisey E, Aleya L (2016a) Prolonged aerobic degradation of shredded and pre-composted municipal solid waste: report from a 21-year study of leachate quality characteristics. Environ Sci Pollut Res 23:800–815
Grisey E, Aleya L (2016b) Assessing the impact of leachate plumes on groundwater quality in the Etueffont landfill (Belfort, France). Environ Earth Sci 75:913. doi:10.1007/s12665-016-5725-z
Guigue J, Mathieu O, Lévêque J, Denimal S, Steinmann M, Milloux MJ, Grisey H (2013) Dynamics of copper and zinc sedimentation in a lagooning system receiving landfill leachate. Waste Manag 33:2287–2295
Haeusler L, Moro-Goubely A-G, Berthoin G (2014) Déchets, les chiffres clés. Edition 2014. ADEME
Hare L (1992) Aquatic insects and trace metals: bioavailability, bioaccumulation, and toxicity. Critical Rev Toxicol 22:327–369
Helsel DR (2012) Statistics for censored environmental data using Minitab and R, 2nd edn. Wiley, New York. 344 p
Hernández AJ, Bartolomé C, Pérez-Leblic MI, Rodríguez J, Álvarez J, Pastor J (2012) Ecotoxicological diagnosis of a sealed municipal landfill. J Environ Manag 95:S50–S54
Ingvertsen ST, Marcussen H, Holm PE (2013) Pollution and potential mobility of Cd, Ni and Pb in the sediments of a wastewater-receiving river in Hanoi, Vietnam. Environ Monit Assess 185:9531–9548
James A, Bonnomet V, Morin A, Fribourg-Blanc B (2009) Implementation of requirements on priority substances within the context of the water framework directive. Prioritization process: monitoring-based ranking, 58 p
Khattabi H, Aleya L (2007) The dynamics of macroinvertebrate assemblages in response to environmental change in four basins of the Etueffont landfill leachate (Belfort, France). Water Air Soil Pollut 185:63–77
Khattabi H, Aleya L, Mania J (2006) Spatio-temporal distribution and characterisation of phytoplankton populations coupled with abiotic and biotic changes in landfill leachate treatment basins (Etuffont, Belfort, France). Water Air Soil Pollut 174:107–125
Kooijman SALM, Baas J, Bontje D, Broerse M, Van Gestel CAM, Jager T (2009) Ecotoxicological applications of dynamic energy budget theory. In: Devillers J (ed) Ecotoxicology modeling. Springer, Berlin, pp. 237–259
Kulikowska D, Klimiuk E (2008) The effect of landfill age on municipal leachate composition. Biores Technol 99:5981–5985
MacDonald DD, Ingersoll CG, Berger TA (2000) Development and evaluation of consensus-based sediment quality guidelines for freshwater ecosystems. Arch Environ Contam Toxicol 39:20–31
Matejczyk M, Płaza GA, Nałęcz-Jawecki G, Ulfig K, Markowska-Szczupak A (2011) Estimation of the environmental risk posed by landfills using chemical, microbiological and ecotoxicological testing of leachates. Chemosphere 82:1017–1023
Meregalli G, Vermeulen AC, Ollevier F (2000) The use of chironomid deformation in an in situ test for sediment toxicity. Ecotoxicol Environ Saf 47:231–238
Mogren CL, Webb SM, Walton WE, Trumble JT (2013) Micro x-ray absorption spectroscopic analysis of arsenic localization and biotransformation in Chironomus riparius Meigen (Diptera: Chironomidae) and Culex tarsalis Coquillett (Culicidae). Environ Pollut 180:78–83
OECD (2004) OECD Guideline 218: sediment-water chironomid toxicity using spiked sediment, pp 1–21. doi:10.1787/9789264070264-en
Péry ARR, Garric J (2006) Modelling effects of temperature and feeding level on the life cycle of the midge Chironomus riparius: an energy-based modelling approach. Hydrobiologia 553:59–66
Péry ARR, Mons R, Flammarion P, Lagadic L, Garric J (2002) A modeling approach to link food availability, growth, emergence, and reproduction for the midge Chironomus riparius. Environ Toxicol Chem 21:2507–2513
Péry ARR, Sulmon V, Mons R, Flammarion P, Lagadic L, Garric J (2003) A model to understand the confounding effects of natural sediments in toxicity tests with Chironomus riparius. Environ Toxicol Chem 22:2476–2481
Péry ARR, Geffard A, Conrad A, Mons R, Garric J (2008) Assessing the risk of metal mixtures in contaminated sediments on Chironomus riparius based on cytosolic accumulation. Ecotoxicol Environ Saf 71:869–873
Rainbow PS, Luoma SN, Wang WX (2011) Trophically available metal - a variable feast. Environ Pollut 159:2347–2349
Senese V, Boriani E, Baderna D, Mariani A, Lodi M, Finizio A, Testa S, Benfenati E (2010) Assessing the environmental risks associated with contaminated sites: definition of an ecotoxicological classification index for landfill areas (ECRIS). Chemosphere 80:60–66
Thomas R, Meybeck M (1992) The use of particulate matter. In: Chapman D (ed) Assessment of the quality of the aquatic Environnement through water, biota and sediment. D. Chapman & Hall, London, pp. 121–170
Timmermans KR, Peeters W, Tonkes M (1992) Cadmium, zinc, lead and copper in Chironomus riparius (Meigen) larvae (Diptera, Chironomidae): uptake and effects. Hydrobiologia 241:119–134
Toušová Z, Kuta J, Hynek D, Adam V, Kizek R, Bláha L, Hilscherová K (2016) Metallothionein modulation in relation to cadmium bioaccumulation and age-dependent sensitivity of Chironomus riparius larvae. Environ Sci Pollut Res Int 23:10504–10513
United Nations, Department of Economic and Social Affairs, Population Division (2015) World Population Prospects: The 2015 Revision, Key Findings and Advance Tables. Working Paper No. ESA/P/WP.241
Urase T, Salequzzaman M, Kobayashi S, Matsuo T, Yamamoto K, Suzuki N (1997) Effect of high concentration of organic and inorganic matters in landfill leachate on the treatment of heavy metals in very low concentration level. Water Sci Technol 36:349–356
van Straalen NM, Donker MH, Vijver MG, van Gestel CAM (2005) Bioavailability of contaminants estimated from uptake rates into soil invertebrates. Environ Pollut 136:409–417
Wallace WG, Luoma SN (2003) Subcellular compartmentalization of Cd and Zn in two bivalves. II. Significance of trophically available metal (TAM). Mar Ecol Prog Ser 257:125–137
Acknowledgements
The authors wish to thank Dr. Hervé Grisey and the SICTOM (Solid Waste Management Service) of Etueffont (Territoire de Belfort, France) for financial support. We also thank C. Amiot and N. Crini for their technical assistance and B. Pauget for fruitful discussions of the results.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Conflict of interest
The authors declare that they have no competing interests.
Additional information
Responsible editor: Philippe Garrigues
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Gimbert, F., Petitjean, Q., Al-Ashoor, A. et al. Encaged Chironomus riparius larvae in assessment of trace metal bioavailability and transfer in a landfill leachate collection pond. Environ Sci Pollut Res 25, 11303–11312 (2018). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11356-016-8261-1
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11356-016-8261-1