Abstract
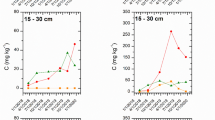
Application of raw and treated wastewater for irrigation is an extensive practice for agricultural production in arid and semiarid regions. Raw textile wastewater has been used for cultivation in urban and peri-urban areas in Pakistan without any systematic consideration to soil quality. We conducted a laboratory incubation study to investigate the effects of low C/N ratio raw textile wastewater on soil nitrogen (N) contents, labile carbon (C) as water-soluble C (WSC) contents, and activities of urease and dehydrogenase enzymes. The 60-day incubation study used an alkaline clay loam aridisol that received 0 (distilled water), 25, 50, and 100% wastewater concentrations, and microcosms were incubated aerobically under room temperature at 70% water holding capacity. Results revealed that raw wastewater significantly (p < 0.05) changed soil N pools and processes, WSC contents, and enzymatic activities. The organic and inorganic N species increased with increasing wastewater concentrations, whereas WSC contents followed an opposite trend. The highest NH4 +-N and NO3 −-N contents were observed in soil treated with 100% wastewater. The extractable organic N (EON) contents always represented >50% of the soil total Kjeldahl N (TKN) contents and served as the major N pool. However, nitrification index (NO3 −-N/NH4 +-N ratio) decreased at high wastewater concentrations. A significant negative correlation was observed between EON and WSC (p < 0.05) and between net nitrification and WSC/EON ratio (p < 0.01). In contrast, nitrification index and WSC contents were correlated, positively suggesting WSC potentially controlling N turnover in nutrient-poor aridisol. We found significant (p < 0.0001) positive correlations of soil urease and dehydrogenase enzymatic activities with soil-extractable mineral N contents indicating coupled N cycling and soil biological activity. Higher production and accumulation of soil NO3 −-N and EON contents in concentrated wastewater-treated soil could pose an ecological concern for soil fertility, biological health, and water quality. However, the EON could lead to mineral N pool but only if sufficient labile C source was present. The effects of wastewater irrigation on soil N cycling need to be assessed before it is recommended for crop production.





Similar content being viewed by others
References
Adeli A, Varco JJ (2001) Swine lagoon effluent as a source of nitrogen and phosphorus for summer forage grasses. Agron J 93:1174–1181
Adeli A, Varco JJ, Rowe DE (2003) Swine effluent irrigation rate and timing effects on bermudagrass growth, nitrogen and phosphorus utilization, and residual soil nitrogen. J Environ Qual 32:681–686
Adrover M, Farrús E, Moyà G, Vadell J (2012) Chemical properties and biological activity in soils of Mallorca following twenty years of treated wastewater irrigation. J Environ Manag 95:188–192
Aguilar MJ (2009) Olive oil mill wastewater for soil nitrogen and carbon conservation. J Environ Manag 90:2845–2848
Almeida LC, Garcia-Segura S, Arias C, Bocchi N, Brillas E (2012) Electrochemical mineralization of the azo dye Acid Red 29 (Chromotrope 2R) by photoelectro-Fenton process. Chemosphere 89:751–758
Angin I, Yaganoglu AV, Turan M (2005) Effects of long-term wastewater irrigation on soil properties. J Sustain Agric 26:31–42
Anwar HN, Nosheen F, Hussain S, Nawaz W (2010) Socio-economics consequences of reusing wastewater in agriculture in Faisalabad. Pak J Life Soc Sci 8:102–105
APHA (1998) Standard methods for the examination of water and wastewater, 20th edn. American Public Health Association, New York
Arif MS, Riaz M, Shahzad SM, Yasmeen T, Buttler A, Garcıa-Gil JC, Roohi M, Rasool A (2016) Contrasting effects of untreated textile wastewater onto the soil available nitrogen-phosphorus and enzymatic activities in aridisol. Environ Monit Assess 188:1–15
Bond WJ (1998) Effluent irrigation: an environmental challenge for soil science. Aust J Soil Res 36:543–555
Bouyoucos GJ (1962) Hydrometer method improved for making particle-size analysis of soils. Agron J 5:464–465
Bremner JM, Keeney DR (1965) Steam distillation methods for determination of ammonium, nitrate, and nitrite. Anal Chem Acta 32:215–163
Bremner JM, Tabatabai MA (1972) Use of an ammonia electrode for determination of ammonium in Kjeldahl analysis of soils. Comm Soil Sci Plant Anal 3:71–80
Cabrera ML, Kissel DE, Vigil MF (2005) Nitrogen mineralization from organic residues: research opportunities. J Environ Qual 3:75–79
Caravaca F, Masciandaro G, Ceccanti B (2002) Land use in relation to soil chemical and biochemical properties in a semiarid Mediterranean environment. Soil Tillage Res 68:23–30
Casida LE, Klein DA, Santoro T (1964) Soil dehydrogenase activity. Soil Sci 98:371–376
Chaerun SK, Pangesti NPD, Toyota K, Whitman WB (2011) Changes in microbial functional diversity and activity in paddy soils irrigated with industrial wastewaters in Bandung, West Java Province, Indonesia. Water Air Soil Pollut 217:491–502
Chen W, Wu L, Frankenberger WT, Chang AC (2008) Soil enzyme activities of long-term reclaimed wastewater-irrigated soils. J Environ Qual 37:S36–S42
da Fonseca AF, Herpin U, Paula AM, Victoria RL, Melfi AJ (2007) Agricultural use of treated sewage effluents: agronomic and environmental implications and perspectives for Brazil. Sci Agric 64:194–209
Elifantz H, Kautsky L, Mor-Yosef M, Tarchitzky J, Bar-Tal A, Chen Y, Minz D (2011) Microbial activity and organic matter dynamics during 4 years of irrigation with treated wastewater. Microb Ecol 62:973–981
Ensink JHJ, Mahmood T, van der Hoek W, Raschid-Sally L, Amerasinghe FP (2004) A nation-wide assessment of wastewater use in Pakistan: an obscure activity or a vitally important one? Water Policy 6:1–10
Fernandes SAP, Bettiol W, Cerri CC (2005) Effect of sewage sludge on microbial biomass, basal respiration, metabolic quotient and soil enzymatic activity. Appl Soil Ecol 30:65–77
Filip Z, Kazanawa S, Berthelin J (2000) Distribution of microorganisms, biomass ATP, and enzyme activities in organic and mineral particles of a long-term wastewater irrigated soil. J Plant Nutr Soil Sci 163:143–150
Friedel JK, Langer T, Siebe C, Stahr K (2000) Effects of long-term waste water irrigation on soil organic matter, soil microbial biomass and its activities in Central Mexico. Biol Fertil Soils 31:414–421
Gamba C, Piovanelli C, Papini R, Pezzarossa B, Ceccarini L, Bonari E (2005) Soil microbial characteristics and mineral nitrogen availability as affected by olive oil waste water applied to cultivated soil. Comm Soil Sci Plant Anal 36:937–950
Garcia C, Hernandez T, Costa F, Ceccanti B (1994) Biochemical parameters in soils regenerated by the addition of organic wastes. Waste Manage Res 12:457–466
Garcia-Gil JC, Plaza C, Soler-Rovira P, Polo A (2000) Long-term effects of municipal solid waste compost application on soil enzyme activities and microbial biomass. Soil Biol Biochem 32:1907–1913
Geisseler D, Horwath WR, Doane TA (2009) Significance of organic nitrogen uptake from plant residues by soil microorganisms as affected by carbon and nitrogen availability. Soil Biol Biochem 41:1281–1288
Ghaly AE, Ananthashankar R, Alhattab M, Ramakrishnan VV (2014) Production, characterization and treatment of textile effluents: a critical review. J Chem Engin Process Technol 5:182
Ghani A, Dexter M, Perrott KW (2003) Hot-water extractable carbon in soils: a sensitive measurement for determining impacts of fertilization, grazing and cultivation. Soil Biol Biochem 35:1231–1243
Gleick PH (2000) The World’s water 2000–2001: the biennial report on freshwater resources. Island Press, Washington, DC
Hamilton A, Stagnitti F, Xiong X, Kreidl SL, Benke KK, Maher P (2007) Wastewater irrigation: the state of play. Vadose Zone J 6:823–840
Haney RL, Franzluebbers AJ, Jin VL, Johnson MV, Haney EB, White MJ, Harmel RD (2012) Soil organic C:N vs. water-extractable organic C:N. J. Soil Sci 2:269–274
Harrison EZ, Oakes SR, Hysell M, Hay A (2006) Organic chemicals in sewage sludges. Sci Total Environ 367:481–497
Henriksen TM, Breland TA (1999) Decomposition of crop residues in the field; evaluation of a simulation model developed from microcosm studies. Soil Biol Biochem 31:1423–1434
Homsi J (2000) The present state of sewage treatment. International Report. Water Supply 18:325–327
Hussain I, Raschid L, Hanjra M, Marikar F, van der Hoek W (2001) A framework for analyzing socioeconomic, health and environmental impacts of wastewater use in agriculture in developing countries. Working Paper 26. International Water Management Institute (IWMI), Colombo
Janssen BH (1996) Nitrogen mineralization in relation to C:N ratio and decomposability of organic materials. Plant Soil 181:39–45
Jarrell WM, Armstrong DE, Griga DF, Kelly EF, Monger HC, Wedin DA (1999) Soil water and temperature status. In: Robertson GP, Coleman DC, Bledsoe CS, Sollins P (eds) Standard soil methods for long-term ecological research. Oxford University Press, Oxford, pp. 55–73
Kandeler E, Gerber H (1988) Short-term assay of soil urease activity using colorimetric determination of ammonium. Biol Fertil Soils 6:68–72
Kandeler E, Kampichler C, Horak O (1996) Influence of heavy metals on the functional diversity of soil microbial communities. Biol Fertil Soils 23:299–306
Kaushik A, Nisha R, Jagjeeta K, Kaushik CP (2005) Impact of long and short term irrigation of a sodic soil with distillery effluent in combination with bioamendments. Bioresour Technol 96:1860–1866
Kayikcioglu HH (2012) Short-term effects of irrigation with treated wastewater on microbiological activity of a Vertic xerofluvent soil under Mediterranean conditions. J Environ Manag 102:108–114
Keeney DR, Nelson DW (1982) Nitrogen-inorganic forms. In: Page AL (ed) Methods of soil analysis. Agronomy: chemical and microbiological properties, 2nd edn. American Society of Agronomy, Madison, WI, pp. 643–698
Khalid A, Saba B, Kanwal H, Nazir A, Arshad M (2013) Responses of pea and wheat to textile wastewater reclaimed by suspended sequencing batch bioreactors. Int Biodeter Biodegr 85:550–555
Kiziloglu FM, Turan M, Sahin U, Kuslu Y, Dursun A (2008) Effects of untreated and treated wastewater irrigation on some chemical properties of cauliflower (Brassica olerecea L. var. botrytis) and red cabbage (Brassica olerecea L. Var. Rubra) grown on calcareous soil in Turkey. Agric. Water Manage 95:716–724
Knechtel RJ (1978) A more economical method for the determination of chemical oxygen demand. Water Pollut Control 166:25–29
Kuzyakov Y, Bol R (2006) Sources and mechanisms of priming effect induced in two grassland soils amended with slurry and sugar. Soil Biol Biochem 38:747–758
Lado M, Bar-Tal A, Azenkot A, Assouline S, Ravina I, Erner Y, Fine P, Dasberg S, Ben-Hur M (2012) Changes in chemical properties of semiarid soils under long-term secondary treated wastewater irrigation. Soil Sci Soc Am J 76:1358–1369
Leal RMP, Firme LP, Herpin U, da Fonseca AF, Montes CR, dos Santos Dias CT, Melfi AJ (2010) Carbon and nitrogen cycling in a tropical Brazilian soil cropped with sugarcane and irrigated with wastewater. Agric Water Manag 97:271–276
Liang Q, Gao RT, Xi BD, Zhang Y, Zhang H (2014) Long term effects of irrigation using water from the river receiving treated industrial wastewater on soil organic carbon fractions and enzyme activities. Agric Water Manag 135:100–108
Lucho-Constantino CA, Álvarez-Suárez M, Beltrán-Hernández RI, Prieto-García F, Poggi-Varaldo HM (2005) A multivariate analysis of the accumulation and fractionation of major and trace elements in agricultural soils in Hidalgo State, Mexico irrigated with raw wastewater. Environ Int 31:313–323
Masciandaro G, Ceccanti B, Garcia C (1997) Changes in soil biochemical and cracking properties induced by living mulch systems. Can J Soil Sci 77:579–587
Masciandaro G, Peruzzi E, Doni S, Macci C (2014) Fertigation with wastewater and vermicompost: soil biochemical and agronomic implications. Pedosphere 24:625–634
Master Y, Laughlin RJ, Stevens RJ, Shaviv A (2004) Nitrite formation and nitrous oxide emissions as affected by reclaimed effluent application. J Environ Qual 33:852–860
Matsumoto S, Ae N (2004) Characteristics of extractable soil organic nitrogen determined by using various chemical solutions and its significance for nitrogen uptake by crops. Soil Sci Plant Nutr 50:1–9
Meli S, Porto M, Belligno A, Bufo SA, Mazzatura A, Scopa A (2002) Influence of irrigation with lagooned urban wastewater on chemical and microbiological soil parameters in a citrus orchard under Mediterranean conditions. Sci Total Environ 285:69–77
Mengel K (1996) Turnover of organic nitrogen in soils and its availability to crops. Plant Soil 81:3–93
Mikanova O (2006) Effects of heavy metals on some soil biological parameters. J Geochem Explor 88:220–223
Mohawesh O, Mahmoud M, Janssen M, Lennartz B (2014) Effect of irrigation with olive mill wastewater on soil hydraulic and solute transport properties. Int J Environ Sci Technol 11:927–934
Mojiri A (2011) Effects of municipal wastewater on physical and chemical properties of saline soil. J Biol Environ Sci 5:71–76
Moraetis D, Stamati FE, Nikolaidis NP, Kalogerakis N (2011) Olive mill wastewater irrigation of maize: impacts on soil and groundwater. Agric Water Manag 98:1125–1132
Mosse KPM, Patti AF, Smernik RJ, Christen EW, Cavagnaro TR (2012) Physicochemical and microbiological effects of long and short-term winery wastewater application to soils. J Hazard Mater 201:219–228
Mulvaney RL, Khan SA, Hoeft RG, Brown HM (2001) A soil organic nitrogen fraction that reduces the need for nitrogen fertilization. Soil Sci Soc Am J 65:1164–1172
Nannipieri P, Kandeler E, Ruggiero P (2002) Enzyme activities and microbiological and biochemical processes in soil. In: Burns RG, Dick R (eds) Enzymes in the environment. Marcel Dekker, Inc., New York, pp. 1–33
Pang YL, Abdullah AZ (2013) Current status of textile industry wastewater management and research progress in Malaysia: a review. Clean–Soil, Air, Water 41:751–764
Pascual JA, Hernandez T, Garcia C, Ayuso M (1998) Enzymatic activities in an arid soil amended with urban wastes: laboratory experiment. Bioresour Technol 64:131–138
Pedrero F, Kalavrouziotis I, Alarcón JJ, Koukoulakis P, Asano T (2010) Use of treated municipal wastewater in irrigated agriculture—review of some practices in Spain and Greece. Agric Water Manag 97:1233–1241
Piotrowska A, Iamarino G, Rao MA, Gianfreda L (2006) Short-term effects of olive mill wastewater (OMW) on chemical and biochemical properties of a semiarid Mediterranean soil. Soil Biol Biochem 38:600–610
Qadir M, Sharma BR, Bruggeman A, Choukr-Allah R, Karajeh F (2007) Nonconventional water resources and opportunities for water augmentation to achieve food security in water scarce countries. Agric Water Manag 87:2–22
Qadir M, Wichelns D, Raschid-Sally L, McCornick PG, Drechsel P, Bahri A, Minhas PS (2010) The challenges of wastewater irrigation in developing countries. Agric Water Manag 97:561–568
Qian YL, Mecham B (2005) Long-term effects of recycled wastewater irrigation on soil chemical properties on golf course fairways. Agron J 97:717–721
Ramirez-Fuentes E, Lucho-Constantino C, Escamilla-Silva E, Dendooven L (2002) Characteristics, and carbon and nitrogen dynamics in soil irrigated with wastewater for different lengths of time. Bioresour Technol 85:179–187
Reddy GB, Faza A, Bennett RJ (1987) Activity of enzymes in rhizosphere and non-rhizosphere soils amended with sludge. Soil Biol Biochem 19:203–205
Ros GH, Hoffland E, van Kessel C, Erwin JM, Temminghoff EJM (2009) Extractable and dissolved soil organic nitrogen—a quantitative assessment. Soil Biol Biochem 41:1029–1039
Rusan MJM, Hinnawi S, Rousan L (2007) Long term effect of wastewater irrigation of forage crops on soil and plant quality parameters. Desalination 215:143–152
Sial RA, Chaudhary MF, Abbas ST, Latif MI, Khan AG (2006) Quality of effluents from Hattar Industrial Estate. J Zhejiang Univ Sci B 7:974–980
Siebe C (1998) Nutrient inputs to soils and their uptake by alfalfa through long-term irrigation with untreated sewage effluent in Mexico. Soil Use Manage 14:119–122
Sierra J, Martí E, Garau MA, Cruañas R (2007) Effects of the agronomic use of olive oil mill wastewater: field experiment. Sci Total Environ 37:90–94
Singh A, Agrawal M (2012) Effects of waste water irrigation on physical and biochemical characteristics of soil and metal partitioning in Beta vulgaris L.. Agric Res 1(4):379–391
Simek M (2000) Nitrification in soil—terminology and methodology (review). Rost Vyroba 46:385–395
Stevenson FJ (1994) Humus chemistry, genesis, composition, reactions. Wiley, New York
Tilman D, Cassman KG, Matson PA, Naylor R, Polasky S (2002) Agricultural sustainability and intensive production practices. Nature 418:671–677
Topac FO, Dindar E, Ucaro˘glu S, Baskaya HS (2009) Effect of a sulfonated azo dye and sulfanilic acid on nitrogen transformation processes in soil. J Hazard Mater 17:1006–1013
Topac-Sagban FO (2011) Impacts of wastewater sludge amendments in restoring nitrogen cycle in p-nitrophenol contaminated soil. J Environ Sci 23:616–623
Toze S (2006) Reuse of effluent water: benefits and risks. Agric Water Manag 80:147–159
Tsiknia M, Tzanakakis VS, Oikonomidis D, Paranychianakis NV, Nikolaidis NP (2014) Effects of olive mill wastewater on soil carbon and nitrogen cycling. Appl Microbiol Biotechnol 98:2739–2749
Walkley A, Black IA (1934) An examination of Degtjareff method for determining soil organic matter and a proposed modification of the chromic acid titration method. Soil Sci 37:29–37
WHO (2006) Guidelines for the safe use of wastewater, excreta and grey water: wastewater use in agriculture. World Health Organization, Geneva, Switzerland
Woodmansee RG, Duncan DA (1980) Nitrogen and phosphorus dynamics and budgets in annual grass-lands. Ecology 61:893–904
Yan J, Pan G (2010) Effects of pulp wastewater irrigation on soil enzyme activities and respiration from a managed wetland. Soil Sediment Contam: An Intern J 19:204–216
Zhang L, Wang S, Imai A (2015) Spatial and temporal variations in sediment enzyme activities and their relationship with the trophic status of Erhai Lake. Ecol Eng 75:365–369
Acknowledgements
The authors are thankful to the Higher Education Commission of Pakistan for providing financial support for this research work via grant no. PM-IPFP/HRD/HEC/2011/2269. The current work is part of the thesis of M. Phil research work of Miss Mahnaz Roohi.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Additional information
Responsible editor: Zhihong Xu
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Roohi, M., Riaz, M., Arif, M.S. et al. Low C/N ratio raw textile wastewater reduced labile C and enhanced organic-inorganic N and enzymatic activities in a semiarid alkaline soil. Environ Sci Pollut Res 24, 3456–3469 (2017). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11356-016-8102-2
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11356-016-8102-2