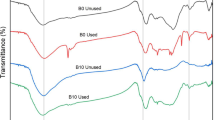
Abstract
This paper reports the results of vermicomposting of water lettuce biomass (WL) spiked with cow dung at ratios of 20, 40, 60, and 80 % employing Eisenia fetida. A total of four treatments were established and changes in chemical properties of mixtures were observed. Vermicomposting caused a decrease in pH, TOC, volatile solids, and C/N ratio by 1.01–1.08-fold, 0.85–0.92-fold, 0.94–0.96-fold, 0.56–0.70-fold, respectively, but increase in EC, totN, totP, totK, totCa, totZn, totFe, and totCu, by 1.19–1.42-fold, 1.33–1.68-fold, 1.38–1.69-fold, 1.13–1.24-fold, 1.04–1.11-fold, 1.16–1.37-fold, 1.05–1.113-fold, 1.10–1.27-fold, respectively. Overall, the treatment with 60–80 % of WL showed the maximum decomposition and mineralization rates. The earthworm showed the growth and reproduction rate in considerable ranges in all treatment setups but setups with 60–80 % WL proportion exhibited the optimum results. Results reveal that biomass of water lettuce can be utilized effectively for production of valuable manure through vermicomposting system.



Similar content being viewed by others
References
Benitez E, Nogales R, Elvira C, Masciandaro G, Ceccanti B (1999) Enzyme activities as indicators of the stabilization of sewage sludge composting with Eisenia foetida. Bioresource Technol 67:297–303
BIS (1982) Methods for analysis of solid wastes (excluding industrial solid wastes). Indian Standards Institution, New Delhi
Butt KR (1993) Utilization of solid paper-mill sludge and spent brewery yeast as a feed for soil-dwelling earthworms. Bioresour Technol 44:105–107
Cordo HA, DeLoach JC, Ferrer R (1981) Biological studies on two weevils, Ochatina bruchi and Onychylis cretatus, collected from Pistia and other aquatic plants in Argentina. Ann Entom Soc Amer 74:363–369
Das D, Bhattacharyya P, Ghosh BC, Banik P (2016) Bioconversion and biodynamics of Eisenia foetida in different organic wastes through microbially enriched vermiconversion technologies. Ecol Eng 86:154–161
Dominguez J (2004) State-of-art and new perspective on vermicomposting research. In: Edwards C A, Earthworm Ecology, second ed CRC Press, pp 401–424
Fang M, Wong JWC (1999) Effects of lime amendments of availability of heavy metals and maturation on sewage sludge composting. Environ Pollut 106:83–89
FAO (2002) Management of problematic aquatic weeds in Africa. FAO efforts and achievement during the period 1991–2001. Food and Agriculture Organization of United Nations, Rome, p. 28
Fu X, Huang K, Cui G, Chen X, Li F, Zhang X, Li F (2015) Dynamics of bacterial and eukaryotic community associated with stability during vermicomposting of pelletized dewatered sludge. International Biodeterior Biodegrad 104:452–459
Gajalakshmi S, Ramasamy EV, Abbasi SA (2001) Assessment of sustainable vermiconversion of water hyacinth at different reactor efficiencies employing Eudrilus eugeniae Kingberg. Bioresour Technol 80:131–135
Garg VK, Suthar S, Yadav A (2012) Management of food industry waste employing vermicomposting technology. Bioresour Technol 126: 437–443
Gomez-Brandon M, Lazcano M, Dominguez J (2013) Changes in chemical and microbiological properties of rabbit manure in a continuous-feeding vermicomposting system. Bioresour Technol 128:310–316
Gupta R, Mutiyar PK, Rawat NK, Saini MS, Garg VK (2007) Development of a water hyacinth based vermireactor using an epigeic earthworm Eisenia fetida. Bioresour Technol 98:2605–2610
Huang GF, Wong JW, Wu QT, Nagar BB (2004) Effect of C/N on composting of pig manure with sawdust. Waste Manag 24(8):805–813
Khwairakpam M, Bhargava R (2009) Vermitechnology for sewage sludge recycling. J Hazard Mater 161:948–954
Lim SL, Lee LH, Wu TY (2016) Sustainability of using composting and vermicomposting technologies for organic solid waste biotransformation: recent overview, greenhouse gases emissions and economic analysis. J Cleaner Product 111:262–278
Mupambwa HA, Ravindran B, Mnkeni PNS (2016) Potential of effective micro-organisms and Eisenia fetida in enhancing vermi-degradation and nutrient release of fly ash incorporated into cow dung–paper waste mixture. Waste Manag 48:165–173
Negi R, Suthar S (2013) Vermistabilization of paper mill wastewater sludge using Eisenia fetida. Bioresour Technol 128:193–198
Orozco FH, Cegarra J, Trujillo LM, Roig A (1996) Vermicomposting of coffee pulp using the earthworm Eisenia foetida: effects on C and N contents and the availability of nutrients. Biol Fert. Soils 22:162–166
Owamah HI, Enaboifo MA, Izinyon OC (2014) Treatment of wastewater from raw rubber processing industry using water lettuce macrophyte pond and the reuse of its effluent as biofertilizer. Agric Water Manag 146:262–269
Pramanik P (2010) Changes in enzymatic activities and microbial properties in vermicompost of water hyacinth as affected by pre-composting and fungal inoculation: a comparative study of ergosterol and chitin for estimating fungal biomass. Waste Manag 30:1472–1476
Rodríguez R, Julio C, Palma J (2000) Nutritive value of water lettuce (Pistia stratiotes) and its possibility in animal feed. Zootec Trop 18:213–226
Singh J, Kalamdhad AS (2013) Assessment of bioavailability and leachability of heavy metals during rotary drum composting of green waste (water hyacinth. Ecol Eng 52:59–69
Singh J, Kaur A, Vig AP, Rup PJ (2010) Role of Eisenia fetida in rapid recycling of nutrients from bio sludge of beverage industry. Ecotoxicol Environ Saf 73:430–435
Soobhany N, Mohee R, Garg VK (2015) Comparative assessment of heavy metals content during the composting and vermicomposting of municipal solid waste employing Eudrilus eugeniae. Waste Managem 39:130–145
Suthar S (2007) Nutrient changes and biodynamics of epigeic earthworm Perionyx excavatus (Perrier) during recycling of some agriculture wastes. Bioresour Technol 98:1608–1614
Suthar S (2010) Recycling of agro-industrial sludge through vermitechnology. Ecol Eng 36:1028–1036
Suthar S (2012) Vermistabilization of wastewater sludge from milk processing industry. Ecol Eng 47:115–119
Suthar S, Gairola S (2014) Nutrient recovery from urban forest leaf litter waste solids using Eisenia fetida. Ecol Eng 694:337–343
Suthar S, Ram S (2008) Does substrate quality affects the earthworm growth and reproduction patterns in vermicomposting system? A study by using three popular composting earthworms. Int J Environ Waste Manag 6(2):584–600
Suthar S, Singh S (2008) Feasibility of vermicomposting in biostabilization of sludge from a distillery industry. Sci Total Environ 394:237–244
Suthar S, Mutiyar PK, Singh S (2012) Vermicomposting of milk processing industry sludge spiked with plant wastes. Bioresour Technol 116:214–219
Suthar S, Sharma K, Mutiyar PK (2015) Nutrient recovery from compostable fractions of municipal solid wastes using vermitechnology. J Mater Recycl Waste Manag 17:174–184
Taeporamaysamai O, Ratanatamskul C (2016) Co-composting of various organic substrates from municipal solid waste using an on-site prototype vermicomposting reactor. Int Biodeter Biodegrad 113:357–366
Tripathi G, Bhardwaj P (2004) Decomposition of kitchen waste amended with cow manure using epigeic species (Eisenia fetida) and an anecic species (Lampito mauritii. Bioresour Technol 92:215–218
Varma VS, Kalamdhad AS, Khwairkpam M (2016) Feasibility of Eudrilus eugeniae and Perionyx excavatus in vermicomposting of water hyacinth. Ecol Eng 94:127–135
Wang L, Zhang Y, Lian J, Chao J, Gao Y, Yang F, Zhang L (2013) Impact of fly ash and phosphatic rock on metal stabilization and bioavailability during sewage sludge vermicomposting. Bioresour Technol 136:281–287
Wasagu RSU, Lawal M, Shehu S, Alfa HH, Muhammad C (2013) Nutritive values, mineral and antioxidant properties of Pistia stratiotes (water lettuce). Nigerian Journal of Basic and Applied Science 21(4):253–257
Yadav A, Garg VK (2011) Vermicomposting—an effective tool for the management of invasive weed Parthenium hysterophorus. Bioresour Technol 102:5891–5895
Zimmels Y, Kirzhner F, Malkovskaja A (2006) Application of Eichhornia crassipes and Pistia stratiotes for treatment of urban sewage in Israel. J Environ Manag 81:420–428
Acknowledgments
The authors are highly thankful to editor Prof. Garrigues and five anonymous reviewers for valuable comments on earlier version of this manuscript.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Additional information
Responsible Editor: Philippe Garrigues
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Suthar, S., Pandey, B., Gusain, R. et al. Nutrient changes and biodynamics of Eisenia fetida during vermicomposting of water lettuce (Pistia sp.) biomass: a noxious weed of aquatic system. Environ Sci Pollut Res 24, 199–207 (2017). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11356-016-7770-2
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11356-016-7770-2