Abstract
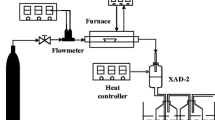
Thermal treatment of polychlorinated biphenyls (PCBs) contaminated soil was shown in earlier work to generate new PCBs, as well as polychlorinated dibenzo-p-dioxins (PCDDs) and polychlorinated dibenzofurans (PCDFs). In this study, this thermal desorption was conducted with addition of three distinct inhibitors, including ammonium sulphate, urea and calcium oxide, to inhibit the formation of PCDDs and PCDFs when remediating PCBs-contaminated soil. Experiments were conducted for 40 min at 400 °C after adding 1 wt.% of inhibitor. Both the total PCDD/Fs and international toxic equivalent quantity (I-TEQ) reduced when inhibitors were introduced. Of the three compounds tested, CaO shows the highest inhibition efficiency, 92.2 % for total PCDD/Fs and 95.6 % for I-TEQ. The amount of CaO added also influences the suppression efficiency of PCDD/Fs. These results suggest that promoting desorption and destruction of precursors is probably the mechanism of suppression.





Similar content being viewed by others
References
Buser HR (1979) Formation of polychlorinated dibenzofurans (PCDF) from the pyrolysis of individual PCB isomers. Chemosphere 8:157–174
Chang MB, Cheng YC, Chi KH (2006) Reducing PCDD/F formation by adding sulfur as inhibitor in waste incineration processes. Sci Total Environ 366:456–465
Chen T, Gu YL, Yan JH, Li XD, Lu SY, Dai HF, Cen KF (2008) Polychlorinated dibenzo-p-dioxins and dibenzofurans in flue gas emissions from municipal solid waste incinerators in China. J Zhejiang Univ-Sci A 9:1296–1303
Fu JY, Li XD, Chen T, Lin XQ, Buekens A, Lu SY, Yan JH, Cen KF (2015) PCDD/F′ suppression by sulphur-amine/ammonium compounds. Chemosphere 123:9–16
Gomes HI, Dias-Ferreira C, Ribeiro AB (2013) Overview of in situ and ex situ remediation technologies for PCB contaminated soils and sediments and obstacles for full-scale application. Sci Total Environ 445-446:237–260
Gullett BK, Bruce KR, Beach LO (1992) Effect of sulfur-dioxide on the formation mechanism of polychlorinated dibenzodioxin and dibenzofuran in municipal waste combustors. Environ Sci Technol 26:1938–1943
Hajizadeh Y, Onwudili JA, Williams PT (2012) Effects of gaseous NH3 and SO2 on the concentration profiles of PCDD/F in fly ash under post-combustion zone conditions. Waste Manag 32:1378–1386
Hu XT, Zhu JX, Ding Q (2011) Environmental life-cycle comparisons of two polychlorinated biphenyl remediation technologies: incineration and base catalysed decomposition. J Hazard Mater 191:258–268
Ji SS, Li XD, Xu X, Chen T (2012) Low-temperature thermal treatment of dioxin in medical waste fly ash under unert atmosphere. J Environ Sci (China) 33:3999–4005
Kasai E, Kuzuhara S, Goto H, Murakami T (2008) Reduction in dioxin emissions by the addition of urea as aqueous solution to high-temperature combustion gas. ISIJ Int 48:1305–1310
Kuzuhara S, Sato H, Tsubouchi N, Ohtsuka Y, Kasai E (2005) Effect of nitrogen-containing compounds on polychlorinated dibenzo-p-dioxin/dibenzofuran formation through de novo synthesis. Environ Sci Technol 39:795–799
Lee JK, Park D, Kim BU, Dong JL, Lee S (1998) Remediation of petroleum-contaminated soils by fluidised thermal desorption. Waste Manag 18:503–507
Lin X, Jin Y, Wu H, Chen T, Li X, Lu S, Jiang X, Yan J (2013) Removal of PCDD/F and PCB from flue gas using a pilot gas cleaning system. J Environ Sci 25:1833–1840
Liu W, Zheng M, Zhang B, Qian Y, Ma X, Liu W (2005) Inhibition of PCDD/F formation from dioxin precursors by calcium oxide. Chemosphere 60:785–790
Liu J, Qi ZF, Li XD, Chen T, Buekens A, Yan JH, Ni MJ (2015a) Effect of oxygen content on the thermal desorption of polychlorinated biphenyl contaminated soil. Environ Sci Pollut Res 22:12289–12297
Liu J, Qi ZF, Zhao ZH, Li XD, Buekens A, Yan JH, Ni MJ (2015b) Thermal desorption of PCB-contaminated soil with sodium hydroxide. Environ Sci Pollut Res 22:19538–19545
Lundin L, Aurell J, Marklund S (2011) The behavior of PCDD and PCDF during thermal treatment of waste incineration ash. Chemosphere 84:305–310
Norris G, Al-Dhahir Z, Birnstingl J, Plant SJ, Cui S, Mayell P (1999) A case study of the management and remediation of soil contaminated with polychlorinated biphenyls. Eng Geol 53:177–185
Pandelova ME, Lenoir D, Kettrup A, Schramm KW (2005) Primary measures for reduction of PCDD/F in co-combustion of lignite coal and waste: effect of various inhibitors. Environ Sci Technol 39:3345–3350
Qi ZF, Chen T, Bai SH, Yan M, Lu SY, Buekens A, Yan JH, Bulmau C, Li XD (2014) Effect of temperature and particle size on the thermal desorption of PCBs from contaminated soil. Environ Sci Pollut Res 21:4697–4704
Raghunathan K, Gullett BK (1996) Role of sulfur in reducing PCDD and PCDF formation. Environ Sci Technol 30:1827–1834
Ruokojârvi P, Asikainen A, Ruuskanen J, Tuppurainen K, Mueller C, Kilpinen P, Yli-Keturi N (2001) Urea as a PCDD/F inhibitor in municipal waste incineration. J Air Waste Manag Assoc 51:422–431
Ruokojarvi PH, Asikainen AH, Tuppurainen KA, Ruuskanen J (2004) Chemical inhibition of PCDD/F formation in incineration processes. Sci Total Environ 325:83–94
Ryan SP, Li XD, Gullett BK, Lee CW, Clayton M, Touati A (2006) Experimental study on the effect of SO2 on PCDD/F emissions: determination of the importance of gas-phase versus solid-phase reactions in PCDD/F formation. Environ Sci Technol 40:7040–7047
Samaras P, Blumenstock M, Lenoir D, Schramm K-W, Kettrup A (2000) PCDD/F prevention by novel inhibitors: addition of inorganic S- and N-compounds in the fuel before combustion. Environ Sci Technol 34:5092–5096
Samaras P, Blumenstock M, Lenoir D, Schramm KW, Kettrup A (2001) PCDD/F inhibition by prior addition of urea to the solid fuel in laboratory experiments and results statistical evaluation. Chemosphere 42:737–743
Sato T, Todoroki T, Shimoda K, Terada A, Hosomi M (2010) Behavior of PCDD/PCDF in remediation of PCB-contaminated sediments by thermal desorption. Chemosphere 80:184–189
Shao K, Yan JH, Li XD, Lu SY, Wei YL, Fu MX (2010) Inhibition of de novo synthesis of PCDD/Fs by SO2 in a model system. Chemosphere 78:1230–1235
Takada M, Uchida R, Taniguchi S, Hosomi M (1997) Chemical dechlorination of PCB by the base catalysed decomposition process. Organohalogen Compd 31:435–440
USEPA (1994) Method 1613: tetra- through octa-chlorinated dioxins and furans by isotope dilution HRGC/HRMS, USEPA. USEPA Press, Washington, DC
Weber R (2007) Relevance of PCDD/PCDF formation for the evaluation of POPs destruction technologies-review on current status and assessment gaps. Chemosphere 67:109–117
Weber R, Sakurai T (2001) Low temperature decomposition of PCB by TiO2-based V2O5/WO3 catalyst evaluation of the relevance of PCDF formation and insights into the first step of oxidative destruction of chlorinated aromatics. Appl Catal B 34:113–127
Weber R, Takasuga T, Nagai K, Shiraishi H, Sakurai T, Matud T, Hiraoka M (2002) Dechlorination and destruction of PCDD, PCDF and PCB on selected fly ash from municipal waste incineration. Chemosphere 46:1255–1262
Wu HL, Lu SY, Li XD, Jiang XG, Yan JH, Zhou MS, Wang H (2012) Inhibition of PCDD/F by adding sulphur compounds to the feed of a hazardous waste incinerator. Chemosphere 86:361–367
Xiao Y, Jiang JG (2014) Base-catalysed decomposition of hexachlorobenzene: effect on dechlorination efficiency of different hydrogen donors, alkalis and catalysts. RSC Adv 4:15713–15719
Zhao L, Hou H, Shimoda K, Terada A, Hosomi M (2012) Formation pathways of polychlorinated dibenzofurans (PCDF) in sediments contaminated with PCB during the thermal desorption process. Chemosphere 88:1368–1374
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Additional information
Responsible editor: Hongwen Sun
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Zhao, Z., Ni, M., Li, X. et al. Suppression of PCDD/Fs during thermal desorption of PCBs-contaminated soil. Environ Sci Pollut Res 23, 25335–25342 (2016). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11356-016-7732-8
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11356-016-7732-8