Abstract
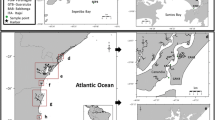
A spatiotemporal evaluation of butyltin contamination was performed between 2010 and 2012 along Todos os Santos Bay (Northeast Brazil) using surface sediments, bivalve tissues (Anomalocardia brasiliana and Mytella guyanensis), and imposex occurrence (Stramonita rustica). The spatial study detected high tributyltin (TBT) levels (maximum values of 262 ng Sn g -1 - 21,833 ng Sn g−1 of total organic carbon - for surface sediments and 421 ng Sn g−1 for bivalve tissues) in the innermost part of the bay. The TBT levels detected in M. guyanensis tissues might cause human health risk since local population consumes these organisms. These high concentrations observed in the bivalves might result in ingestions higher than the safe limits established by European Food Safety Authority (250 ng TBT kg−1 day−1). Considering the temporal evaluation, no difference (p > 0.05) was observed between TBT concentrations in sediments obtained during the two sampling campaigns (2010/2011 and 2012). However, the increasing predominance of TBT metabolites (butyltin degradation index (BDI) >1) in more recent sediments indicates further degradation of old TBT inputs. In spite of that, recent inputs are still evident at this region. Nevertheless, a reduction of imposex parameters in S. rustica over the last decade suggests an overall decline in the TBT contamination, at least in the outermost and possible less impacted region of the bay. The TBT contamination is probably reducing due to the national and international legislative restrictions on the use of TBT as antifouling biocide. The contamination levels, however, are still relevant especially in the inner part of Todos os Santos Bay since they are above those that are likely to cause toxicity to the biota.

Similar content being viewed by others
References
Abidli S, Santos MM, Lahbib Y, Castro LFC, Reis-Henriques MA, Trigui El Menif N (2012) Tributyltin (TBT) effects on Hexaplex trunculus and Bolinus brandaris (Gastropoda: Muricidae): imposex induction and sex hormone levels insights. Ecol Indic 13:13–21
Azevedo D, Rocha-Barreira C, Matthews-Cascon H, Castro Í (2012) Pugilina morio L., a new imposex exhibitor from South American estuarine environments: approach for a non-lethal method to evaluate imposex. Bull Environ Contamination Toxicol 89:786–792
Bezerra FJ (2008) O bosque de mangues e a pesca artesanal no Distrito de Acupe (Santo Amaro, Bahia): uma abordagem etnoecológica. Acta Scentarium 30:267–273
Bigatti G, Primost MA, Cledón M, Averbuj A, Theobald N, Gerwinski W, Arntz W, Morriconi E, Penchaszadeh PE (2009) Biomonitoring of TBT contamination and imposex incidence along 4700 km of Argentinean shoreline (SW Atlantic: From 38S to 54S). Mar Pollut Bull 58:695–701
Birchenough AC, Evans SM, Moss C, Welch R (2002) Re-colonisation and recovery of populations of dogwhelks Nucella lapillus (L.) on shores formerly subject to severe TBT contamination. Mar Pollut Bull 44:652–659
Burton ED, Phillips IR, Hawker DW (2006) Tributyltin partitioning in sediments: Effect of aging. Chemosphere 63:73–81
Cao D, Jiang G, Zhou Q, Yang R (2009) Organotin pollution in China: an overview of the current state and potential health risk. J Environ Manag 90:S16–S24
Castro ÍB, Fillmann G (2012) High tributyltin and imposex levels in the commercial muricid Thais chocolata from two Peruvian harbor areas. Environ Toxicol Chem 31:955–960
Castro IB, Meirelles CAO, Matthews-Cascon H, Fernandez MAS (2004) Thais (Stramonita) rustica (Lamarck, 1822) (Mollusca: Gastropoda: Thaididae), a potential bioindicator of contamination by organotin Northeast Brazil. Braz J Oceanogr 52:135–139
Castro IB, Lima AFA, Braga ARC, Rocha-Barreira CA (2007) Imposex in two muricid species (Mollusca: Gastropoda) from the Northeastern Brazilian coast. J Bra Soc Ecotoxicol 2:81–91
Castro IB, Perina F, Fillmann G (2012a) Organotin contamination in South American coastal areas. Environ Monit Assess 184:1781–1799
Castro ÍB, Rossato M, Fillmann G (2012b) Imposex reduction and residual butyltin contamination in southern Brazilian harbors. Environ Toxicol Chem 31:947–954
Castro IB, Arroyo M, Costa P, Fillmann G (2012c) Butyltin compounds and imposex levels in Ecuador. Arch Environ Contam Toxicol 62:68–77
Castro IB, Rocha-Barreira C de A, Fernandez MA, Bigatti G (2012d) Transplant bioassay induces different imposex responses in two species of the genus Stramonita. Mar Biol Res 8:397–404
Cirano M, Lessa GC (2007) Oceanographic characteristics of Baía de Todos os Santos, Brazil. Revista Brasileira de Geofísica 25:363–387
Culmo RF, Swanson KJ, Brennan WP (2003). Application of the PE2400 CHN elemental analyzer for organic particulate matter in water. Elemental Analysis Newsletter [S.1.], v.31.
Di Toro DM, Rosa LD (1991) Equilibrium partitioning and organic carbon normalization. National Sediment Bioaccumulation Conference, New Jersey
Díez S, Abalos M, Bayona JM (2002) Organotin contamination in sediments from the Western Mediterranean enclosures following 10 years of TBT regulation. Water Res 36:905–918
EFSA (2004) Opinion of the Scientific Panel on Contaminants in the Food Chain on a request from the Commission to assess the health risks to consumers associated with exposure to organotins in foodstuffs. EFSA J 102:1–119
Felizzola JF, de Luca Rebello Wagener A, Almeida AC, Lin WO (2008) Butyltin speciation in sediments from Todos os Santos Bay (Bahia, Brazil) by GC-PFPD. Quim Nov. 31:89–93
Fernandez MAS, De Luca Rebello Wagener A, Limaverde AM, Scofield AL, Pinheiro FM, Rodrigues EF (2005a) Imposex and surface sediment speciation: a combined approach to evaluate organotin contamination in Guanabara Bay, Rio de Janeiro, Brazil. Mar Environ Res 59:435–452
Fernandez MA, Limaverde AM, Scofield AL, de Luca Rebello Wagener A (2005b) Preliminary evaluation of human health risks from ingestion of organotin contamined seafood in Brazil. Braz J Oceanogr 53:75–77
Galante-Oliveira S, Oliveira I, Jonkers N, et al (2009) Imposex levels and tributyltin pollution in Ria de Aveiro (NW Portugal) between 1997 and 2007: evaluation of legislation effectiveness. J Environ Monit 11:1405–1411
Galante-Oliveira S, Oliveira I, Ferreira N, et al (2011) Nucella lapillus L. imposex levels after legislation prohibiting TBT antifoulants: temporal trends from 2003 to 2008 along the Portuguese coast. J Environ Monit 13:304–312
Genz F, Lessa GC, Cirano M (2006) The impact of an extreme flood upon the mixing zone of the Todos os Santos Bay, Northeastern Brazil. J Coast Res 39:707–712
Gibbs PE, Bryan GM, Pascoe PL, Burt GR (1987) The use of dog-whelk Nucella lapillus, as an indicator of tributyltin (TBT) contamination. J Mar Biol Assoc U K 67:507–523
Gipperth L (2009) The legal design of the international and European Union ban on tributyltin antifouling paint: Direct and indirect effects. J Environ Manage 90:S86–S95
Graceli JB, Cena GC, Lopes PF, Zamprogno GC, da Costa MB, Godoi AF, Dos Santos DM, de Marchi MR, dos Santos Fernandez MA (2013) Organotins: a review of their reproductive toxicity, biochemistry, and environmental fate. Reprod Toxicol 36:40–52
Gray JS (1981) The ecology of marine sediments. Cambridge University Press, New York
Grimón ROR, Arroyo MF, Freitas DM, Castro ÍB (2016) Tributyltin impacts in Galapagos Islands and Ecuadorian shore: marine protected areas under threat. Mar Policy 69:24–31. doi:10.1016/j.marpol.2016.03.017
Guomundsdóttir LÓ, Ho KKY, Lam JCW, Svavarsson J, Leung KMY (2011) Long-term temporal trends (1992-2008) of imposex status associated with organotin contamination in the dogwhelk Nucella lapillus along the Icelandic coast. Marine Pollution Bulletin. In Press.
Hatje V, Andrade JB (2009) Baía de Todos os Santos: Aspectos Oceanográficos. EDUFBA, Savaldor, p 303
Hoch M (2001) Organotin compounds in the environment—an overview. Appl Geochem 16:719–743
Hoch M, Schwesig D (2004) Parameters controlling the partitioning of tributyltin (TBT) in aquatic systems. Appl Geochem 19:323–334
Horiguchi T (2009) The endocrine-disrupting effect of organotin compounds for aquatic organisms. In: Arai T, Harino H, Ohji M, Langston WJ (eds) Ecotoxicology of antifouling biocides. Springer, Tokyo, pp 125–146
IMO (2008) Summary of the status of conventions as at 31 May 2007. International Maritime Organization, United Kingdom, http://www.imo.org/
IUPAC (International Union of Pure and Applied Chemistry) (2002) Analytical, applied, clinical, inorganic, and physical chemistry divisions interdivisional working party for harmonization of quality assurance schemes for analytical laboratories. Pure Appl Chem 74:835–855
Jorundsdottir K, Svavarsson K, Leung KMY (2005) Imposex levels in the dogwhelk Nucella lapillus (L.)—continuing improvement at high latitudes. Mar Pollut Bull 51:744–749
Kotrikla A (2009) Environmental management aspects for TBT antifouling wastes from the shipyards. J Environ Manag 90:S77–S85
Louppis AP, Georgantelis D, Paleologos EK, Kontominas MG (2010) Determination of tributyltin through ultrasonic assisted micelle mediated extraction and GFAAS: application to the monitoring of tributyltin levels in greek marine species. Food Chemistry. In Press, Accepted Manuscript
Matthiessen P, Gibbs PE (1998) Critical appraisal of the evidence for tributyltin-mediated endocrine disruption in mollusks. Environ Toxicol Chem 17:37–43
Meador JP, Sommers FC, Cooper KA, Yanagida G (2011) Tributyltin and the obesogen metabolic syndrome in a salmonid. Environ Res 111:50–56
Morabito R, Massanisso P, Quevauviller P (2000) Derivatization methods for the determination of organotin compounds in environmental samples. TrAC Trends Anal Chem 19:113–119
NORMAM (2007) Normas da Autoridade Marítima para o Controle de Sistemas Anti-incrustantes Danosos em Embarcações—NORMAM/23. Marinha do Brasil, Rio de Janeiro
Oehlmann J, Schulte-Oehlmann U (2003) Molluscs as bioindicators. In: Markert BA (ed) Trace metals and other contaminants in the environment bioindicators & biomonitors principles, concepts and applications. Elsevier, Philadelphia, pp 577–635
Oliveira IB, Richardson CA, Sousa AC, et al (2009) Spatial and temporal evolution of imposex in dogwhelk Nucella lapillus (L.) populations from North Wales, UK. J Environ Monit 11:1462–1468
Oliveira CR, Santos DM, Santos Madureira LA, Marchi MR (2010) Speciation of butyltin derivatives in surface sediments of three southern Brazilian harbors. J Hazard Mater 181:851–856
Otchere FA (2005) Organochlorines (PCBs and pesticides) in the bivalves Anadara (Senilis) senilis, Crassostrea tulipa and Perna perna from the lagoons of Ghana. Sci Total Environ 348:102–114
Paz-Villarraga CA, Castro IB, Miloslavich P, Fillmann G (2015) Venezuelan Caribbean Sea under the threat of TBT. Chemosphere 119:704–710
Pinochet H, Tessini C, Bravo M, Quiroz W, De Gregori I (2009) Butyltin compounds and their relation with organic matter in marine sediments from San Vicente Bay, Chile. Environ Monit Assess 155:341–353
Pletsch LA, Beretta M, Tania Mascarenhas Tavares MT (2010) Distribuição espacial de compostos orgânicos de estanho em sedimentos costeiros e em Phallusia nigra da baía de Todos os Santos e litoral norte da Bahia - Brasil. Quim Nov. 33(2):451–457
Rittschof D, McClellan-Green P (2005) Molluscs as multidisciplinary models in environment toxicology. Mar Pollut Bull 50:369–373
Santos DM, Araújo IP, Machado EC, Carvalho-Filho MAS, Fernandez MA, Marchi MRR, Godoi AF (2009) Organotin compounds in the Paranaguá Estuarine Complex, Paraná, Brazil: evaluation of biological effects, surface sediment, and suspended particulate matter. Mar Pollut Bull 58:1926–1931
Sericano JL, Wade TL, Jackson TJ, Brooks JM, Tripp BW, Farrington JW, Mee LD, Readmann JW, Villeneuve JP, Goldberg ED (1995) Trace organic contamination in the Americas: an overview of the US National Status and Trends and the International Mussel Watch programmes. Mar Pollut Bull 31:214–225
Sousa A, Laranjeiro F, Takahashi S, Tanabe S, Barroso CM (2009) Imposex and organotin prevalence in a European post-legislative scenario: temporal trends from 2003 to 2008. Chemosphere 77:566–573
Toste R, Fernandez MA, Pessoa I de A, Parahyba MA, Dore MP (2011) Organotin pollution at Arraial do Cabo, Rio de Janeiro State, Brazil: increasing levels after the TBT ban. Braz J Oceanogr 59:111–117
Toste R, Pessoas IA, Dore DP, Parayba MA, Ferandez MA (2013) Aphallic vas deferens development in females related to the distance from organotin sources? A study with Stramonita haemastoma. Ecotoxicol Environ Saf 91:162–170
Town RM, Filella M (2002) Implications of natural organic matter binding heterogeneity on understanding lead(II) complexation in aquatic systems. Sci Total Environ 300:143–154
Waite ME, Waldock MJ, Thain JE, Smith DJ, Milton SM (1991) Reductions in TBT concentrations in UK estuaries following legislation in 1986 and 1987. Mar Environ Res 32:89–111
Wang J, Yao P, Bianchi TS, Li D, Zhao B, Xingqian C, Pan H, Zhang T, Yu Z (2015) The effect of particle density on the sources, distribution, and degradation of sedimentary organic carbon in the Changjiang Estuary and adjacent shelf. Chem Geol 402:52–67
Yebra DM, Kiil S, Dam-Johansen K (2004) Antifouling technology: past, present and future steps towards efficient and environmentally friendly antifouling coatings. Prog Org Coat 50:75–104
Acknowledgments
We thank FINEP for the financial support (project no. 01.11.0038.00). V. Artifon was sponsored by CAPES, Í.B. Castro by CAPES (802-16/2012) and FAPERGS (0885/12-1), and G. Fillmann by CNPq (PQ 312341/2013-0). We also thank Vanessa Hatje and Gilmara Eça from the Universidade Federal da Bahia (UFBA) for supplying the samples of campaign 1.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Additional information
Responsible editor: Cinta Porte
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Artifon, V., Castro, Í.B. & Fillmann, G. Spatiotemporal appraisal of TBT contamination and imposex along a tropical bay (Todos os Santos Bay, Brazil). Environ Sci Pollut Res 23, 16047–16055 (2016). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11356-016-6745-7
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11356-016-6745-7