Abstract
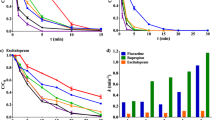
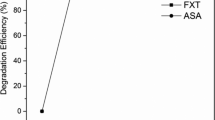
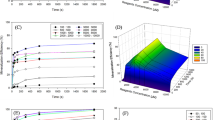
Electron beam irradiation (EBI) has been considered an advanced technology for the treatment of water and wastewater, whereas very few previous investigations reported its use for removing pharmaceutical pollutants. In this study, the degradation of fluoxetine (FLX), an antidepressant marketed as Prozac®, was investigated by using EBI at FLX initial concentration of 19.4 ± 0.2 mg L−1. More than 90 % FLX degradation was achieved at 0.5 kGy, with FLX below the detection limit (0.012 mg L−1) at doses higher than 2.5 kGy. The elucidation of organic byproducts performed using direct injection mass spectrometry, along with the results of ion chromatography, indicated hydroxylation of FLX molecules with release of fluoride and nitrate anions. Nevertheless, about 80 % of the total organic carbon concentration remained even for 7.5 kGy or higher doses. The decreases in acute toxicity achieved 86.8 and 9.6 % for Daphnia similis and Vibrio fischeri after EBI exposure at 5 kGy, respectively. These results suggest that EBI could be an alternative to eliminate FLX and to decrease residual toxicity from wastewater generated in pharmaceutical formulation facilities, although further investigation is needed for correlating the FLX degradation mechanism with the toxicity results.





Similar content being viewed by others
References
Abdou LAW, Hakeim OA, Mahmoud MS, El-Naggar AM (2011) Comparative study between the efficiency of electron beam and gamma irradiation for treatment of dye solutions. Chem Eng J 168:752–758. doi:10.1016/j.cej.2011.01.071
ABNT-Associação Brasileira de Normas Técnicas (2009) Ecotoxicologia Aquática – Toxicidade aguda – Método de ensaio com Daphnia spp (Crustacea, Cladocera). Rio de Janeiro: ABNT. (NBR 12713).
ABNT-Associação Brasileira de Normas Técnicas (2012) Ecotoxicologia aquática – Determinação do efeito inibitório de amostras de água sobre a emissão de luz de Vibrio fischeri (Ensaio de bactéria luminescente). Parte 3: Método utilizando bactérias liofilizadas. Rio de Janeiro: ABNT. (NBR 15411–3)
Batista APS, Pires FCC, Teixeira ACSC (2014) The role of oxygen species in sulfamethazine degradation using UV-based technologies and products identification. J Photochem Photobiol A Chem 290:77–85. doi:10.1016/j.jphotochem.2014.06.006
Bedner M, MacCrehan WA (2006) Reactions of the amine-containing drugs FLX and metoprolol during chlorination and dechlorination processes used in wastewater treatment. Chemosphere 65:2130–2137. doi:10.1016/j.chemosphere.2006.06.016
Borrely SI, Gonçalves AA, Oikawa H, Duarte CL, Rocha FR (2004) Electron beam accelerator for detoxification of effluents. When radiation processing can enhance the acute toxicity? Radiat Phys Chem 71:453–456. doi:10.1016/j.radphyschem.2004.03.087
Boström ML, Berglund O (2015) Influence of pH-dependent aquatic toxicity of ionizable pharmaceuticals on risk assessments over environmental pH ranges. Water Res 72:154–161. doi:10.1016/j.watres.2014.08.040
Brooks BW, Foran CM, Richards SM, Weston J, Turner PK, Stanley JK, Solomon KR, Slattery M, La Point TW (2003) Aquatic ecotoxicology of FLX. Toxicol Lett 142:169–183. doi:10.1016/S0378-4274(03)00066-3
Brooks BW, Chambliss CK, Stanley JK, Ramirez A, Banks KE, Johnson RD, Lewis RJ (2005) Determination of select antidepressants in fish from an effluent-dominated stream. Environ Toxicol Chem 24:464–469. doi:10.1897/04-081R.1
Cooper WJ, Gehringer P, Pikaev AK, Kurucz CN, Mincher BJ (2004) Radiation Processes. In: Parsons S (ed) Advanced oxidation processes for water and wastewater. IWA Publishing, London
Deblonde T, Cossu-Leguille C, Hartemann P (2011) Emerging pollutants in wastewater: a review of the literature. Int J Hyg Environ Health 214:442–448. doi:10.1016/j.ijheh.2011.08.002
Fong PP (1998) Zebra mussel spawning is induced in low concentrations of putative serotonin reuptake inhibitors. Biol Bull 194:143–149. doi:10.2307/1543044
Furlong ET, Kinney CA, Ferrer I, Werner SL, Cahill JD, Ratterman G (2004) Pharmaceutical and personal care products in solids: analysis and field results for sediment, soil, and biosolid samples. In: Proceedings, 228th American Chemical Society National Meeting, Philadelphia, PA
Garrido EM, Garrido J, Calheiros R, Marques MPM, Borges F (2009) Fluoxetine and norfluoxetine revisited: new insights into the electrochemical and spectroscopic properties. J Phys Chem A 113:9934–9944. doi:10.1021/jp904306b
Gaworecki KM, Klaine SJ (2008) Behavioral and biochemical responses of hybrid striped bass during and after FLX exposure. Aquat Toxicol 88:207–213. doi:10.1016/j.aquatox.2008.04.011
Gelsleichter J, Szabo NJ (2013) Uptake of human pharmaceuticals in bull sharks (Carcharhinus leucas) inhabiting a wastewater-impacted river. Sci Total Environ 456–457:196–201. doi:10.1016/j.scitotenv.2013.03.078
Glassmeyer ST, Furlong ET, Kolpin DW, Cahill JD, Zaugg SD, Werner SL, Meyer MT, Kryak DD (2005) Transport of chemical and microbial compounds from known wastewater discharges: Potential for use as indicators of human fecal contamination. Environ Sci Technol 39:5157–5169. doi:10.1021/es048120k
Guo Z, Zhou F, Zhao Y, Zhang C, Liu F, Bao C, Lin M (2012) Gamma irradiation-induced sulfadiazine degradation and its removal mechanisms. Chem Eng J 191:256–262. doi:10.1016/j.cej.2012.03.012
Han B, Kim JK, Kim Y, Choi JS, Jeong KY (2012) Operation of industrial-scale electron beam wastewater treatment plant. Radiat Phys Chem 81:1475–1478. doi:10.1016/j.radphyschem.2012.01.030
Homlok R, Takács E, Wojnárovits L (2011) Elimination of diclofenac from water using irradiation technology. Chemosphere 85:603–608. doi:10.1016/j.chemosphere.2011.06.101
Hua WY, Bennett ER, Maio X-S, Metcalfe CD, Letcher RJ (2006) Seasonality effects on pharmaceuticals and S-triazine herbicides in wastewater effluent and surface water from the Canadian side of the upper Detroit River. Environ Toxicol Chem 25:2356–2365. doi:10.1897/05-571R.1
Kim SD, Cho J, Kim IS, Vanderford BJ, Snyder SA (2007) Occurrence and removal of pharmaceuticals and endocrine disruptors in South Korean surface, drinking, and waste waters. Water Res 41:1013–1021. doi:10.1016/j.watres.2006.06.034
Kim T-H, Kim SD, Kim HY, Lim SJ, Lee M, Yu S (2012) Degradation and toxicity assessment of sulfamethoxazole and chlortetracycline using electron beam, ozone and UV. J Hazard Mater 227–228:237–242. doi:10.1016/j.jhazmat.2012.05.038
Kolpin DW, Furlong ET, Meyer MT, Thurman EM, Zaugg SD, Barber LB, Buxton HT (2002) Pharmaceuticals, hormones, and other organic wastewater contaminants in U.S. streams, 1999-2000: a national reconnaissance. Environ Sci Technol 36:1202–1211. doi:10.1021/es011055j
Kwon JW, Armbrust KL (2006) Laboratory persistence and fate of FLX in aquatic environments. Environ Toxicol Chem 25:2561–2568. doi:10.1897/05-613R.1
Lajeunesse A, Smyth SA, Barclay K, Sauvé S, Gagnon C (2012) Distribution of antidepressant residues in wastewater and biosolids following different treatment processes by municipal wastewater treatment plants in Canada. Water Res 46:5600–5612. doi:10.1016/j.watres.2012.07.042
Lam MW, Young CJ, Mabury SA (2005) Aqueous photochemical reaction kinetics and transformations of FLX. Environ Sci Technol 39:513–522. doi:10.1021/es0494757
Larsson DGJ, de Pedro C, Paxeus N (2007) Effluent from drug manufactures contains extremely high levels of pharmaceuticals. J Hazard Mater 148:751–755. doi:10.1016/j.jhazmat.2007.07.008
Lester Y, Mamane H, Zucker I, Avisar D (2013) Treating wastewater from a pharmaceutical formulation facility by biological process and ozone. Water Res 47:4349–4356. doi:10.1016/j.watres.2013.04.059
Li W, Nanaboina V, Zhou Q, Korshin GV (2012) Effects of Fenton treatment on the properties of effluent organic matter and their relationships with the degradation of pharmaceuticals and personal care products. Water Res 46:403–412. doi:10.1016/j.watres.2011.11.002
Méndez-Arriaga F, Otsu T, Oyama T, Gimenez J, Esplugas S, Hidaka H, Serpone N (2011) Photooxodation of the antidepressant drug FLX (Prozac®) in aqueous media by hybrid catalytic/ozonation processes. Water Res 45:2782–2794. doi:10.1016/j.watres.2011.02.030
Metcalfe CD, Miao XS, Koenig BG, Struger J (2003) Distribution of acidic and neutral drugs in surface waters near sewage treatment plants in the lower great lakes, Canada. Environ Toxicol Chem 22:2881–2889. doi:10.1897/02-627
Metcalfe CD, Chu SG, Judt C, Li HX, Oakes KD, Servos MR, Andrews DM (2010) Antidepressants and their metabolites in municipal wastewater, and downstream exposure in an urban watershed. Environ Toxicol Chem 29:79–89. doi:10.1002/etc.27
Nakamura Y, Yamamoto H, Sekizawa J, Kondo T, Hirai N, Tatarazako N (2008) The effects of pH on FLX in Japanese medaka (Oryzias latipes): acute toxicity in fish larvae and bioaccumulation in juvenile fish. Chemosphere 70:865–873. doi:10.1016/j.chemosphere.2007.06.089
Parsons S (2004) Advanced oxidation processes for water and wastewater treatment. IWA Publishing, London
Paul J, Rawat KP, Sarma KSS, Sabharwal S (2011) Decoloration and degradation of Reactive Red-120 dye by electron beam irradiation in aqueous solution. Appl Radiat Isot 69:982–987. doi:10.1016/j.apradiso.2011.03.009
Redshaw CH, Cooke MP, Talbot HM, McGrath S, Rowland SJ (2008) Low biodegradability of FLX HCl, diazepam and their human metabolities in sewage slude-amended soil. J Soil Sediments 8:217–230. doi:10.1007/s11368-008-0024-2
Romanelli MF, Moraes MCF, Villavicencio ALCH, Borrely SI (2004) Evaluation of toxicity reduction of sodium dodecyl sulfate submitted to electron beam radiation. Radiat Phys Chem 71:409–411. doi:10.1016/j.radphyschem.2004.03.038
Santos LHMLM, Gros M, Rodriguez-Mozaz S, Delerue-Matos C, Pena A, Barceló D, Montenegro MCBSM (2013) Contribution of hospital effluents to the load of pharmaceuticals in urban wastewaters: Identification of ecologically relevant pharmaceuticals. Sci Total Environ 461–462:302–316. doi:10.1016/j.scitotenv.2013.04.077
Segura Y, Martínez F, Melero JA (2013) Effective pharmaceutical wastewater degradation by Fenton oxidation with zero-valent iron. Appl Catal B Environ 136–137:64–69. doi:10.1016/j.apcatb.2013.01.036
Serna-Galvis EA, Silva-Agredo J, Giraldo-Aguirre AL, Torres-Palma RA (2015) Sonochemical degradation of the pharmaceutical FLX: Effect of parameters, organic and inorganic additives and combination with a biological system. Sci Total Environ 524–525:354–360. doi:10.1016/j.scitotenv.2015.04.053
Snyder SA, Wert EC, Rexing DJ, Zegers RE, Drury DD (2006) Ozone oxidation of endocrine disruptors and pharmaceuticals in surface water and wastewater. Ozone-Sci Eng 28:445–460. doi:10.1080/01919510601039726
Stackelberg PE, Gibs J, Furlong ET, Meyer MT, Zaugg SD, Lippincott RL (2007) Efficiency of conventional drinking-water-treatment processes in removal of pharmaceuticals and other organic compounds. Sci Total Environ 377:255–272. doi:10.1016/j.scitotenv.2007.01.095
Stanley JK, Ramirez AJ, Chambliss K, Brooks BW (2007) Enantiospecific sublethal effects of the antidepressant FLX to a model aquatic vertebrate and invertebrate. Chemosphere 69:9–16. doi:10.1016/j.chemosphere.2007.04.080
Uslu MO, Rahman MF, Jasim SY, Yanful EK, Biswas N (2012) Evaluation of the reactivity of organic pollutants during O3/H2O2 process. Water Air Soil Pollut 223:3173–3180. doi:10.1007/s11270-012-1099-3
Vahdat A, Bahrami SH, Arami M, Motahari A (2010) Decomposition and decoloration of a direct dye by electron beam radiation. Radiat Phys Chem 79:33–35. doi:10.1016/j.radphyschem.2009.08.012
Vasskog T, Anderssen T, Pedersen-Bjergaard S, Kallenborn R, Jensen E (2008) Occurrence of selective serotonin reuptake inhibitors in sewage and receiving waters at Spitsbergen and in Norway. J Chromatogr A 1185:194–205. doi:10.1016/j.chroma.2008.01.063
Westerhoff P, Yoon Y, Snyder S, Wert E (2005) Fate of endocrine-disruptor, pharmaceutical, and personal care product chemicals during simulated drinking water treatment processes. Environ Sci Technol 39:6649–6663. doi:10.1021/es0484799
Wu C, Spongberg AL, Witter JD, Fang M, Czajkowski KP (2010) Uptake of pharmaceutical and personal care products by soybean plants from soils applied with biosolids and irrigated with contaminated water. Environ Sci Technol 44:6157–6161. doi:10.1021/es1011115
Xu G, Yao J-z, Tang L, Yang X-y, Zheng M, Wang H, Wu M-h (2015) Electron beam induced degradation of atrazine in aqueous solution. Chem Eng J 275:374–380. doi:10.1016/j.cej.2015.04.063
Yang R, Wang M, Shen Z, Wang W, Ma H, Gu J (2007) The degradation and mineralization of 4-chlorophenol in aqueous solutions by electron beam irradiation in the presence of TiO2 nanoparticles. Radiat Phys Chem 76:1122–1125. doi:10.1016/j.radphyschem.2006.10.008
Acknowledgments
The authors thank the Brazilian National Council of Scientific and Technological Development, CNPq, the International Atomic Energy Agency and São Paulo Research Foundation (FAPESP) grants #2013/50218-2 and #2014/17996-4 for the financial support. The authors are also grateful to the LAPAt Laboratory (Institute of Astronomy, Geophysics, and Atmospheric Sciences, University of São Paulo) for the ion chromatography analysis. They are also grateful to Dr. Maria Anita Mendes (Department of Chemical Engineering, University of São Paulo) for her valuable assistance with the UHR-QqTOF mass spectrometry analysis.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Additional information
Responsible editor: Angeles Blanco
Highlights
• The feasibility of electron beam irradiation (EBI) to remove fluoxetine (FLX) from water is shown for the first time.
• The effect of the radiation dose needed to remove FLX and acute toxicity was investigated.
• EBI resulted in the reduction of acute toxicity of FLX solutions at low irradiation doses.
• Byproducts were elucidated and the pathway of FLX degradation by EBI is proposed.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Silva, V.H.O., dos Santos Batista, A.P., Silva Costa Teixeira, A.C. et al. Degradation and acute toxicity removal of the antidepressant Fluoxetine (Prozac®) in aqueous systems by electron beam irradiation. Environ Sci Pollut Res 23, 11927–11936 (2016). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11356-016-6410-1
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11356-016-6410-1