Abstract
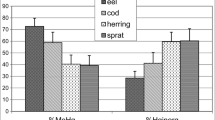
This paper presents the results of seasonal (wet and dry seasons) and spatial (five sites) variation of mercury concentration in seven marine organisms representative for shallow Senegalese coastal waters and including species of commercial importance. Total mercury levels were recorded in the green algae (Ulva lactuca); the brown mussel (Perna perna); the Caramote prawn (Penaeus kerathurus); and in the liver and muscles of the following fish: Solea senegalensis, Mugil cephalus, Saratherondon melanotheron, and Sardinella aurita. The total selenium (Se) contents were determined only in the edible part of Perna perna, Penaeus kerathurus and in the muscles of Sardinella aurita and Solea senegalensis. Hg concentration in fish species was higher in liver compared to the muscle. Between species differences in Hg, concentrations were recorded with the highest concentration found in fish and the lowest in algae. The spatiotemporal study showed that there was no clear seasonal pattern in Hg concentrations in biota, but spatial differences existed with highest concentrations in sites located near important anthropogenic pressure. For shrimp, mussel, and the muscles of sardine and sole, Hg concentrations were below the health safety limits for human consumption as defined by the European Union. The Se/Hg molar ratio was always higher than one whatever the species or location suggesting a protection of Se against Hg potential adverse effect.




Similar content being viewed by others
References
Agusa T, Kunito T, Iwata H et al (2005) Mercury contamination in human hair and fish from Cambodia: levels, specific accumulation and risk assessment. Environ Pollut 134(1):79–86
Ali H, Khan E, Sajad MA (2013) Phytoremediation of heavy metals concepts and applications. Chemosphere 91(7):869–881
Amiard JC, Amiard-Triquet C, Barka S et al (2006) Metallothioneins in aquatic invertebrates: their role in metal detoxification and their use as biomarkers. Aquat Toxicol 76:160–202
Belabed BE, Laffray X, Dhib A et al (2013) Factors contributing to heavy metal accumulation in sediments and in the intertidal mussel Perna perna in the Gulf of Annaba (Algeria). Mar Pollut Bull 74(1):477–489
Biney CA, Ameyibor E (1992) Trace metal concentrations in the pink shrimp Penaeus notialis from the coast of Ghana. Water Air Soil Pollut 63(3–4):273–279
Birame N, Momar N, Abdoulaye D et al (2015) Determination of methyl mercury in biological samples from Dakar coast using CV-AAS and a simple ultrasound method. Res J Chem Env 19:1–7
Bosch AC, O'Neill B, Sigge GO et al (2016) Heavy metals in marine fish meat and consumer health: a review. J Sci Food Agric 96(1):32–48
Braham CB, Fréon P, Laurec A et al (2014) New insights in the spatial dynamics of sardinella stocks off Mauritania (North-West Africa) based on logbook data analysis. Fish Res 154:195–204
Branco V, Vale C, Canário J et al (2007) Mercury and selenium in blue shark (Prionace glauca, L. 1758) and swordfish (Xiphias gladius, L. 1758) from two areas of the Atlantic Ocean. Environ Pollut 150(3):373–380
Burger J, Gochfeld M (2004) Mercury in canned tuna: white versus light and temporal variation. Environ Res 96(3):239–249
Costa S, Crespo D, Henriques BMG (2011) Kinetics of mercury accumulation and its effects on Ulva lactuca growth rate at two salinities and exposure conditions. Water Air Soil Pollut 217:689–699
Cresson P, Fabri MC, Bouchoucha M et al (2014) Mercury in organisms from the Northwestern Mediterranean slope: importance of food sources. Sci Total Environ 497:229–238
Cropper TE, Hanna E, Bigg GR (2014) Spatial and temporal seasonal trends in coastal upwelling off Northwest Africa, 1981–2012. Deep Sea Rese Pt I 86:94–111
Crump KL, Trudeau VL (2009) Mercury‐induced reproductive impairment in fish. Environ Toxicol Chem 28(5):895–907
Crump KS, Kjellström T, Shipp AM et al (1998) Influence of prenatal mercury exposure upon scholastic and psychological test performance: benchmark analysis of a New Zealand cohort. Risk Anal 18(6):701–713
Diop C, Dewaelé D, Diop M et al (2014) Assessment of contamination, distribution and chemical speciation of trace metals in water column in the Dakar coast and the Saint Louis estuary from Senegal, west Africa. Mar Pollut Bull 86:539–546
Diop C, Dewaelé D, Cazier F et al (2015) Assessment of trace metals contamination level, bioavailability and toxicity in sediments from Dakar coast and Saint Louis estuary in Senegal, West Africa. Chemosphere 138:980–987
Diop M, Howsam M, Diop C et al (2016a) Spatial and seasonal variations of trace elements concentrations in liver and muscle of round sardinelle (Sardinella Aurita) and senegalese sole (Solea Senegalensis) along the Senegalese coast. Chemosphere 144:758–766
Diop M, Howsam M, Diop C et al (2016b) Assessment of trace element contamination and bioaccumulation in algae (Ulva lactuca), mussels (Perna perna), shrimp (Penaeus kerathurus), and fish (Mugil cephalus, Saratherondon melanotheron) along the Senegalese coast. Mar Pollut Bull
Donkor AK, Bonzongo JC, Nartey VK et al (2006) Mercury in different environmental compartments of the Pra River Basin, Ghana. Sci Total Environ 368(1):164–176
Driscoll CT, Mason RP, Chan HM et al (2013) Mercury as a global pollutant: sources, pathways, and effects. Environ Sci Technol 47(10):4967–4983
EC (2006) No 1881/2006 of 19 December 2006 setting maximum levels for certain contaminants in foodstuffs. Official J European 364:5–24
EC (2008) No 629/2008 of 2 July 2008 amending Regulation (EC) No 1881/2006 setting maximum levels for certain contaminants in foodstuffs. Official J European 173(6), 4 pages
U.S. EPA (2008) Model-based analysis and tracking of airborne mercury emissions to assist in watershed planning
FAO (2006) Report of the FAO Working Group on the assessment of small pelagic fish off Northwest Africa. Banjul, Gambia, 2–11 May 2006. FAO Fish. Report 811, 192 pages
Gras G, Mondain J (1982) Rapport methylmercure/mercure total dans difgferentes espèces de poissons péchés sur les côtes de l'Afrique de l'Ouest. Toxicol Eur Res 4:191–195
Gushchin A, Corten A (2015) Feeding of pelagic fish in waters of Mauritania: 1. European anchovy Engraulis encrasicolus, European sardine Sardina pilchardus, round sardinella Sardinella aurita, and flat sardinella S. maderensis. J Ichthyol 55:77–85
Hajeb P, Jinap S, Ismail A et al (2009) Assessment of mercury level in commonly consumed marine fishes in Malaysia. Food Control 20(1):79–84
Hall B, Bodaly R, Fudge R et al (1997) Food as the dominant pathway of methylmercury uptake by fish. Water Air Soil Pollut 100(1–2):13–24
Henriques B, Rodrigues S, Coelho C et al (2013) Risks associated with the transfer of toxic organo-metallic mercury from soils into the terrestrial feed chain. Environ Int 59:408–417
Henriques B, Rocha LS, Lopes CB (2015) Study on bioaccumulation and biosorption of mercury by living marine macroalgae: prospecting for a new remediation biotechnology applied to saline waters. Chem Eng J 281:759–770
Hightower JM, Moore D (2003) Mercury levels in high-end consumers of fish. Environ Health Perspect 111(4):604
Hogstrand C, Haux C (1991) Binding and detoxification of heavy metals in lower vertebrates with reference to metallothionein. Comp Biochem Physiol C 100(1):137–141
Joiris CR, Holsbeek L (1999) Total and methylmercury in sardines Sardinella aurita and Sardina pilchardus from Tunisia. Mar Pollut Bull 38(3):188–192
Joiris CR, Holsbeek L, Otchere FA (2000) Mercury in the bivalves Crassostrea tulipa and Perna perna from Ghana. Mar Pollut Bull 40:457–460
Kalay M, Ay Ö, Canli M (1999) Heavy metal concentrations in fish tissues from the Northeast Mediterranean Sea. Bull Environ Contam Toxicol 63(5):673–681
Misheer N, Kindness A, Jonnalagadda S (2006) Seaweeds along KwaZulu-Natal coast of South Africa—3: elemental uptake by Ulva lactuca (sea lettuce). J Environ Sci Health C 41(6):1249–1259
Net S, Henry F, Rabodonirina S et al (2015) Accumulation of PAHs, Me-PAHs, PCBs and total mercury in sediments and marine species in coastal areas of Dakar, Senegal: contamination level and impact. Int J Environ Res 9(2):419–432
Niane B, Guédron S, Moritz R, Cosio C et al (2015) Human exposure to mercury in artisanal small-scale gold mining areas of Kedougou region, Senegal, as a function of occupational activity and fish consumption. Environ Sci Pollut Res 22(9):7101–7111
Obasohan E, Eguavoen O (2008) Seasonal variations of bioaccumulation of heavy metals in a freshwater fish (Erpetoichthys calabaricus) from Ogba River, Benin City, Nigeria. Afr J General Agr 4(3):153–163
Ouédraogo O, Amyot M (2013) Mercury, arsenic and selenium concentrations in water and fish from sub-Saharan semi-arid freshwater reservoirs (Burkina Faso). Sci Total Environ 444:243–254
Peterson SA, Ralston NV, Peck DV et al (2009) How might selenium moderate the toxic effects of mercury in stream fish of the western US? Envir Sci Tech Lib 43(10):3919–3925
Ralston NVC, Raymond LJ (2010) Dietary selenium's protective effects against methylmercury toxicity. Toxicology 278:112–123
Romeo M, Siau Y, Sidoumou Z, Gnassia-Barelli M (1999) Heavy metal distribution in different fish species from the Mauritania coast. Sci Total Environ 232:169–175
Schuhmacher M, Domingo J, Llobet J et al (1993) Chromium, copper, and zinc concentrations in edible vegetables grown in Tarragona Province, Spain. Bull Environ Contam Toxicol 50(4):514–521
Sormo EG, Tomasz MC, Ida BØ et al (2011) Selenium moderates mercury toxicity in free-ranging freshwater fish. Environ Sci Technol 45(15):6561–6566
Squadrone S, Benedetto A, Brizio P et al (2015) Mercury and selenium in European catfish (Silurus glanis) from northern Italian rivers: can molar ratio be a predictive factor for mercury toxicity in a top predator? Chemosphere 119:24–30
Staudinger MD (2011) Species-and size-specific variability of mercury concentrations in four commercially important finfish and their prey from the northwest Atlantic. Mar Pollut Bull 62(4):734–740
Stringari J, Nunes AK, Franco JL et al (2008) Prenatal methylmercury exposure hampers glutathione antioxidant system ontogenesis and causes long-lasting oxidative stress in the mouse brain. Toxicol Appl Pharmacol 227(1):147–154
Trudel M, Rasmussen JB (2001) Predicting mercury concentration in fish using mass balance models. Ecol Appl 11(2):517–529
Turkmen G (2012) Seasonal variation of heavy metals in shrimp Penaeus kerathurus (forskal, 1775) from Izmir bay, Turkey. J Anim Vet Adv 11:2839–2844
Turner A, Furniss O (2012) An evaluation of the toxicity and bioaccumulation of thallium in the coastal marine environment using the macroalga, Ulva lactuca. Mar Pollut Bull 64(12):2720–2724
Vieira C, Morais S, Ramos S et al (2011) Mercury, cadmium, lead and arsenic levels in three pelagic fish species from the Atlantic Ocean: intra-and inter-specific variability and human health risks for consumption. Food Chem Toxicol 49(4):923–932
Vinagre C, Fonseca V, Cabral H et al (2006) Habitat suitability index models for the juvenile soles, Solea solea and Solea senegalensis, in the Tagus estuary: defining variables for species management. Fish Res 82(1):140–149
Wang Y, Chen P, Cui R et al (2010) Heavy metal concentrations in water, sediment, and tissues of two fish species (Triplohysa pappenheimi, Gobio hwanghensis) from the Lanzhou section of the Yellow River, China. Environ Monit Assess 165(1–4):97–102
Watanabe C (2002) Modification of mercury toxicity by selenium: practical importance? Tohoku J Exp Med 196(2):71–77
WHO (World Health Organization) (1996) Health criteria other supporting information. In: Guidelines for drinking water quality, vol 2, 3rd edn. Geneva, pp 31–388
Yamashita Y, Omura Y, Okazaki E (2005) Total mercury and methylmercury levels in commercially important fishes in Japan. Fish Sci 71(5):1029–1035
Zhang L, Wong M (2007) Environmental mercury contamination in China: sources and impacts. Environ Int 33(1):108–121
Acknowledgments
A doctoral grant was funded for M. Diop by Bourses de Coopération et d’Action Culturelle de l’ambassade de France à Dakar and ERASMUS ANGLE grant. The authors sincerely thank Drs. Michael Howsam and Lucie Courco for their assistance with the Hg and Se analyses.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Additional information
Responsible editor: Philippe Garrigues
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Diop, M., Amara, R. Mercury concentrations in the coastal marine food web along the Senegalese coast. Environ Sci Pollut Res 23, 11975–11984 (2016). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11356-016-6386-x
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11356-016-6386-x