Abstract
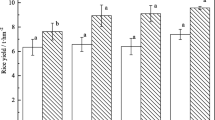
A field experiment was established to support the hypothesis that application of different silicon (Si) fertilizers can simultaneously reduce cadmium (Cd) and arsenic (As) concentration in rice grain. The “semi-finished product of Si-potash fertilizer” treatment at the high application of 9000 kg/ha (NP+S-KSi9000) significantly reduced the As concentration in rice grain by up to 20.1 %, compared with the control. Si fertilization reduces the Cd concentration in rice considerably more than the As concentration. All Si fertilizers apart from sodium metasilicate (Na2SiO3) exhibited a high ability to reduce Cd concentration in rice grain. The Si-calcium (CaSi) fertilizer is the most effective in the mitigation of Cd concentration in rice grain. The CaSi fertilizer applied at 9000 kg/ha (NPK+CaSi9000) and 900 kg/ha (NPK+CaSi900) reduced the Cd concentration in rice grain about 71.5 and 48.0 %, respectively, while the Si-potash fertilizer at 900 kg/ha (NP+KSi900), the semi-finished product of Si-potash fertilizer at both 900 kg/ha (NP+S-KSi900) and 9000 kg/ha (NP+S-KSi9000), and the rice straw (NPK+RS) treatments reduced the Cd concentration in rice grain about 42, 26.5, 40.7, and 23.1 %, respectively. The results of this investigation demonstrated the potential effects of Si fertilizers in reducing Cd and As concentrations in rice grain.


Similar content being viewed by others
References
Areao T, Kawasaki A, Baba K, Mori S, Matsumoto S (2009) Effects of water management on cadmium and arsenic accumulation and dimethylarsinic acid concentrations in Japanese rice. Environ Sci Technol 43:9361–9367
Bernard A, Lauwerys R (1986) Effects of cadmium exposure in humans. Cadmium, Springer, New York, In, pp 135–177
Bogdan K, Schenk MK (2008) Arsenic in rice (Oryza sativa L.) related to dynamics of arsenic and silicic acid in paddy soils. Environ Sci Technol 42(21):7885–7890
Chan K, Van Zwieten L, Meszaros I, Downie A, Joseph S (2008) Agronomic values of greenwaste biochar as a soil amendment. Soil Res 45(8):629–634
Chen HM, Zheng CR, Tu C, Shen ZG (2000) Chemical methods and phytoremediation of soil contaminated with heavy metals. Chemosphere 41(1):229–234
Clemens S (2006) Toxic metal accumulation, responses to exposure and mechanisms of tolerance in plants. Biochimie 88(11):1707–1719
Clemens S, Aarts MG, Thomine S, Verbruggen N (2013) Plant science: the key to preventing slow cadmium poisoning. Trends Plant Sci 18:92–99
Da Cunha KPV, Do Nascimento CWA (2009) Silicon effects on metal tolerance and structural changes in maize (Zea mays L.) grown on a cadmium and zinc enriched soil. Water Air Soil Pollut 197(1-4):323–330
Drees LR, Wilding LP, Smeck NE, Senkayi AL (1989) Silica in soils: quartz and disordered silica polymorphs. Minerals in Soil Environments (mineralsinsoile):913-974
Epstein E (1994) The anomaly of silicon in plant biology. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A 91(1):11–17
Epstein E (1999) Silicon. Annu Rev Plant Biol 50(1):641–664
Fleck AT, Mattusch J, Schenk MK (2013) Silicon decreases the arsenic level in rice grain by limiting arsenite transport. J Plant Nutr Soil Sci 176(5):785–794
Fraysse F, Pokrovsky OS, Schott J, Meunier J-D (2006) Surface properties, solubility and dissolution kinetics of bamboo phytoliths. Geochim Cosmochim Acta 70(8):1939–1951
GB15618-1995. Environmental quality standard for soils. National Standards of the People’s Republic of China
GB2762-2012. Maximum levels of contaminants in food. Chinese Food Standards Agency
Guo W, Zhu Y-G, Liu W-J, Liang Y-C, Geng C-N, Wang S-G (2007) Is the effect of silicon on rice uptake of arsenate (AsV) related to internal silicon concentrations, iron plaque and phosphate nutrition? Environ Pollut 148:251–257
Guo W, Zhang J, Teng M, Wang LH (2009) Arsenic uptake is suppressed in a rice mutant defective in silicon uptake. J Plant Nutr Soil Sci 172(6):867–874
Halim M, Majumder R, Nessa S, Hiroshiro Y, Uddin M, Shimada J, Jinno K (2009) Hydrogeochemistry and arsenic contamination of groundwater in the Ganges Delta Plain, Bangladesh. J Hazard Mater 164(2):1335–1345
Kim Y-H, Khan AL, Kim D-H, Lee S-Y, Kim K-M, Waqas M, Jung H-Y, Shin J-H, Kim J-G, Lee I-J (2014) Silicon mitigates heavy metal stress by regulating P-type heavy metal ATPases, Oryza sativa low silicon genes, and endogenous phytohormones. BMC Plant Biol 14(1):13
King E, Stacy B, Holt P, Yates DM, Pickles D (1955) The colorimetric determination of silicon in the micro-analysis of biological material and mineral dusts. Analyst 80(951):441–453
Li R-Y, Stroud JL, Ma J-F, McGrath SP, Zhao F-J (2009) Mitigation of arsenic accumulation in rice with water management and silicon fertilization. Environ Sci Technol 43(10):3778–3783
Li L, Zheng C, Fu Y, Wu D, Yang X, Shen H (2012) Silicate-mediated alleviation of Pb toxicity in banana grown in Pb-contaminated soil. Biol Trace Elem Res 145(1):101–108
Liang Y-C (1999) Effects of silicon on enzyme activity and sodium, potassium and calcium concentration in barley under salt stress. Plant and Soil 209(2):217–224
Liang Y-C, Wong J, Wei L (2005) Silicon-mediated enhancement of cadmium tolerance in maize (Zea mays L.) grown in cadmium contaminated soil. Chemosphere 58(4):475–483
Liang Y-C, Sun W, Zhu Y-G, Christie P (2007) Mechanisms of silicon-mediated alleviation of abiotic stresses in higher plants: a review. Environ Pollut 147(2):422–428
Ma J-F, Miyake Y, Takahashi E (2001) Silicon as a beneficial element for crop plants. Stud Plant Sci 8:17–39
Marin A, Masscheleyn P, Patrick WH Jr (1993) Soil redox-pH stability of arsenic species and its influence on arsenic uptake by rice. Plant and Soil 152(2):245–253
Marmiroli M, Pigoni V, Savo-Sardaro ML, Marmiroli N (2014) The effect of silicon on the uptake and translocation of arsenic in tomato (Solanum lycopersicum L.). Environ Exp Bot 99:9–17
Marschner H, Rimmington G (1988) Mineral nutrition of higher plants. Plant Cell Environ 11:147–148
Masscheleyn PH, Delaune RD, Patrick WH Jr (1991) Effect of redox potential and pH on arsenic speciation and solubility in a contaminated soil. Environ Sci Technol 25(8):1414–1419
Meharg C, Meharg AA (2015) Silicon, the silver bullet for mitigating biotic and abiotic stress, and improving grain quality, in rice? Environ Exp Bot 120:8–17
Meharg AA, Williams PN, Adomako E, Lawgali YY, Deacon C, Villada A, Cambell RC, Sun G-X, Zhu Y-G, Feldmann J (2009) Geographical variation in total and inorganic arsenic content of polished (white) rice. Environ Sci Technol 43(5):1612–1617
Naidu R, Bolan NS, Kookana RS, Tiller K (1994) Ionic‐strength and pH effects on the sorption of cadmium and the surface charge of soils. Eur J Soil Sci 45(4):419–429
Ng JC, Wang J, Shraim AA (2003) Global health problem caused by arsenic from natural sources. Chemosphere 52(9):1353–1359
Peryea FJ (1998) Phosphate starter fertilizer temporarily enhances soil arsenic uptake by apple trees grown under field conditions. Hortscience 33(5):826–829
Peryea FJ, Kammereck R (1997) Phosphate-enhanced movement of arsenic out of lead arsenate-contaminated topsoil and through uncontaminated subsoil. Water Air Soil Pollut 93(1-4):243–254
Putwattana N, Kruatrachue M, Pokethitiyook P, Chaiyarat R (2010) Immobilization of cadmium in soil by cow manure and silicate fertilizer, and reduced accumulation of cadmium in sweet basil (Ocimum basilicum). Science Asia 36(4):349–354
Raven KP, Jain A, Loeppert RH (1998) Arsenite and arsenate adsorption on ferrihydrite: kinetics, equilibrium, and adsorption envelopes. Environ Sci Technol 32(3):344–349
Reddy C, Patrick W (1977) Effect of redox potential and pH on the uptake of cadmium and lead by rice plants. J Environ Qual 6(3):259–262
Seyfferth AL, Fendorf S (2012) Silicate mineral impacts on the uptake and storage of arsenic and plant nutrients in rice (Oryza sativa L.). Environ Sci Technol 46(24):13176–13183
Shi X, Zhang C, Wang H, Zhang F (2005) Effect of Si on the distribution of Cd in rice seedlings. Plant and Soil 272(1-2):53–60
Shi G, Cai Q, Liu C, Wu L (2010) Silicon alleviates cadmium toxicity in peanut plants in relation to cadmium distribution and stimulation of antioxidative enzymes. Plant Growth Regul 61(1):45–52
Shuman L (1985) Fractionation method for soil microelements. Soil Sci 140(1):11–22
Sun Y, Li Z, Guo B, Chu G, Wei C, Liang Y-C (2008) Arsenic mitigates cadmium toxicity in rice seedlings. Environ Exp Bot 64(3):264–270
Sun G-X, Liu X, Williams PN, Zhu Y-G (2010) Distribution and translocation of selenium from soil to grain and its speciation in paddy rice (Oryza sativa L.). Environ Sci Technol 44(17):6706–6711
Sun G-X, Van de Wiele T, Alava P, Tack F, Du Laing G (2012) Arsenic in cooked rice: Effect of chemical, enzymatic and microbial processes on bioaccessibility and speciation in the human gastrointestinal tract. Environ Pollut 162:241–246
Tripathi P, Tripathi RD, Singh RP, Dwivedi S, Goutam D, Shri M, Chakrabarty D (2013) Silicon mediates arsenic tolerance in rice (Oryza sativa L.) through lowering of arsenic uptake and improved antioxidant defence system. Ecol Eng 52:96–103
Verbruggen N, Hermans C, Schat H (2009) Mechanisms to cope with arsenic or cadmium excess in plants. Curr Opin Plant Biol 12(3):364–372
Wang L, Wang Y, Chen Q, Cao W, Li M, Zhang F (2000) Silicon induced cadmium tolerance of rice seedlings. J Plant Nutr 23(10):1397–1406
Wang J, Zhao FJ, Meharg AA, Raab A, Feldmann J, McGrath SP (2002) Mechanisms of arsenic hyperaccumulation in Pteris vittata. Uptake kinetics, interactions with phosphate, and arsenic speciation. Plant Physiol 130(3):1552–1561
Williams PN, Lei M, Sun G-X, Huang Q, Lu Y, Deacon C, Meharg AA, Zhu Y-G (2009) Occurrence and partitioning of cadmium, arsenic and lead in mine impacted paddy rice: Hunan, China. Environ Sci Technol 43(3):637–642
Zhang C, Wang L, Nie Q, Zhang W, Zhang F (2008) Long-term effects of exogenous silicon on cadmium translocation and toxicity in rice (Oryza sativa L.). Environ Exp Bot 62(3):300–307
Zhao F-J, Ma J-F, Meharg AA, McGrath SP (2009) Arsenic uptake and metabolism in plants. New Phytol 181(4):777–794
Zhu Z, Wei G, Li J, Qian Q, Yu J (2004) Silicon alleviates salt stress and increases antioxidant enzymes activity in leaves of salt-stressed cucumber (Cucumis sativus L.). Plant Sci 167(3):527–533
Acknowledgments
This project was financially supported by the Natural Science Foundation of China (No. 41371459), the State Key Program of Natural Science Foundation of China (No. 41330853), the Special Fund for Agro-scientific Research in the Public Interest of China (201503122), and the National High Technology Research and Development Program of China (863 Program, 2013AA06A209).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Additional information
Responsible editor: Elena Maestri
Hong-Yan Wang and Shi-Lin Wen contributed equally to this work.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Wang, HY., Wen, SL., Chen, P. et al. Mitigation of cadmium and arsenic in rice grain by applying different silicon fertilizers in contaminated fields. Environ Sci Pollut Res 23, 3781–3788 (2016). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11356-015-5638-5
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11356-015-5638-5