Abstract
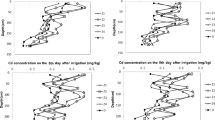
Drip irrigation systems have been widely applied in semiarid and arid regions of China. However, little is known about the migration of heavy metals in cultivated soil under drip irrigation. Therefore, the concentrations of Cd, Cr, Cu, Ni, Pb, and Zn in soil were determined. The mean contents of Cd, Cr, Cu, Pb, Zn, and Ni in surface soil subjected to irrigation with low and high amounts of water (W1 and W2) were 0.11, 117.50, 37.51, 13.53, 78.10, and 38.41 mg/kg and 0.20, 94.45, 29.71, 22.48, 63.00, and 36.62 mg/kg, respectively. Metal concentrations in deep soil varied slightly between W1 and W2. Among different distances from the dropper, the metal levels in surface soil varied widely, while they varied slightly in deep soil. The I geo (geo-accumulation index) values indicated that the soil was usually contaminated by Cr, Cu, and Cd. Under W1, Cd and Cu usually accumulated in surface soil near the dropper, while the other metals leached into subsurface soil. Moreover, the metals generally accumulated in soil away from the dropper. However, significant leaching of metals to the subsurface and deep soil was observed near the dropper under W2. Away from the dropper, Cd, Cr, Cu, Ni, and Pb usually accumulated in surface and deep soil. This suggested that heavy metals generally migrated to the soil away from the dropper when subjected to lower amounts of irrigation, while metals usually moved to surface soil and deep soil under high irrigation amounts. These findings indicate that drip irrigation greatly affected the distribution and migration of heavy metals in soil, with irrigation with lower amounts of irrigation water significantly affecting the horizontal migration of heavy metals and higher amounts influencing the vertical movement of heavy metals.



Similar content being viewed by others
References
Ajwa HA, Trout T (2004) Drip application of alternative fumigants to methyl bromide for strawberry production. Hortic Sci 39:1707–1715
Al-Hwaiti M, Al-Khashman O (2015) Health risk assessment of heavy metals contamination in tomato and green pepper plants grown in soils amended with phosphogypsum waste materials. Environ Geochem Health 37:287–304
Badr AE, Abuarab ME (2013) Soil moisture distribution patterns under surface and subsurface drip irrigation systems in sandy soil using neutron scattering technique. Irrig Sci 31:317–332
Baldantoni D, Leone A, Iovieno P, Morra L, Zaccardelli M, Alfani A (2010) Total and available soil trace element concentrations in two Mediterranean agricultural systems treated with municipal waste compost or conventional mineral fertilizers. Chemosphere 80:1006–1013
Burges A, Epelde L, Garbisu C (2015) Impact of repeated single-metal and multi metal pollution events on soil quality. Chemosphere 120:8–15
Chen B, Cao J, Wang L, Mao J (2010) Research on distribution and movement rules of soil water under different drip irrigation conditions. Water Sav Irrig 7:6–10
Cheraghi M, Lorestani B, Merrikhpour H (2012) Investigation of the effects of phosphate fertilizer application on the heavy metal content in agricultural soils with different cultivation patterns. Biol Trace Elem Res 145:87–92
CNEMC (China National Environmental Monitoring Centre) (1990) The background values of Chinese soils. Environmental Science Press of China, Beijing
Cote CM, Bristow KL, Charlesworth PB, Cook FJ, Thorburn PJ (2003) Analysis of soil wetting and solute transport in subsurface trickle irrigation. Irrig Sci 22:143–156
Fonseca AF, Melfi AJ, Montes CR (2005) Maize growth and changes in soil fertility after irrigation with treated sewage effluent. II. Soil acidity, exchangeable cations, and sulfur, boron, and heavy metals availability. Commun Soil Sci Plant 36:1983–2003
Gärdenäs AI, Hopmans JW, Hanson BR, Šimůnek J (2005) Two dimensional modeling of nitrate leaching for various fertigation scenarios under micro-irrigation. Agric Water Manag 74:219–242
Guan H, Li J, Li Y (2013) Effects of drip system uniformity and irrigation amount on water and salt distributions in soil under arid conditions. J Integr Agric 12(5):924–939
Hu H, Tian F, Hu H (2011) Soil particle size distribution and its relationship with soil water and salt under mulched drip irrigation in Xinjiang of China. Sci China Technol Sci 54:1568–1574
Ji Y, Feng Y, Wu J, Zhu T, Bai Z, Duan C (2008) Using geo-accumulation index to study source profiles of soil dust in China. J Environ Sci 20:571–578
Kandelous MM, Šimůnek J, van Genuchten MT, Malek K (2011) Soil water content distributions between two emitters of a subsurface drip irrigation system. Soil Sci Soc Am J 75:488–497
Koedrith P, Kim H, Weon JI, Seo YR (2013) Toxicogenomic approaches for understanding molecular mechanisms of heavy metal mutagenicity and carcinogenicity. Int J Hyg Environ Health 216:587–598
Liu M, Yang J, Li X, Yu M, Wang J (2012) Effects of irrigation water quality and drip tape arrangement on soil salinity, soil moisture distribution, and cotton yield (Gossypium hirsutum L.) under mulched drip irrigation in Xinjiang, China. J Integr Agric 11(3):502–511
Liu M, Yang J, Li X, Liu G, Yu M, Wang J (2013) Distribution and dynamics of soil water and salt under different drip irrigation regimes in northwest China. Irrig Sci 31:675–688
Luo X, Xue Y, Wang Y, Cang L, Xu B, Ding J (2015) Source identification and apportionment of heavy metals in urban soil profiles. Chemosphere 127:152–157
Maimaitiniyazi N, Zheng X, Batur B, Li H, Ruxian M, He F (2011) An analysis of water and salt transport under drip irrigation conditions. J Shandong Agr Univ 42(4):551–554
Muller G (1969) Index of geo-accumulation in sediments of the Rhine River. GeoJournal 2:108–118
Negreanu Y, Pasternak Z, Jurkevitch E, Cytryn E (2012) Impact of treated wastewater irrigation on antibiotic resistance in agricultural soils. Environ Sci Technol 46:4800–4808
Qiao Z, Peng S, Xu J, Gao X, Song J (2011) Chemical forms and migration of soil heavy metals in paddy and effects or irrigation. J Anhui Agric Sci 39(16):9698–9700
Rai S, Gupta S, Mittal PC (2015) Dietary intakes and health risk of toxic and essential heavy metals through the food chain in agriculture, industrial, and coal mining areas of Northern India. Hum Ecol Risk Assess 21:913–933
Rajmohan N, Prathapar SA, Jayaprakash M, Nagarajan R (2014) Vertical distribution of heavy metals in soil profile in a seasonally waterlogging agriculture field in Eastern Ganges Basin. Environ Monit Assess 186:5411–5427
Savic R, Ondrasek G, Josimov-Dundjerski J (2015) Heavy metals in agricultural landscapes as hazards to human and ecosystem health: a case study on zinc and cadmium in drainage channel sediments. J Sci Food Agric 95:466–470
Selim T, Bouksila F, Berndtsson R, Persson M (2013) Soil water and salinity distribution under different treatments of drip irrigation. Soil Sci Soc Am J 77:1144–1156
Soltani N, Keshavarzi B, Moore F, Tavakol T, Lahijanzadeh AR, Jaafarzadeh N, Kermani M (2015) Ecological and human health hazards of heavy metals and polycyclic aromatic hydrocarbons (PAHs) in road dust of Isfahan metropolis, Iran. Sci Total Environ 505:712–723
Soodan RK, Pakade YB, Nagpal A, Katnoria JK (2014) Analytical techniques for estimation of heavy metals in soil ecosystem: a tabulated review. Talanta 125:405–410
Surdyk N, Cary L, Blagojevic S, Jovanovic Z, Stikic R, Vucelic-Radovic B, Zarkovic B, Sandei L, Pettenati M, Kloppmann W (2010) Impact of irrigation with treated low quality water on the heavy metal contents of a soil-crop system in Serbia. Agric Water Manag 98:451–457
Tan J, Kang Y, Jiao Y, Liu W, Dong F (2009) Effects of cropping years on soil salinity and pH value in fields under drip irrigation condition. Trans CSAE 25(9):43–50
Thorburn PJ, Cook FJ, Bristow KL (2003) Soil-dependent wetting from trickle emitters: Implications for system design and management. Irrig Sci 22:121–127
Wei B, Yang L (2010) A review of heavy metal contaminations in urban soils, urban road dusts and agricultural soils from China. Microchem J 94:99–107
Wei B, Jiang F, Li X, Mu S (2010) Heavy metal induced ecological risk in the city of Urumqi, NW China. Environ Monit Assess 160:33–45
Yang L, Peterson PJ, Williams WP, Wang WY, Hou SF, Tan JA (2002) The relationship between exposure to arsenic concentrations in drinking water and the development of skin lesions in farmers from Inner Mongolia, China. Environ Geochem Health 24:293–303
Zhang XW, Yang LS, Li YH, Li HR, Wang WY, Ye BX (2012) Impacts of lead/zinc mining and smelting on the environment and human health in China. Environ Monit Assess 184:2261–2273
Zheng X, Batur B, Li H, Jia W, Zhao H (2011) Effect of irrigation methods on movement of soil water and salt in arid area. J Northeast Agric Univ 42(5):95–98
Zhou L, Yang B, Xue N, Li F, Seip HM, Cong X, Yan Y, Liu B, Han B, Li H (2014) Ecological risks and potential sources of heavy metals in agricultural soils from Huanghuai Plain, China. Environ Sci Pollut Res 21:1360–1369
Żukowska J, Biziuk M (2008) Methodological evaluation of method for dietary heavy metal intake. J Food Sci 73:R21–R29
Acknowledgments
The work described in this article was financially supported by the National Public Welfare Sectors (Agriculture) special research (No. 201203012–6) and the State Key Program of National Natural Science of China (No. 41230749).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding authors
Additional information
Responsible editor: Zhihong Xu
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Wei, B., Yu, J., Dong, Y. et al. Effects of drip irrigation on migration and distribution of heavy metals in soil profile. Environ Sci Pollut Res 23, 3632–3640 (2016). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11356-015-5515-2
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11356-015-5515-2