Abstract
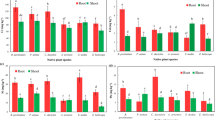
Willows are a group of versatile tree species that may have multiple environmental applications. In the present study, Salix jiangsuensis J172 plants were grown in the fixed mats as an economic plant-based treatment system to evaluate its potential for removing nutrients in wastewater. Plants grew normally in wastewater compared with those in Hoagland solution. However, wastewater containing a high concentration of chlorine ions was toxic to S. jiangsuensis J172 plants. The plants accumulated large amounts of nitrogen and phosphorus in aboveground tissues under conditions of abundant supply. The removal efficiency for raw wastewater was 82.18–87.78 % for nitrogen, 57.35–65.58 % for phosphorus, and 58.24–59.90 % for chemical oxygen demand. Nutrient removal efficiency was positively correlated with the initial nutrient supply. The results show that S. jiangsuensis J172 grown in the fixed mat economic plant-based treatment system with nutrient-rich, eutrophic water may be an effective, low-cost phytoremediation technology to treat water containing undesirable levels of wastewater.




Similar content being viewed by others
References
Amofah LR, Mattsson J, Hedström A (2012) Willow bed fertigated with domestic wastewater to recover nutrients in subarctic climates. Ecol Eng 47:174–181
Białowiec A, Davies L, Albuquerque A, Randerson PF (2012) Nitrogen removal from landfill leachate in constructed wetlands with reed and willow: redox potential in the root zone. J Environ Manag 97:22–27
Bindu T, Sylas VP, Mahesh M, Rakesh PS, Ramasamy EV (2008) Pollutant removal from domestic wastewater with Taro (Colocasia esculenta) planted in a subsurface flow system. Ecol Eng 33:68–82
Börjesson P, Berndes G (2006) The prospects for willow plantations for wastewater treatment in Sweden. Biomass Bioenerg 30:428–438
Calheiros CSC, Rangel AOOS, Castro PML (2007) Constructed wetland systems vegetated with different plants applied to the treatment of tannery wastewater. Water Res 41:1790–1791
Dimitriou I, Aronsson P (2011) Wastewater and sewage sludge application to willows and poplars grown in lysimeters—Plant response and treatment efficiency. Biomass Bioenerg 35:161–170
Dimitriou I, Rosenqvist H (2011) Sewage sludge and wastewater fertilisation of Short Rotation Coppice (SRC) for increased bioenergy production—Biological and economic potential. Biomass Bioenerg 35:835–842
Elowson S (1999) Willow as a vegetation filter for cleaning of polluted drainage water from agricultural land. Biomass Bioenerg 16:281–290
Ericsson K, Rosenqvist H, Ganko E, Pisarek M, Nilsson L (2006) An agro-economic analysis of willow cultivation in Poland. Biomass Bioenerg 60:16–27
Fang YY, Yang XE, Chang HQ, Pu PM, Ding XF, Rengel Z (2007) Phytoremediation of nitrogen-polluted water using water hyacinth. J Plant Nutr 30:1753–1765
Fillion M, Brisson J, Guidi W, Labrecque M (2011) Increasing phosphorus removal in willow and poplar vegetation filters using arbuscular mycorrhizal fungi. Ecol Eng 37:199–205
Gopal B (1999) Natural and constructed wetlands for wastewater treatment: potentials and problems. Water Sci Technol 40:27–35
Holm B, Heinsoo K (2013) Municipal wastewater application to Short Rotation Coppice of willows—Treatment efficiency and clone response in Estonian case study. Biomass Bioenerg 57:126–135
Hu MH, Ao YS, Yang XE, Li TQ (2008) Treating eutrophic water for nutrient reduction using an aquatic macrophyte (Ipomoea aquatica Forsskal) in a deep flow technique system. Agric Water Manag 95:607–615
Im JH, Woo HJ, Choi MW, Han KB, Kim CW (2001) Simultaneous organic and nitrogen removal from municipal landfill leachate using an anerobic-aerobic system. Water Res 35:2403–2410
Kadlec RH, Tanner CC, Hally VM, Gibbs MM (2005) Nitrogen spiraling in subsurface-flow constructed wetlands: implications for treatment response. Ecol Eng 25:365–381
Kuzovkina YA, Quigley MF (2005) Willows beyond wetland uses of Salix L. species for environmental projects. Water Air Soil Pollut 162:183–204
Leto C, Tuttolomondo T, Bella SL, Leone R, Licata M (2013) Effects of plant species in a horizontal subsurface flow constructed wetland—phytoremediation of treated urban wastewater with Cyperus alternifolius L. and Typha latifolia L. in the west of Sicily (Italy). Ecol Eng 61:282–291
Li M, Sheng GP, Wu YJ, Yu ZL, Bañuelos GS, Yu HQ (2014) Enhancement of nitrogen and phosphorus removal from eutrophic water by economic plant annual ryegrass (Lolium multiflorum) with ion implantation. Environ Sci Pollut Res 21:9617–9625
Madejon P, Murillo JM, Maranon T, Cabrera F, Soriano MA (2003) Trace element and nutrient accumulation in sunflower plants two years after the Aznalcollar mine spill. Sci Total Environ 307:239–257
Mant C, Peterkin J, May E, Butler J (2003) A feasibility study of a Salix viminalis gravel hydroponic system to renovate primary settled wastewater. Bioresource Technol 90:19–25
Mbuligwe SE (2004) Comparative effectiveness of engineered wetland systems in the treatment of anaerobic ally pre-treated domestic wastewater. Ecol Eng 23:269–284
Nissim WG, Voicu A, Labrecque M (2014) Willow short-rotation coppice for treatment of polluted groundwater. Ecol Eng 62:102–114
Rytter L, Ericsson T (1993) Leaf nutrient analysis in Salix viminalis (L.) energy forest stands growing on agricultural land. Z Pflanzenernähr Bodenkd 156:349–356
Shin JY, Park SS, An KG (2004) Removal of nitrogen and phosphorus using dominant riparian plants in a hydroponic culture system. J Environ Sci Health A 39:821–834
Sooknah RD, Wilkie AC (2004) Nutrient removal by floating aquatic macrophytes cultured in anaerobically digested flushed dairy manure wastewater. Ecol Eng 22:27–42
Steer D, Fraser L, Boddy J, Seibert B (2002) Efficiency of small constructed wetlands for subsurface treatment of single-family domestic effluent. Ecol Eng 18:429–440
Stephens W, Tyrrel SF, Tiberghien J (2000) Irrigating short rotation coppice with landfill leachate: constraints to productivity due to chloride. Bioresource Technol 75:227–229
Sun LP, Liu Y, Jin H (2009) Nitrogen removal from polluted river by enhanced floating bed grown canna. Ecol Eng 35:135–140
Türker OC, Böcük H, Yakar A (2013) The phytoremediation ability of a polyculture constructed wetland to treat boron from mine effluent. J Hazard Mater 252–253:132–141
Vaillant N, Monnet F, Vernay P, Sallanon H, Coudret A, Hitmi A (2002) Urban wastewater treatment by a nutrient film technique system with a valuable commercial plant species (Chrysanthemum cinerariaefolium Trev.). Environ Sci Technol 36:2101–2106
Vaillant N, Monnet F, Sallanon H, Coudret A, Hitmi A (2003) Treatment of domestic wastewater by an hydroponic NFT system. Chemosphere 50:121–129
Watson C, Pulford ID, Riddell-Black D (2003) Development of a hydroponic screening technique to assess heavy metal resistance in willow (Salix). Int J Phytoremediation 5:333–349
Weih M, Nordh NE (2002) Characterising willows for biomass and phytoremediation: growth, nitrogen and water use of 14 willow clones under different irrigation and fertilization regimes. Biomass Bioenerg 23:397–413
Wu SB, Austin D, Liu L, Dong RJ (2011) Performance of integrated household constructed wetland for domestic wastewater treatment in rural areas. Ecol Eng 37:948–954
Zhang XB, Liu P, Yang YS, Chen WR (2007) Phytoremediation of urban wastewater by model wetlands with ornamental hydrophytes. J Environ Sci 19:902–909
Zhang ZH, Rengel Z, Meney K (2008) Interactive effects of nitrogen and phosphorus loadings on nutrient removal from simulated wastewater using Schoenoplectus validus in wetland microcosms. Chemosphere 72:1823–1828
Zhao FL, Yang WD, Zeng Z, Li H, Yang XE, He ZL, Gu BH, Rafiq MT, Peng HY (2012) Nutrient removal efficiency and biomass production of different bioenergy plants in hypereutrophic water. Biomass Bioenerg 42:212–218
Acknowledgments
Thanks are due to Dr. Lee Y H for editing this manuscript. This study was supported in part by the Public Project of Science and Technology Department of Zhejiang Province (No. 2011C22003); special funds from the Central Scientific Research Institute of Public Welfare (RISF 6907); and the Introduced Project of Advanced Science and Technology of Forestry (948) (No. 2006–4–06).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Additional information
Responsible editor: Elena Maestri
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Shi, X., Sun, H., Pan, H. et al. Growth and efficiency of nutrient removal by Salix jiangsuensis J172 for phytoremediation of urban wastewater. Environ Sci Pollut Res 23, 2715–2723 (2016). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11356-015-5508-1
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11356-015-5508-1