Abstract
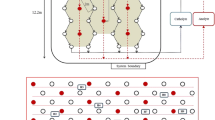
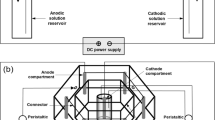
The applicability of an in situ electrokinetic process with a parallel electrode configuration was evaluated to treat an As-, Cu-, and Pb-contaminated paddy rice field in full scale (width, 17 m; length, 12.2 m; depth, 1.6 m). A constant voltage of 100 V was supplied and electrodes were spaced 2 m apart. Most As, Cu, and Pb were bound to Fe oxide and the major clay minerals in the test site were kaolinite and muscovite. The electrokinetic system removed 48.7, 48.9, and 54.5 % of As, Cu, and Pb, respectively, from the soil during 24 weeks. The removal of metals in the first layer (0–0.4 m) was higher than that in the other three layers because it was not influenced by groundwater fluctuation. Fractionation analysis showed that As and Pb bound to amorphous Fe and Al oxides decreased mainly, and energy consumption was 1.2 kWh/m3. The standard deviation of metal concentration in the soil was much higher compared to the hexagonal electrode configuration because of a smaller electrical active area; however, the electrode configuration removed similar amounts of metals compared to the hexagonal system. From these results, it was concluded that the electrokinetic process could be effective at remediating As-, Cu-, and Pb-contaminated paddy rice field in situ.






Similar content being viewed by others
References
Alshawabkeh AN, Gale RJ, Ozsu-Acar E, Bricka RM (1999a) Optimization of 2-D electrode configuration for electrokinetic remediation. J Soil Contam 8:617–635
Alshawabkeh AN, Yeung AT, Bricka MR (1999b) Practical aspects of in-situ electrokinetic extraction. J Environ Eng-Asce 125:27–35
Datta D (1981) Principles and practices of rice production. Int Rice Res Inst
Jarup L (2003) Hazards of heavy metal contamination. Br Med Bull 68:167–182
Jeon E-K, Jung J-M, Kim W-S, Ko S-H, Baek K (2014) In situ electrokinetic remediation of As-, Cu-, and Pb-contaminated paddy soil using hexagonal electrode configuration: a full scale study. Environ Sci Pollut Res 1–10
Jiang W, Hou Q, Yang Z, Zhong C, Zheng G, Yang Z, Li J (2014) Evaluation of potential effects of soil available phosphorus on soil arsenic availability and paddy rice inorganic arsenic content. Environ Pollut 188:159–165
Jo S-U, Kim D-H, Yang J-S, Baek K (2012) Pulse-enhanced electrokinetic restoration of sulfate-containing saline greenhouse soil. Electrochim Acta 86:57–62
Kim B-K, Baek K, Ko S-H, Yang J-W (2011) Research and field experiences on electrokinetic remediation in South Korea. Sep Purif Technol 79:116–123
Kim W-S, Park G-Y, Kim D-H, Jung H-B, Ko S-H, Baek K (2012) In situ field scale electrokinetic remediation of multi-metals contaminated paddy soil: Influence of electrode configuration. Electrochim Acta 86:89–95
Kim W-S, Jeon E-K, Jung J-M, Jung H-B, Ko S-H, Seo C-I, Baek K (2014) Field application of electrokinetic remediation for multi-metal contaminated paddy soil using two-dimensional electrode configuration. Environ Sci Pollut Res 21:4482–4491
Krishna AK, Mohan KR, Murthy NN, Periasamy V, Bipinkumar G, Manohar K, Rao SS (2013) Assessment of heavy metal contamination in soils around chromite mining areas, Nuggihalli, Karnataka, India. Environ Earth Sci 70:699–708
Mulligan CN, Yong RN, Gibbs BF (2001) Remediation technologies for metal-contaminated soils and groundwater: an evaluation. Eng Geol 60:193–207
Rauret G, Lopez-Sanchez JF, Sahuquillo A, Rubio R, Davidson C, Ure A, Quevauviller P (1999) Improvement of the BCR three step sequential extraction procedure prior to the certification of new sediment and soil reference materials. J Environ Monit 1:57–61
Ryu B-G, Yang J-S, Kim D-H, Baek K (2010) Pulsed electrokinetic removal of Cd and Zn from fine-grained soil. J Appl Electrochem 40:1039–1047
Ryu B-G, Park G-Y, Yang J-W, Baek K (2011) Electrolyte conditioning for electrokinetic remediation of As, Cu, and Pb-contaminated soil. Sep Purif Technol 79:170–176
Smith AH, Hopenhaynrich C, Bates MN, Goeden HM, Hertzpicciotto I, Duggan HM, Wood R, Kosnett MJ, Smith MT (1992) Cancer risks from arsenic in drinking-water. Environ Health Perspect 97:259–267
Virkutyte J, Sillanpaa M, Latostenmaa P (2002) Electrokinetic soil remediation - critical overview. Sci Total Environ 289:97–121
Wenzel WW, Kirchbaumer N, Prohaska T, Stingeder G, Lombi E, Adriano DC (2001) Arsenic fractionation in soils using an improved sequential extraction procedure. Anal Chim Acta 436:309–323
Yang J-S, Lee JY, Baek K, Kwon T-S, Choi J (2009) Extraction behavior of As, Pb, and Zn from mine tailings with acid and base solutions. J Hazard Mater 171:443–451
Compliance with Ethical Standards
This work was supported by a grant from Korea Environment Industry and Technology Institute (KEITI) through GAIA project. The authors declare that they have no conflict of interest.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Additional information
Responsible editor: Bingcai Pan
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Jeon, EK., Jung, JM., Ryu, SR. et al. In situ field application of electrokinetic remediation for an As-, Cu-, and Pb-contaminated rice paddy site using parallel electrode configuration. Environ Sci Pollut Res 22, 15763–15771 (2015). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11356-015-4765-3
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11356-015-4765-3