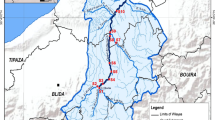
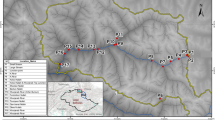
Abstract
Hydropsyche angustipennis (Insecta, Trichoptera) larvae were used as indicators of stream contamination in the city of Łódź, Poland. The larvae of H. angustipennis were present at 9 sampling sites established for this study. Significant differences between the sampling sites were noted for environmental parameters as well as concentration of chemicals in water and biodiversity of aquatic invertebrates. Statistical analyses showed significant correlations between quantity and quality of water pollutants and density of H. angustipennis larvae, concentration of metals in larval bodies, and the appearance of morphological anomalies in tracheal gills and anal papillae. In comparison to literature data, the level of contaminants in water, including heavy metals, for each of the studied streams of Łódź was surprisingly low while concentration of these metals in the whole bodies of H. angustipennis larvae was very high. Some of the heavy metals present in the water might be identified only after conducting analyses of their concentration in the larval bodies. Therefore, long life cycle of H. angustipennis and heavy metal tolerance with a possibility of their accumulation in the larval bodies may constitute a support to traditional chemical assessment of water quality or traditional biomonitoring.






Similar content being viewed by others
References
Abdel-Haleem AS, Sroor A, El-Bahi SM, Zohny E (2001) Heavy metals and rare earth elements in phosphate fertilizer components using instrumental neutron activation analysis. Appl Radiat Isot 55:569–573
Adakole JA, Anunne PA (2003) Benthic macroinvertebrates as indicators of environmental quality of an urban stream, Zaria, Northern Nigeria. J Aquat Sci 18:85–92
Axtmann EV, Cain DJ, Luoma SN (1997) Effect of tributary inflows on the distribution of trace metals in fine-grained bed sediments and benthic insects of the Clark Fork River, Montana. Environ Sci Technol 31:750–758
Barata C, Lekumberri I, Vila-Escalé M, Prat N, Porte C (2005) Trace metal concentration, antioxidant enzyme activities and susceptibility to oxidative stress in the trichoptera larvae Hydropsyche exocellata from the Llobregat river basin (NE Spain). Aquat Toxicol 74:3–19
Bascombe AD, Ellis JB, Revitt DM, Shutes RBE (1990) Development of ecotoxicological criteria in urban catchments. Water Sci Technol 22:173–179
Bonada N, Zamora-Muñoz C, Rieradevall M, Prat N (2004) Ecological profiles of caddisfly larvae in Mediterranean streams: implications for bioassessment methods. Environ Pollut 132:509–521
Bonada N, Vives S, Rieradevall M, Prat N (2005) Relationship between pollution and fluctuating asymmetry in the pollution-tolerant caddisfly Hydropsyche exocellata (Trichoptera, Insecta). Arch Hydrobiol 162:167–185
Brinkman SF, Johnston WD (2008) Acute toxicity of aqueous copper, cadmium, and zinc to the mayfly Rhithrogena hageni. Arch Environ Contam Toxicol 54:466–472
Buchwalter DB, Cain DJ, Clements WH, Luoma SN (2007) Using biodynamic models to reconcile differences between laboratory toxicity tests and field biomonitoring with aquatic insects. Environ Sci Technol 41:4821–4828
Cain DJ, Luoma SN (1998) Metal exposures to native populations of the caddisfly Hydropsyche (Trichoptera: Hydropsychidae) determined from cytosolic and whole body metal concentrations. Hydrobiologia 386:103–117
Cain DJ, Luoma SN, Carter JL, Fend SV (1992) Aquatic insects as bioindicators of trace element contamination in cobble-bottom rivers and streams. Can J Fish Aquat Sci 49:2141–2154
Cain DJ, Carter JL, Fend SV, Luoma SN, Alpers CN, Taylor HE (2000) Metal exposure in a benthic macroinvertebrate, Hydropsyche californica, related to mine drainage in the Sacramento River. Can J Fish Aquat Sci 57:380–390
Cain DJ, Buchwalter DB, Luoma SN (2006) Influence of metal exposure history on the bioaccumulation and subcellular distribution of aqueous cadmium inthe insect Hydropsyche californica. Environ Toxicol Chem 25:1042–1049
Camargo JA (1991) Toxic effects of residual chlorine on larvae of Hydropsyche pellucidula (Trichoptera; Hydropsychidae): a proposal of biological indicator. Bull Environ Contam Toxicol 47:261–265
Camargo JA, De Jalon DG, Muñoz MJ, Tarazona JV (1992a) Sublethal effects of sodium fluoride (NaF) on net-spinning caddisfies (trichoptera). Aquat Insect 14:23–30
Camargo JA, Ward JV, Martin KL (1992b) The relative sensitivity of competing hydropsychid species to fuoride toxicity in the Cache la Poudre River (Colorado). Arch Environ Contam Toxicol 22:107–113
Chinwe OU, Obinna CN, Akeem A, Alo BI (2010) Assessment of heavy metals in urban highway runoff from Ikorodu expressway Lagos, Nigeria. J Environ Chem Ecotoxicol 2:34–37
Clements WH, Kiffney PM (1994) Integrated laboratory and field approach for assessing impacts of heavy metals at the Arkansas River, Colorado. Environ Toxicol Chem 13:397–404
Damásio J, Fernández-Sanjuan M, Sánchez-Avila J, Lacorte S, Prat N, Rieradevall M, Soares AMVM, Barata C (2011) Multi-biochemical responses of benthic macroinvertebrate species as a complementary tool to diagnose the cause of community impairment in polluted rivers. Water Res 45:3599–3613
Diehl J (1997) Assumptions of environmental policy for the Łódź City. The goverment of Łódź City. Department of Environment Protection of the Łódź City. Issue I. Informatic publishing house, Łódź City (in Polish)
Directive 2000/60/EC - The Water Framework Directive of the European Parliament and of the Council of 23 October 2000 establishing a framework for Community action in the field of water policy
Duelli P, Obrist MK (2003) Biodiversity indicators: the choice of values and measures. Agric Ecosyst Environ 98:87–98
Elliott JM (1977) Some methods for the statistical analysis of samples of benthic invertebrates, 2nd edn. Freshwater Biol Assoc, Sci Publ, Westmorland, UK, Ambleside
Ellis JB, Revitt DM (2008) Quantifying diffuse pollution sources and loads for environmental quality standards in urban catchments. Water Air Soil Pollut 8:577–585
Ellis JB, Revitt DM, Lundy L (2012) An impact assessment methodology for urban surface runoff quality following best practice treatment. Sci Total Environ 416:172–179
Evans RD, Balch GC, Evans HE, Welbourn PM (2002) Simultaneous measurement of uptake and elimination of cadmium by caddisfly (Trichoptera: Hydropsychidae) larvae using stable isotope tracers. Environ Toxicol Chem 21:1032–1039
Girgin S, Kazanci N, Dügel M (2010) Relationship between aquatic insects and heavy metals in an urban stream using multivariate techniques. Int J Environ Sci Technol 7:653–664
Gray JS (2000) The measurement of marine species diversity, with an application to the benthic fauna of the Norwegian continental shelf. J Exp Mar Biol Ecol 250:23–49
Hare L (1992) Aquatic insects and trace metals: bioavailability, bioaccumulation and toxicity. CRC Crit Rev Toxicol 22:327–369
Hare L, Campbell PGC (1992) Temporal variations of trace metals in aquatic insects. Freshw Biol 27:13–27
Higler LWG, Tolkamp HH (1983) Hydropsychidae as bio-indicators. In: ecological indicators for the assessment of the quality of air, water, soil, and ecosystems (Eds. Best EPH, Haeck J). Springer, Netherlands, pp 331–341
Hildrew AG, Edington JM (1979) Factors facilitating the coexistence of hydropsychid caddis larvae (Trichoptera) in the same river system. J Anim Ecol 48:557–576
Johnson RK, Wiederholm T, Rosenberg DM (1993) Freshwater biomonitoring using individual organisms, populations and species assemblages of benthic macroinvertebrates. Chapman and Hall, New York, pp 40–125
Jop KM (1991) Concentration of metals in various larval stages of four Ephemeroptera species. Bull Environ Contam Toxicol 46:901–905
Kiffney PM, Clements WH (2003) Ecological effects of metals on benthic invertebrates. In: Biological response signatures indicator patterns using aquatic communities (Eds. Simon TP). CRC Press, pp 135–154
Lenat DR (1993) Using mentum deformities of Chironomus larvae to evaluate the effects of toxicity and organic loading in streams. J N Am Benthol Soc 21:265–269
Luoma SN (1989) Can we determine the biological availability of sediment-bound trace elements? Hydrobiologia 176/177:379–396
Magurran AE (1988) Ecological diversity and its measurement. Princeton University Press, Princeton
Marqués MJ, Martínez-Conde E, Rovira JV (2003) Effects of zinc and lead mining on the benthic macroinvertebrates of a fluvial ecosystem. Water Air Soil Pollut 148:363–388
Nyholm NEI, Sawicka-Kapasta K, Swiergosz R, Laczewska B (1995) Effects of environmental pollution on breeding populations of birds in southern Poland. Water Air Soil Pollut 85:829–834
Obrist MK, Duelli P (2010) Rapid biodiversity assessment of arthropods for monitoring average local species richness and related ecosystem services. Biodivers Conserv 19:2201–2220
Poepperl R (2000) The filter feeders Hydropsyche angustipennis and H. pellucidula (Trichoptera: Hydropsychidae) in a Northern German Lowland Stream: microdistribution, larval development, emergence pattern, and secondary production. Limnologica 30:65–72
Poteat MD, Jacobus LM, Buchwalter DB (2015) The importance of retaining a phylogenetic perspective in traits-based community analyses. Freshw Biol. doi:10.1111/fwb.12571
Poteat MD, Garland T Jr, Fisher NS, Wang WX, Buchwalter DB (2013) Evolutionary patterns in trace metal (Cd and Zn) efflux capacity in aquatic organisms. Environ Sci Technol 47:7989–7995
Rosenberg DM, Resh VH (1993) Freshwater biomonitoring and benthic macroinvertebrates. Chapman and Hall, New York
Savci S (2012) An agricultural pollutant: chemical fertilizer. Int J Environ Sci Dev 3:77–79
Schindler PW, Stumm W (1987) The surface chemistry of oxides, hydroxides and oxide minerals. In: Aquatic surface chemistry: chemical processes at the particle-water interface (Eds. Stumm W). John Wiley and Sons, New York
Scholes L, Revitt DM, Ellis JB (2008) A systematic approach for the comparative assessment of stormwater pollutant removal potentials. J Environ Manag 88:467–478
Shutes RBE (1985) A comparison of benthic macroinvertebrate fauna of two North London streams. Environ Technol Lett 6:395–404
Sokal RR, Rohlf F (1969) Biometry: the principles and practice of statistics in biological research. WH Freeman, San Francisco
Solà C, Prat N (2006) Monitoring metal and metalloid bioaccumulation in Hydropsyche (Trichoptera, Hydropsychidae) to evaluate metal pollution in a mining river. Whole body versus tissue content. Sci Total Environ 359:221–231
Solà C, Burgos M, Plazuelo Á, Toja J, Prat N (2004) Heavy metal bioaccumulation and macroinvertebrate community changes in a Mediterranean stream affected by acid mine drainage and an accidental spill (Guadiamar River, SW Spain). Sci Total Environ 333:109–126
StatSoft Inc (2011) STATISTICA (data analysis software system) version 10. www.statsoft.com
Statzner B, Hildrew AG, Resh VH (2001) Species traits and environmental constraints: entomological research and the history of ecological theory. Annu Rev Entomol 46:291–316
Stuijfzand SC, Engels S, Van Ammelrooy E, Jonker M (1999) Caddisflies (Trichoptera: Hydropsychidae) used for evaluating water quality of large European rivers. Arch Environ Contam Toxicol 36:186–192
Vuori KM (1994) Rapid behavioural and morphological responses of hydropsychid larvae (Trichoptera, Hydropsychidae) to sublethal cadmium exposure. Environ Pollut 84:291–299
Vuori KM (1995) Species- and population-specific responses of translocated hydropsychid larvae (Trichoptera, Hydropsychidae) to runoff from acid sulphate soils in the River Kyrönjoki, western Finland. Freshw Biol 33:305–318
Vuori KM, Kukkonen J (1996) Metal concentrations in Hydropsyche pellucidula larvae (Trichoptera, Hydropsychidae) in relation to the anal papillae abnormalities and age of exocuticle. Water Res 30:2265–2272
Washington HG (1984) Diversity, biotic, and similarity indices: a review with special relevance to aquatic ecosystems. Water Res 18:653–694
Zar JH (1999) Biostatistical analysis, 4th edn. Prentice Hall, Upper Saddle River
Acknowledgments
We thank Janusz Mazur from the Laboratory of Computer and Analytic Techniques, Faculty of Biology and Environmental Protection, University of Łódź for analyzing the heavy metal concentrations in studied samples and Łukasz Głowacki, PhD, for help in improving the English language quality in text.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Additional information
Responsible editor: Thomas Braunbeck
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Tszydel, M., Markowski, M., Majecki, J. et al. Assessment of water quality in urban streams based on larvae of Hydropsyche angustipennis (Insecta, Trichoptera). Environ Sci Pollut Res 22, 14687–14701 (2015). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11356-015-4638-9
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11356-015-4638-9