Abstract
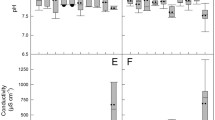
The aim of the study was to determine the effects of land use management on changes in the fecal contamination of water in the Łyna River, one of the main lowland watercourses in the southern watershed of the Baltic Sea (northern Poland). A total of 120 water samples were collected in different seasons of 2011 and 2012 at 15 sites where the river intersected forest (FA), agricultural (AA), and urbanized (UA) areas. Fecal indicator bacteria (FIB), the counts of Enterobacteriaceae and Escherichia coli, total bacterial counts (TBCs), and domain Bacteria (EUB338) were determined by culture-dependent and culture-independent methods. Temperature, pH, chemical oxygen demand, dissolved oxygen, total dissolved solids, ammonia nitrogen, nitrite nitrogen, nitrate nitrogen, orthophosphate, and total phosphorus were also determined. The lowest bacterial counts were noted in water samples collected in FA, and the highest in samples collected in UA. Statistically significant differences were determined between bacterial populations across the analyzed land use types and in different sampling seasons. Significant correlations were also observed between the populations of FIB and physicochemical parameters. The results indicate that land use type influenced FIB concentrations in river water. The combined use of conventional and molecular methods improves the accuracy of fecal contamination analyses in river ecosystems.



Similar content being viewed by others
References
Amann RI, Binder BJ, Olson RJ, Chisholm SW, Devereux R, Stahl DA (1990) Combination of 16S rRNA-targeted oligonucleotide probes with flow cytometry for analyzing mixed microbial populations. Appl Environ Microbiol 56(6):1919–1925
Amann R, Snaidr J, Wagner M, Ludwig W, Schleifer KH (1996) In situ visualization of high genetic diversity in a natural microbial community. J Bacteriol 178(12):3496–3500
APHA (American Public Health Association) (1998) Standard method for the examination of water and wastewater, 19th edn. American Public Health Association, Washington DC
Araújo MFF, Godinho MJL (2008) Seasonal and spatial distribution of bacterioplankton in a fluvial-lagunar system of a tropical region: density, biomass, cellular volume and morphologic variation. Braz Arch Biol Technol 51(1):203–212, ISSN 1516–8913
Bonadonna L, Cataldo C, Semproni M (2007) Comparison of methods and confirmation tests for the recovery Escherichia coli in water. Desalination 213(1–3):18–23
Bouvy M, Arfi R, Bernard C, Carré C, Got P, Pagano M, Troussellier M (2010) Estuarine microbial community characteristics as indicators of human-induced changes (Senegal River, West Africa). Estuar Coast Shelf Sci 87(6):573–582
Bu H, Meng W, Zhang Y, Wan J (2014) Relationships between land use patterns and water quality in the Taizi River basin. Chin Ecol Indic 41:187–197
Daly E, Kolotelo P, Schang C, Osborne CA, Coleman R, Deletic A, McCarthy DT (2013) Escherichia coli concentrations and loads in an urbanised catchment: the Yarra River, Australia. J Hydrol 497:51–61
Directive 2006/7/EC of the European Parliament and of the Council of 15 February 2006 concerning the management of bathing water quality. Off J Eur Commun L64: 37–51
Donderski W, Wilk I (2002a) Bacteriological studies of water and bottom sediments of the Vistula River between Wyszogród and Toruń. Pol J Environ Stud 11(1):33–40
Donderski W, Wilk I (2002b) The sanitary state of water in the River Vistula between Wyszogród and Toruń. Pol J Environ Stud 11(5):509–515
Economou V, Gousia P, Kansouzidou A, Sakkas H, Karanis P, Papadopoulou C (2013) Prevalence, antimicrobial resistance and relation to indicator and pathogenic microorganisms of Salmonella enterica isolated from surface waters within an agricultural landscape. Int J Hyg Environ Health 216(4):435–444
Edge TA, Droppo I, El-Shaarawi A, Gannon V, Hewitt M, Kent R, Khan I, Koning W, Lapen D, Marcogliese D, Marvin C, Miller J, Neumann N, Phillips R, Robertson W, Schreier H, Shtepani I, Topp E, van Bochove E (2009) An evaluation of Escherichia coli as a potential agri-environmental waterborne pathogen standard. Environment Canada, Gatineau, Quebec, Synthesis report 14. National Agri- Environmental Standards Initiative, p 48
Finney M, Smullen J, Foster HA, Brokx S, Storey DM (2003) Evaluation of chromocult coliform agar for the detection and enumeration of Enterobacteriaceae from faecal samples from healthy subjects. J Microbiol Methods 54(3):353–358
Friedrich U, Van Langenhove H, Altendorf K, Lipski A (2003) Microbial community and physicochemical analysis of an industrial waste gas biofilter and design of 16S rRNA-targeting oligonucleotide probes. Environ Microbiol 5(3):183–201
Garcia-Arminsen T, Servais P (2004) Enumeration of viable E. coli in rivers and wastewaters by fluorescent in situ hybridization. J Microbiol Method 58:269–279
Glińska-Lewczuk K (2006) Effect of land use and lake presence on chemical diversity of the Lyna river system. Pol J Environ Stud 15(2):259–269
Glińska-Lewczuk K, Burandt P (2011) Effect of river straightening on the hydrochemical properties of floodplain lakes: observations from the Łyna and Drwęca Rivers, N Poland. Ecol Eng 37:786–795
Gołaś I, Zmysłowska I, Harnisz M, Korzekwa K, Skowrońska A, Teodorowicz M, Górniak D, Gros M, Brzozowa S (2008a) Nitrogen cycle bacteria in the waters of the Drwęca River. Pol J Environ Stud 17(2):215–225
Gołaś I, Zmysłowska I, Harnisz M, Korzekwa K, Skowrońska A, Teodorowicz M, Górniak D, Dudziec E (2008b) Anthropogenic impact on quantitative differentiation of nitrogen cycling bacteria in waters of the River Drwęca. Pol J Nat Sci 23(3):667–680
Gołaś I, Korzekwa K, Harnisz M, Zmysłowska I, Teodorowicz M, Terech-Majewska E, Rodziewicz W, Bieńkowska M (2009) Influence of fishery management and environmental factors on occurrence of heterotrophic, hemolytic and mesophilic bacteria and Aeromonas hydrophila in waters of Drwęca River, Poland. Arch Environ Protect 35(2):27–40
Gotkowska-Płachta A, Niewolak S, Korzeniewska E (2005) Pollution degree and sanitary state indicator bacteria as the indicators of the purity of Lake Hańcza waters. Arch Environ Protect 31(2):53–68
Gotkowska-Płachta A, Filipkowska Z, Korzeniewska E, Janczukowicz W, Dixon B, Gołaś I, Szwalgin D (2013) Airborne microorganisms emitted from wastewater treatment plant treating domestic wastewater and meat processing industry wastes. CLEAN Soil Air Water 41(5):429–436
Haller L, Pote’ J, Loizeau J-L, Wildi W (2009) Distribution and survival of faecal indicator bacteria in the sediments of the Bay of Vidy, Lake Geneva, Switzerland. Ecol Indic 9:540–547
Harnisz M (2013) Total resistance of native bacteria as an indicator of changes in the water environment. Environ Pollut 174:85–92
Harnisz M, Gołaś I, Pietruk M (2011) Tetracycline-resistant bacteria as indicators of antimicrobial resistance in protected waters—the example of the Drwęca River nature reserve (Poland). Ecol Indic 11:663–668
Hatt BE, Fletcher TD, Walsh CJ, Taylor SL (2004) The influence of urban density and drainage infrastructure on the concentrations and loads of pollutants in small streams. Environ Manag 34:112–124
Hermanowicz W, Dożańska W, Dojlido J, Koziorowski B (1999) Physicochemical methods of water and wastewater examination. (in Polish). Arkady, Warsaw
Huachang H, Jianwen Q, Liang Y (2010) Environmental factors influencing the distribution of total and fecal coliform bacteria in six water storage reservoirs in the Pearl River Delta Region. Chin J Environ Sci 22(5):663–668
Juhna T, Birzniece D, Rubulis J (2007) Effect of phosphorus on survival of Escherichia coli in drinking water biofilms. Appl Environ Microbiol 73(11):3755–3758
Kacar A (2011) Analysis of spatial and temporal variation in the levels of microbial fecal indicators in the major rivers flowing into the Aegean Sea, Turkey. Ecol Indic 11:1360–1365
Kay D, Edwards AC, Ferrier RC, Francis C, Kay C, Rushby L, Watkins J, McDonald AT, Wyer M, Crowther J, Wilkinson J (2007) Catchment microbial dynamics: the emergence of a research agenda. Prog Phys Geogr 31(1):59–76
Korzeniewska E, Harnisz M (2012) Culture-dependent and culture-independent methods in evaluation of emission of Enterobacteriaceae from sewage to the air and surface water. Water Air Soil Pollut 223:4039–4046
Korzeniewska E, Harnisz M (2013) Extended-spectrum beta-lactamase (ESBL)-positive Enterobacteriaceae in municipal sewage and their emission to the environment. J Environ Manag 128:904–911
Korzeniewska E, Korzeniewska A, Harnisz M (2013) Antibiotic resistant Escherichia coli in hospital and municipal sewage and their emission to the environment. Ecotoxicol Environ Saf 91:96–102
Lew S, Lew M, Mieszczyński T, Szarek J (2010) Selected fluorescent techniques for identification of the physiological state of individual water and soil bacterial cells—review. Folia Microbiol 55(2):107–118
Loy A, Maixner F, Wagner M, Horn M (2007) ProbeBase—an online resource for rRNA-targeted oligonucleotide probes: new features 2007. Nucleic Acids Res 3(1):00–804
Łuczkiewicz A, Felis E, Ziembińska A, Gnida A, Kotlarska E, Olańczuk-Neyman K, Surmacz-Górska J (2013) Resistance of Escherichia coli and Enterococcus spp. to selected antimicrobial agents present in municipal wastewater. J Water Health 11(4):600–612
Neef A, Amann R, Schleifer KH (1995) Detection of microbial cells in aerosols using nucleic acid probes. Syst Appl Microbiol 18(1):113–122
Nnane DE, Ebdon JE, Taylor HD (2011) Integrated analysis of water quality parameters for cost-effective faecal pollution management in river catchments. Water Res 45(6):2235–2246
Okeke BC, Thomson MS, Moss EM (2011) Occurrence, molecular characterization and antibiogram of water quality indicator bacteria in river water serving a water treatment plant. Sci Total Environ 409(23):4979–4985
Olapade OA, Weage EA (2010) Comparison of fecal indicator bacterial populations in surface waters of the Kalamazoo River, USA. Microbes Environ 25(1):41–44
Oliver DM, Fish RD, Hodgson CJ, Heathwaite AL, Chadwick DR, Winter M (2009) A cross-disciplinary toolkit to assess the risk of faecal indicator loss from grassland farm systems to surface waters. Agric Ecosyst Environ 129(4):401–412
Pernthaler J, Glöckner FO, Schönhuber W, Amann R (2001) Fluorescence in situ hybridization with rRNA-targeted oligonucleotide probes. In: J Paul (ed), London: Academic Press Ltd. Methods in Microbiology 30: 207–226
Rompré A, Servais P, Baudart J, De Roubin MR, Laurent P (2002) Methods of detection and enumeration of coliforms in drinking water a review. J Microbiol Methods 49(1):31–54
Rowan NJ (2004) Viable but non-culturable forms of food and waterborne bacteria: Quo vadis? Trends Food Sci Technol 15:462–467
Savichtcheva O, Okabe S (2006) Alternative indicators of fecal pollution: relations with pathogens and conventional indicators, current methodologies for direct pathogen monitoring and future application perspectives. Water Res 40(13):2463–2476
Servais P, Garcia-Armisen T, George I, Billen G (2007) Fecal bacteria in the rivers of the Seine drainage network (France): sources, fate and modeling. Sci Total Environ 375(1–3):152–167
Shah AH, Abdelzaher AM, Phillips M, Hernandez R, Solo-Gabriele HM, Kish J, Scorzetti G, Fell JW, Diaz MR, Scott TM, Lukasik J, Harwood VJ, McQuaig S, Sinigalliano CD, Gidle ML, Wanless D, Ager A, Lui J, Stewart JR, Plano LRW, Fleming LE (2011) Indicator microbes correlate with pathogenic bacteria, yeasts and helminthes in sand at a subtropical recreational beach site. J Appl Microbiol 110(6):1571–1583
Stanisz A (2006) A straightforward course in statistics based on the STATISTICA PL program as applied in medicine. Volume Basic statistics . (In Polish). StatSoft Poland. Cracow, 2006. ISBN 83-88724-18-5
Tiquia SM (2010) Metabolic diversity of the heterotrophic microorganisms and potential link to pollution of the Rouge River. Environ Pollut 158(5):1435–1443
Tryland I, Surman S, Berg JD (2002) Monitoring faecal contamination of the Thames estuary using semiautomated early warning system. Water Sci Technol 46:25–31
Wallner G, Amann R, Beisker W (1993) Optimizing fluorescent in situ hybridization with rRNA-targeted oligonucleotide probes for flow cytometric identification of microorganisms. Cytometry 14(2):136–143
WFD, (2000) Directive 2000/60/EC of the European Parliament and of the Council of 23 October 2000 establishing a framework for Community action in the field of water policy. J Eur Union
Wilkes G, Edge T, Gannon V, Jokinen C, Lyautey E, Medeiros D, Neumann N, Ruecker N, Topp E, Lapen DR (2009) Seasonal relationships among indicator bacteria, pathogenic bacteria, Cryptosporidium oocysts, Giardia cysts, and hydrological indices for surface waters within an agricultural landscape. Water Res 43(8):2209–2223
Wilkes G, Edge TA, Gannon VPJ, Jokinen C, Lyautey E, Neumann NF, Ruecker N, Scott A, Sunohara M, Topp E, Lapen DR (2011) Associations among pathogenic bacteria, parasites, and environmental and land use factors in multiple mixed-use watersheds. Water Res 45(18):5807–5825
Zhu X, Wang JD, Solo-Gabriele HM, Fleming LE (2011) A water quality modeling study of non-point sources at recreational marine beaches. Water Res 45(9):2985–2995
Acknowledgments
This study was supported by grants No. 528-0807-0806 and No. 1010.0804 from the Ministry of Science and Higher Education (Poland).
Conflict of interest
The authors declare that they have no conflict of interest.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Additional information
Responsible editor: Philippe Garrigues
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Gotkowska-Płachta, A., Gołaś, I., Korzeniewska, E. et al. Evaluation of the distribution of fecal indicator bacteria in a river system depending on different types of land use in the southern watershed of the Baltic Sea. Environ Sci Pollut Res 23, 4073–4085 (2016). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11356-015-4442-6
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11356-015-4442-6