Abstract
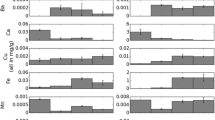
Extensive uranium mining in the former German Democratic Republic (GDR) in eastern Thuringia and Saxony took place during the period of 1946–1990. During mining activities, pelitic sediments rich in organic carbon and uranium were processed and exposed to oxygen. Subsequent pyrite oxidation and acidic leaching lead to partial contamination of the area with heavy metals and acid mine drainage (AMD) even few years after completion of remediation. One of those areas is the former heap Gessen (Ronneburg, Germany) were the residual contamination can be found 10 m under the base of the former heap containing partly permeable drainage channels. Actually, in such a system, a rapid but locally restricted mineralization of Mn oxides takes place under acidic conditions. This formation can be classified as a natural attenuation process as certain heavy metals, e.g., Cd (up to 6 μg/g), Ni (up to 311 μg/g), Co (up to 133 μg/g), and Zn (up to 104 μg/g) are bound to this phases. The secondary minerals occur as colored layers close to the shallow aquifer in glacial sediments and could be identified as birnessite and todorokite as Mn phase. The thermodynamic model shows that even small changes in the system are sufficient to shift either the pH or the Eh in the direction of stable Mn oxide phases in this acidic system. As a consequence of 9–15-year-long formation process (or even less), the supergene mineralization provides a cost-efficient contribution for remediation (natural attenuation) strategies of residual with heavy metals (e.g., Cd, Co, Ni, Zn) contaminated substrates.







Similar content being viewed by others
References
Ad-hoc AG Boden (2005) Pedological mapping guideline. E. Schweizbart’sche Verlagsbuchhandlung, (in German)
Akob DM et al (2014) Identification of Mn(II)-oxidizing bacteria from a low pH contaminated former uranium mine. Appl Environ Microbiol. doi:10.1128/AEM.01296-14
Bargar JR, Tebo BM, Bergmann U, Webb SW, Glatzel P (2005) Biotic and abiotic products of Mn(II) oxidation by spores of the marine Bacillus sp. strain SG-1. Am Mineral 90:143–154
Belzile N, Lebel J (1986) Capture of arsenic by pyrite in near-shore marine sediments. Chem Geol 54:279–281
Blasius J (1995) Lehrbuch der analytischen und praparativen anorganischen Chemie. S. Hirzel Verlag, Stuttgart-Leipzig, Germany (in German)
Burkhardt EM, Meißner S, Merten D, Svatos A, Büchel G, Küsel K (2009) Heavy metal retention and microbial activities in geochemical barriers formed in glacial sediments subjacent to a former uranium mining leaching heap. Chem Erde 69:21–34
Carlsson E, Büchel G (2005) Screening of residual contamination at a former uranium heap leaching site, Thuringia, Germany. Chem Erde 65:75–95
Cidu R, Frau F, Da Pelo S (2011) Drainage at abondoned mine sites: natural attenuation of contaminants in different seasons. Mine Water Environ 30:113–126
Diem D, Stumm W (1984) Is dissolved Mn2+ being oxidized by O2 in absense of Mn-bacteria or surface catalysts? Geochim Cosmochim Acta 48:1571–1573
DIN 14688-1 (2002) Geotechnical investigation and testing - Identification and classification of soil - Part 1: Identification and description
DIN 19683-13 (1973) Determination of matrix and pore proportions in inorganic soils (in German)
DIN 19683-4 (1973) Determination of the water content in soil (in German)
DIN 19683-5 (1973) Determination of soil water tension (in German)
DIN 19683-9 (1998) Determination of water permeability in water saturated soil sampling rings (in German)
DIN ISO 11277 (2002) Determination of particle size distribution in inorganic soil (in German)
Dong DM, Nelson YM, Lion LW, Shuler ML, Ghiorse WC (2000) Adsorption of Pb and Cd onto metal oxides and organic material in natural surface coatings as determined by selective extractions: new evidence for the importance of Mn and Fe oxides. Water Res 34:427–436
Downs RT, Hall-Wallace M (2003) The american mineralogist crystal structure database. Am Mineral 88:247–250
Eißmann L (1997) The quarternary ice age in Saxony and northeastern Thuringia. Altenburger Naturwissenschaftliche Forschungen, Leipzig (Germany) 8:1–98 (in German)
Elderfield H, Hawkesworth CJ, Greaves MJ, Calvert SE (1981) Rare earth element geochemistry of oceanic ferromanganese nodules and associated sediments. Geochim Cosmochim Acta 45(4):513–528
Fengler HJ (2008) The open pit uranium mine Lichtenberg near Ronneburg—history, mining and geology. Beitr Geol Thüring 15:205–245 (in German)
Fuller C, Harvey J (2000) Reactive uptake of trace metals in the hyporheic zone of mining-contaminated stream, Pinal creek, Arizona. Environ Sci Technol 34:1150–1155
Gabelmann JW (1971) Sedimentology and uranium prospecting. Sediment Geol 6:145–186
Gatzweiler R, Paul M, Fengler HJ, Schulze G (1997) Geology, mining and remediation of the eastern Thuringian uranium mining area. In: Lützner H, Seidel G (eds) Hauptversammlung DGG, Regionale Geologie von Mitteleuropa, Exkursionsführer., vol 3. Schriftenreihe Deutsche Geologische Gesellschaft pp 239–261 (in German)
Geological Society of America (1995) Munsell rock-color chart
Gramm-Osipov LM (1997) Precambrian to modern manganese mineralization: changes in ore type and depositional environment. In: Nicholson K, Hein JR, Bühn B, Dasgupta S (eds), vol 119. Geological Society Special Publication, pp 301–308
Grawunder A, Lonschinksi M, Merten D, Büchel G (2009) Distribution and bonding of residual contamination in glacial sediments at the former uranium mining leaching heap of Gessen/Thuringia, Germany. Chem Erde 69:5–19
Guggenheim S, Zhan W (1999) Crystal structures of two partially dehydrated chlorites: the “modified” chlorite structure. Am Mineral 84:1415–1421
Guinier A (1994) X-ray diffraction. In: Crystals, imperfect crystals, and amorphous bodies. Dover Publications, Mineola
Haack EA, Warren LA (2003) Biofilm hydrous manganese oxyhydroxides and metal dynamics in acid rock drainage. Environ Sci Technol 37:4138–4147
Hinz W, Lindner T, Schmidt H, Sänger HJ, Großmann T, Hoepfner U (1998) Revaluation of the areas within the framework of the project “Remediation and recultivation of the basement of the Gessenheap and the operation area of the leaching site Gessen” Part I Central section of the basement of the Gessenheap and the area around the drilling position 769/94. Wismut (in German)
Hoth N, Rammlmair D, Gerth J, Häfner F (2008) Natürliche Schadstoffminderungsprozesse an großräumigen Bergbaukippen/-halden und Flussauensedimenten. Empfehlungen zur Untersuchung und Bewertung der natürlichen Quelltermminimierung BMBF-Förderschwerpunkt KORA, Themenverbund 6 (TV 6) Bergbau und Sedimente (in German). 111
Huerta-Diaz MA, Morse JW (1992) Pyritization of trace metals in anoxic marine sediments. Geochim Cosmochim Acta 56:2681–2702
Ivarson KC, Heringa PK (1972) Oxidation of manganese by microorganisms in maganese deposits of Newfoundland soil. Can J Soil Sci 52:401–416
Jenne EA (1972) Controls on Mn, Fe, Co, Ni, Cu, and Zn concentrations in soils and water: the significant role of hydrous Mn and Fe oxides. Adv Chem Ser 73:337–387
Jönsson J, Lövgren L (2006) Precipitation of secondary Fe(III) minerals from acid mine drainage. Appl Geochem 21:437–445
Junta JL, Hochella MF Jr (1994) Manganese(II) oxidation at mineral surfaces: a microscopic and spectroscopic study. Geochim Cosmochim Acta 58:4985–4999
Kay J, Conklin MH, Fuller C, O’Day PA (2001) Process of nickel and cobalt uptake by a manganese oxide forming sediment in Pinal Creek, Globe Mining District, Arizona. Environ Sci Technol 35:4719–4725
Koitzsch R, Günther R (1990) Model for the perennial simulation of evaporation and soil moisture of agricultural land with and without vegetation. Arch Acker Pflanzenbau Bodenkd 34:803–810 (in German)
Komárek M, Vanĕk A, Ettler V (2013) Chemical stabilization of metals and arsenic in contaminated soils using oxides—a review. Environ Pollut 172:9–22
Kothe E, Bergmann H, Büchel G (2005) Molecular mechanisms in bio-geo-interactions: from a case study to general mechanism. Chem Erde 65(S1):7–27
Lange G, Dietel W, Schuster D, Motz H (1998) Geology of the uranium deposits Culmitzsch and Ronneburg. Lapis 7–8:65–77 (in German)
Learman DR, Wankel SD, Webb SM, Martinez N, Madden AS, Hansel CM (2011) Coupled biotic-abiotic Mn(ii) oxidation pathway mediates the formation and structural evolution of biogenic Mn oxides. Geochim Cosmochim Acta 75:6048–6063
Leutwein F (1951) Geochemical analsyis of the alumn and siliceous shale of Thuringia. Archiv Lagerstättenforsch 82:1–45 (in German)
Lopano CL, Heaney PJ, Post JE, Hanson J, Komarneni S (2007) Time-resolved structural analysis of K- and Ba-exchange reactions with synthetic Na-birnessite using synchroton X-ray difraction. Am Mineral 92:380–387
McKenzie RM (1972) The sorption of some heavy metals by the lower oxides of manganese. Geoderma 8:29–35
Mench M, Vangronsfeld J, Didier V, Clijsters H (1994) Evaluation of metal mobility, plant availability and immobilization by chemical agents in a limed-silty soil. Environ Pollut 86:279–286
Mirgorodsky D (2013) Field scaled phytoremediation experiments on a heavy metal and radionuclide contaminated site in the former uranium mining area Ronneburg (eastern Thuringia). Dissertation, Friedrich Schiller University
Morgan JJ, Stumm W (1965) The role of multivalent metal oxides in limnological transformations as exemplified by iron and manganese. Paper presented at the Proceedings of Second International Water Pollution Research Conference, Tokyo
Nagai T, Kagi H, Yamanaka T (2003) Variation of hydrogen bonded O…O distances in goethite at high pressure. Am Mineral 88:1423–1427
Nealson KH (2006) The manganese-oxidizing bacteria. Prokaryotes 5:222–231
Post JE, Bish DL (1988) Rietveld refinement of the todorokite structure. Am Mineral 73:861–869
Post JE, Veblen DR (1990) Crystal structure determinations of synthetic sodium, magnesium, and potassium birnessite using TEM and the Rietveld method. Am Mineral 75:477–489
Pracejus B, Bolton BR, Frakes LA (1988) Nature and development of supergene manganese deposits, Groote Eyelandt, northern territory, Australia. Ore Geol Rev 4:71–98
Richter D (1995) Results of methodology analysis for correction of the systematic measurement error of the Hellmann rain gauge. Ber Dtsch Wetterdienstes 194:93, in German
Rößler A (2001) Pedological acceptance documentation: Basement Gessenheap 24
Sappin-Didier V, Mench M, Gomez AN, Lambrot C (1997) Remediation of soils contaminated with metals. In: Iskandar IK, Adriano DC (eds) Science reviews, pp 85–98
Scheffer F, Schachtschabel P (2002) Textbook of soil science. Spektrum Heidelberg, Germany (in German)
Schippers A, Hallmann R, Wentzien S, Sand W (1995) Microbial diversity in uranium mine waste heaps. Appl Environ Microbiol 61:2930–2935
Šimůnek J, Šejna M, van Genuchten MT (1999) The HYDRUS-2D Software Package for Siumlating the Two-Dimensional Movement of Water, Heat, and Mulitple Solutes in Variably-Saturated Media. Version 2.0. U.S. Salinity Laboratory Agricultural Research Service
Stoppel D, Gundlach H (1983) Barite mineralisation and stratigraphy of the Upper Permian Rocks (Zechstein) in the Richelsdorfer Hills (Northeastern Hesse). ZDGG 134:247–268
Stumm W, Morgan JJ (1996) Aquatic chemistry: chemical equilibria and rates in natural waters. Wiley, New York
Szurowski H (1985) Catalog of rock properties (a short petrographical, mineralogical, geochemcial and pysico-mechanical characteristic of rocks in the area of Ronneburg). 165 S., Gera, unveröffentl. Betriebsunterlagen SDAG Wismut
Tan H, Zhang G, Heaney PJ, Webb SM, Burgos WD (2010) Characterization of mangaese oxide precipitation from Appalachian coal mine drainage treatment systems. Appl Geochem 25:389–399
Tani Y, Ohashi M, Miyata N, Seyama H, Iwahori K, Soma M (2004) Sorption of Co(II), Ni(II), and Zn(II) on biogenic manganese oxides produced by a Mn-oxidizing fungus, strain KR21-2. Environ Sci Health 39:2641–2660
Taylor SR, McLennan SM (1985) The Continental Crust: its composition and evolution. Blackwell, Oxford
Tebo BM et al (2004) Biogenic manganese oxides: properties and mechanisms of formation. Annu Rev Earth Planet Sci 32:287–328
Wismut (1994) Draft of the remediation strategie for the Ronneburg site
Wismut (2013) Wismut Datenbank AL.VIS Thüringen
Young LB, Harvey H (1992) The relative importance of manganese and iron oxide and organic matter in the sorption of trace metals by surficial lake sediments. Geochim Cosmochim Acta 56:1175–1186
Zeien H, Brümmer GW (1989) Chemcial extraction for determination of bonding structures of heavy metals in soils. Mitt Dtsch Bodenkundlichen Ges 59:505–515 (in German)
Acknowledgments
The authors thank the German Research Foundation (DFG) under the grant GRK 1257/1: “Alteration and element mobility at the microbe-mineral interface” for financial support. Further, we are grateful to I. Kamp and G. Weinzierl for total digestions and analytics, Daniel Mirgorodsky for providing groundwater data, and Matthias Händel for support during sampling and fruitful discussions. Finally, we thank the reviewers and associate editors for their helpful comments to improve the manuscript.
Conflict of interest
No conflict of interest.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Additional information
Responsible editor: Céline Guéguen
Electronic supplementary material
Below is the link to the electronic supplementary material.
Online Resource 1
(PDF 35 kb)
Online Resource 2
(PDF 9 kb)
Online Resource 3
(PDF 45 kb)
Online Resource 4
(PDF 78 kb)
Online Resource 5
(PDF 9 kb)
Online Resource 6
(PDF 16 kb)
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Schäffner, F., Merten, D., Pollok, K. et al. Fast formation of supergene Mn oxides/hydroxides under acidic conditions in the oxic/anoxic transition zone of a shallow aquifer. Environ Sci Pollut Res 22, 19362–19375 (2015). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11356-015-4404-z
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11356-015-4404-z