Abstract
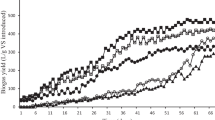
A novel pretreatment method combining ultrasonic with thermophilic bacteria (Geobacillus sp. G1) was employed to pretreat waste-activated sludge (WAS) for enhancing the WAS hydrolysis and subsequent volatile fatty acids (VFAs) production. The soluble protein and carbohydrate were mostly released from intracellular ultrasonic-assisted Geobacillus sp. G1 pretreatment, and accumulated to 917 ± 70 and 772 ± 89 mg COD/L, respectively, which were 2.53- and 2.62-fold higher than that obtained in control test. Excitation emission matrix (EEM) fluorescence spectroscopy revealed the highest fluorescence intensity (FI) of protein-like substances, indicating the synergistic effect of ultrasonic and Geobacillus sp. G1 pretreatments on WAS hydrolysis. The maximum VFAs accumulation was 4437 ± 15 mg COD/L obtained in ultrasonic-assisted Geobacillus sp. G1 pretreatment test. High-throughput pyrosequencing analysis investigated that the microbial communities were substantial determined by the pretreatment used. The hydrolysis enhancement was caused by an increase in extracellular enzymes, which was produced by one of dominant species Caloramator sp. The positive effect was well explained to the enhancement of WAS hydrolysis and final VFAs accumulation.






Similar content being viewed by others
References
Andersen CM, Bro R (2003) Practical aspects of PARAFAC modeling of fluorescence excitation-emission data. J Chemometr 17:200–215
Bougrier C, Delgenès JP, Carrère H (2007) Impacts of thermal pre-treatments on the semi-continuous anaerobic digestion of waste activated sludge. Biochem Eng J 34:20–27
Bro R, Kiers HAL (2003) A new efficient method for determining the number of components in PARAFAC models. J Chemometr 17:274–286
Cesaro A, Belgiorno V (2014) Pretreatment methods to improve anaerobic biodegradability of organic municipal solid waste fractions. Chem Eng J 240:24–37
Dean CR, Ward OP (1991) Nature of Escherichia coli cell lysis by culture supernatants of Bacillus species. Appl Environ Microbiol 57:1893–1898
Feng L, Chen Y, Zheng X (2009) Enhancement of waste activated sludge protein conversion and volatile fatty acids accumulation during waste activated sludge anaerobic fermentation by carbohydrate substrate addition: the effect of pH. Environ Sci Technol 43:4373–4380
Foladori P, Tamburini S, Bruni L (2010) Bacteria permeabilisation and disruption caused by sludge reduction technologies evaluated by flow cytometry. Water Res 44:4888–4899
Frølund B, Palmgren R, Keiding K, Nielsen PH (1996) Extraction of extracellular polymers from activated sludge using a cation exchange resin. Water Res 30:1749–1758
Héry M, Sanguin H, Perez Fabiel S, Lefebvre X, Vogel TM, Paul E, Alfenore S (2010) Monitoring of bacterial communities during low temperature thermal treatment of activated sludge combining DNA phylochip and respirometry techniques. Water Res 44:6133–6143
Hasegawa S, Shiota N, Katsura K, Akashi A (2000) Solubilization of organic sludge by thermophilic aerobic bacteria as a pretreatment for anaerobic digestion. Water Sci Technol 41:163–169
Hery M, Sanguin H, Perez Fabiel S, Lefebvre X, Vogel TM, Paul E, Alfenore S (2010) Monitoring of bacterial communities during low temperature thermal treatment of activated sludge combining DNA phylochip and respirometry techniques. Water Res 44:6133–6143
Hu K, Jiang J-Q, Zhao Q-L, Lee D-J, Wang K, Qiu W (2011) Conditioning of wastewater sludge using freezing and thawing: role of curing. Water Res 45:5969–5976
Jaenicke S, Ander C, Bekel T, Bisdorf R, Droge M, Gartemann KH, Junemann S, Kaiser O, Krause L, Tille F, Zakrzewski M, Puhler A, Schluter A, Goesmann A (2011) Comparative and joint analysis of two metagenomic datasets from a biogas fermenter obtained by 454-pyrosequencing. PLoS One 6:e14519
Ji Z, Chen G, Chen Y (2010) Effects of waste activated sludge and surfactant addition on primary sludge hydrolysis and short-chain fatty acids accumulation. Bioresource Technol 101:3457–3462
Jie W, Peng Y, Ren N, Li B (2014) Utilization of alkali-tolerant stains in fermentation of excess sludge. Bioresource Technol 157:52–59
Li X, Peng Y, Ren N, Li B, Chai T, Zhang L (2014) Effect of temperature on short chain fatty acids (SCFAs) accumulation and microbiological transformation in sludge alkaline fermentation with Ca(OH)2 adjustment. Water Res 61:34–45
Liu S, Zhu N, Li LY, Yuan H (2011a) Isolation, identification and utilization of thermophilic strains in aerobic digestion of sewage sludge. Water Res 45:5959–5968
Liu W, Huang S, Zhou A, Zhou G, Ren N, Wang A, Zhuang G (2012) Hydrogen generation in microbial electrolysis cell feeding with fermentation liquid of waste activated sludge. Int J Hydrogen Energ 37:13859–13864
Liu Z, Wang Y, He N, Huang J, Zhu K, Shao W, Wang H, Yuan W, Li Q (2011b) Optimization of polyhydroxybutyrate (PHB) production by excess activated sludge and microbial community analysis. J Hazard Mater 185:8–16
Lu L, Xing D, Liu B, Ren N (2012a) Enhanced hydrogen production from waste activated sludge by cascade utilization of organic matter in microbial electrolysis cells. Water Res 46:1015–1026
Lu L, Xing D, Ren N (2012b) Pyrosequencing reveals highly diverse microbial communities in microbial electrolysis cells involved in enhanced H2 production from waste activated sludge. Water Res 46:2425–2434
Luo J, Feng L, Zhang W, Li X, Chen H, Wang D, Chen Y (2014) Improved production of short-chain fatty acids from waste activated sludge driven by carbohydrate addition in continuous-flow reactors: Influence of SRT and temperature. Appl Energ 113:51–58
Luo K, Yang Q, X-m L, H-b C, Liu X, G-j Y, G-m Z (2013) Novel insights into enzymatic-enhanced anaerobic digestion of waste activated sludge by three-dimensional excitation and emission matrix fluorescence spectroscopy. Chemosphere 91:579–585
Pilli S, Bhunia P, Yan S, LeBlanc RJ, Tyagi RD, Surampalli RY (2011) Ultrasonic pretreatment of sludge: a review. Ultrason Sonochem 18:1–18
Riviere D, Desvignes V, Pelletier E, Chaussonnerie S, Guermazi S, Weissenbach J, Li T, Camacho P, Sghir A (2009) Towards the definition of a core of microorganisms involved in anaerobic digestion of sludge. ISME J 3:700–714
Salsabil MR, Prorot A, Casellas M, Dagot C (2009) Pre-treatment of activated sludge: effect of sonication on aerobic and anaerobic digestibility. Chem Eng J 148:327–335
Sanchez NP, Skeriotis AT, Miller CM (2013) Assessment of dissolved organic matter fluorescence PARAFAC components before and after coagulation–filtration in a full scale water treatment plant. Water Res 47:1679–1690
Sheng G-P, Yu H-Q (2006) Characterization of extracellular polymeric substances of aerobic and anaerobic sludge using three-dimensional excitation and emission matrix fluorescence spectroscopy. Water Res 40:1233–1239
Tan H-Q, Li T-T, Zhu C, Zhang X-Q, Wu M, Zhu X-F (2012a) Parabacteroides Chartae sp. nov., an obligately anaerobic species from wastewater of a paper mill. IJSEM 62:2613–2617
Tan R, Miyanaga K, Uy D, Tanji Y (2012b) Effect of heat-alkaline treatment as a pretreatment method on volatile fatty acid production and protein degradation in excess sludge, pure proteins and pure cultures. Bioresource Technol 118:390–398
Tang Y, Y-l Y, X-m L, Yang Q, D-b W, G-m Z (2011) The isolation, identification of sludge-lysing thermophilic bacteria and its utilization in solubilization for excess sludge. Environ Technol 33:961–966
Yang C, Zhou A, Hou Y, Zhang X, Guo Z, Wang A, Liu W (2014) Optimized culture condition for enhancing lytic performance of waste activated sludge by Geobacillus sp. G1. Water Sci Technol 70:200–208
Yang Q, Yi J, Luo K, Jing X, Li X, Liu Y, Zeng G (2013a) Improving disintegration and acidification of waste activated sludge by combined alkaline and microwave pretreatment. Process Saf Environ Prot 91:521–526
Yang S-S, Guo W-Q, Meng Z-H, Zhou X-J, Feng X-C, Zheng H-S, Liu B, Ren N-Q, Cui Y-S (2013b) Characterizing the fluorescent products of waste activated sludge in dissolved organic matter following ultrasound assisted ozone pretreatments. Bioresource Technol 131:560–563
Yu G-H, He P-J, Shao L-M, Zhu Y-S (2008) Extracellular proteins, polysaccharides and enzymes impact on sludge aerobic digestion after ultrasonic pretreatment. Water Res 42:1925–1934
Zhang Y, Zhang P, Guo J, Ma W, Xiao L (2013) Spectroscopic analysis and biodegradation potential study of dissolved organic matters in sewage sludge treated with high-pressure homogenization. Bioresource Technol 135:616–621
Zhang Y, Feng Y, Yu Q, Xu Z, Quan X (2014) Enhanced high-solids anaerobic digestion of waste activated sludge by the addition of scrap iron. Bioresource Technol 159:297–304
Zheng X, Su Y, Li X, Xiao N, Wang D, Chen Y (2013) Pyrosequencing reveals the key microorganisms involved in sludge alkaline fermentation for efficient short-chain fatty acids production. Environ Sci Technol 47:4262–4268
Zhou A, Yang C, Kong F, Chen Z, Ren N, Wang A (2013) Improving the short-chain fatty acids production of waste activated sludge stimulated by a bi-frequency ultrasonic pretreatment. J Environ Biol 34:381–389
Zhu L, Qi HY, Lv ML, Kong Y, Yu YW, Xu XY (2012) Component analysis of extracellular polymeric substances (EPS) during aerobic sludge granulation using FTIR and 3D-EEM technologies. Bioresource Technol 124:455–459
Acknowledgment
This research was supported by the National Science Foundation for Distinguished Young Scholars (Grant No. 51225802), by the Science Fund for Creative Research Groups (Grant No. 51121062), by the National Natural Science Foundation of China (Grant No. 51208496), by the National High-tech R&D Program of China (863 Program, Grant No. 2012AA051502), by the “Hundred Talents Program” of the Chinese Academy of Sciences, by the Heilongjiang Science Foundation for Distinguished Young Scholars (Grant No. JC201003), and by the Chinese Academy of Sciences (135 Project, Grant No. YSW2013B06).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding authors
Additional information
Responsible editor: Gerald Thouand
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Yang, C., Zhou, A., He, Z. et al. Effects of ultrasonic-assisted thermophilic bacteria pretreatment on hydrolysis, acidification, and microbial communities in waste-activated sludge fermentation process. Environ Sci Pollut Res 22, 9100–9109 (2015). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11356-014-3985-2
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11356-014-3985-2