Abstract
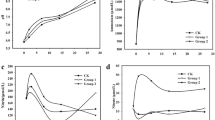
The biological reaction process of sulfur in biofilms and sediments causes serious problems of corrosion and odor in sewage systems. This study aims to reveal the distribution and shift of microbial diversity that survives inside the sediment in response to surrounding changes in sewage systems. The successions of microbial community were compared via denaturing gradient gel electrophoresis and by constructing phylogenetic trees via maximum likelihood method. The results indicated that the shift of microbial diversity is not significant along the vertical layer inside the sediment. The influences of sediment accumulation time on the shift in microbial diversity are evident, particularly with the switch of the accumulation stage. Implementing a control strategy for oxygen injection and nitrate addition evidently inhibits and stimulates some dominant sulfate-reducing bacterial strains in the sediment. The diversity in the total bacteria is positively related with ORP, dissolved oxygen, and sulfide concentration.





Similar content being viewed by others
References
Acinas SG, Sarma-Rupavtarm R, Klepac-Ceraj V, Polz M (2005) PCR-induced sequence artifacts and bias: Insights from comparison of two 16S rRNA clone libraries constructed from the same sample. Appl Environ Microbiol 71(12):8966–8969
Chen WM, Tseng ZJ, Lee KS, Chang JS (2005) Fermentative hydrogen production with Clostridium butyricum CGS5 isolated from anaerobic sewage sludge. Intern J of Hydr Energy 35(10):1063–1070
Dong XL, Reddy GB (2010) Soil bacterial communities in constructed wetlands treated with swine wastewater using PCR-DGGE technique. Biores Tech 101(4):1175–1182
Foti M, Sorokin DY, Lomans B, Mussman M, Zacharova EE, Pimenov NV, Kuenen JG, Muyzer G (2007) Diversity, activity and abundance of sulfate-reducing racteria in saline and hypersaline soda lakes. Appl and Environ Microb 73(7):2093–2100
Garcia-de-Lomas J, Corzo A, Portillo C, Gonzalez JM, Andrades JA, Saiz-Jimenez C, Garcia-Robledo E (2007) Nitrate stimulation of indigenous nitrate reducting sulfide oxidising bacterial community in wastewater anaerobic biofilms. Wat Res 41(14):3121–3131
Guan J, Xia LP, Wang LY, Liu JF, Gu JD, Mu BZ (2013) Diversity and distribution of sulfate-reducing bacteria in four petroleum reservoirs detected by using 16S rRNA and dsrAB genes. Internat Biodeter and Biodeg 76:58–66
Gutierrez O, Mohanakrishnan J, Sharma KR, Meyer RL, Keller J, Yuan Z (2008) Evaluation of oxygen injection as a means of controlling sulfide production in a sewer system. Wat Res 42(17):4549–4561
Hiibel SR, Pereyra LP, Breazeal MVR, Reisman DJ, Reardon KF, Pruden A (2010) Effect of organic substrate on the microbial community structure in pilot-scale sulfate-reducing biochemical reactors treating mine drainage. Environ Eng Sci 28(8):563–572
Jiang GM, Keating A, Corrie S, O′halloran K, Nguyen L, Yuan Z (2013) Dosing free nitrous acid for sulfide control in sewers: results of field trials in Australia. Wat Res 47(13):4331–4339
Jiang G, Keller J, Bond PL (2014a) Determining the long-term effects of H2S concentration, relative humidity and air temperature on concrete sewer corrosion. Wat Res 65(15):157–169
Jiang G, Wightman E, Donose BC, Yuan Z, Bond PL, Keller J (2014b) The role of iron in sulfide induced corrosion of sewer concrete. Wat Res 49(1):166–174
Jorge WSD, Randy PR, Brandon I, Vicente GA, Jarissa G, John S, James W (2011) Molecular survey of concrete sewer biofilm microbial communities. Biofouling 27(9):993–1001
Liu WT, Chan OC, Fang HHP (2002) Microbial community dynamics during start-up of acidogenic anaerobic reactors. Wat Res 36(13):3203–3210
Marques JM, Almeida FP, Lins U, Seldin L, Korenblum E (2012) Nitrate treatment effects on bacterial community biofilm formed on carbon steel in produced water stirred tank bioreactor. World Journal of Microbiol and Biotech 28(6):2355–2363
Mizuno K, Morishita Y, Ando A, Tsuchiya N, Hirata M, Tanaka K (2012) Genus-specific and phase-dependent effects of nitrate on a sulfate-reducing bacteria community as revealed by dsrB-based DGGE analyses of wastewater reactors. World Journal of Microbiol and Biotech 28(2):677–686
Nielsen AH, Vollertsen J, Hvitved-Jacobsen T (2003) Determination of kinetics and stoichiometry of chemical sulfide oxidation in wastewater of sewer networks. Environ Sci and Tech 37(17):3853–3858
Okabe S, Itoh T, Satoh H, Watanabe Y (1999) Analyses of spatial distributions of sulfate-reducing bacteria and their activity in aerobic wastewater biofilms. Appl Environ Microbiol 65(11):5107–5116
Ogino A, Koshikawa H, Nakahara T, Uchiyama H (2001) Succession of microbial communities during a biostimulation process as evaluated by DGGE and clone library analyses. Jour of Appl Microbiol 91(4):625–635
Ren N, Xing D, Rittmann BE, Zhao L, Xie T, Zhao X (2007) Microbial community structure of ethanol type fermentation in bio-hydrogen production. Environ Microbiol 9(5):1112–1125
Saraiva IH, Newman DK, Louro RO (2012) Functional Characterization of the FoxE Iron Oxidoreductase from the photoferrotroph Rhodobacter ferrooxidans SW2. Jour of Biolog Chem 287:25541–25548
Vishnivetskaya TA, Mosher JJ, Palumbo AV, Yang ZK, Podar M, Brown SD, Drake MM, Brandt CC, Southworth GR, Drake MM, Brandt CC, Elias DA (2011) Mercury and other heavy metals influence bacterial community structure in contaminated Tennessee streams. Appl and Environ Microbiol 77(1):302–311
Wang J, Shi M, Lu H, Wu D, Shao MF, Zhang T, Ekama GA, Loosdrecht MCM, Chen GH (2011) Microbial community of sulfate-reducing up-flow sludge bed in the SANI process for saline sewage treatment. Appl Microbiol Biotech 90(6):2015–2025
Ye L, Shao MF, Zhang T, Tong AH, Lok S (2011) Analysis of the bacterial community in a laboratory-scale nitrification reactor and a wastewater treatment plant by 454-pyrosequencing. Wat Res 45(15):4390–4398
Zhang L, Schryver PD, Gusseme BD, Muynck WD, Boon N, Verstraete W (2008) Chemical and biological technologies for hydrogen sulfide emission control in sewer systems. Wat Res 42(1–2):1–12
Acknowledgments
This research was supported by the National Natural Science Foundation of China (No. 50908131), Major Science and Technology Program for Water Pollution Control and Treatment of China (No. 2011ZX07301-002), State Environmental Protection Key Laboratory of Microorganism Application and Risk Control Open Fund (No. MARC2012D003), and Tsinghua University Initiative Scientific Research Program (No. 20121087922).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Additional information
Responsible editor: Philippe Garrigues
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Liu, Y., Dong, Q., Wu, C. et al. Study of the succession of microbial communities for sulfur cycle response to ecological factors change in sediment of sewage system. Environ Sci Pollut Res 22, 9250–9259 (2015). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11356-014-3934-0
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11356-014-3934-0