Abstract
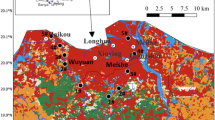
With rapid response to environmental changes, phytoplankton communities have been used as a favorable bioindicator to evaluate environmental stress and anthropogenic impacts in aquatic ecosystems. The feasibility for their community-based bioassessment was studied in a mid-subtropical canal (Tiesha River), southern China, during a 1-year cycle (November 2009–December 2010). Samples were monthly collected at four sampling stations within a contamination gradient. Environmental variables, such as water temperature, dissolved oxygen (DO), chemical oxygen demand (COD), biological oxygen demand (BOD5), total phosphorus (TP), and total nitrogen (TN), were measured synchronously for comparison with biotic parameters. The phytoplankton community structures showed a significant difference among four stations. The spatial variation in abundance was significantly correlated with the changes in environmental variables, especially TN, TP, and COD. Four dominant species (Aulacoseira granulata, Leptocylindrus danicus, Oscillatoria tenuis, and Radiococcus nimbatus) were significantly correlated with nutrients, while the species richness index represented a significant correlation with BOD5. The phytoplankton-based Saprobien indices could not reveal the spatial variation in water quality status although may reflect water pollution levels (from β- to α-mesosaprobic zone) in the canal system. It is suggested that phytoplankton communities might be used as a potentially robust bioindicator for discriminating environmental quality status in mid-tropical canal systems.



Similar content being viewed by others
References
Aktan Y (2011) Large-scale patterns in summer surface water phytoplankton (except picophytoplankton) in the Eastern Mediterranean. Estuar Coast Shelf Sci 91:551–558
Anderson MJ, Gorleyn RN, Clarke KR (2008) PERMANOVA+ for PRIMER guide to software and statistical methods. PRIMER-E Ltd, Plymouth
APHA (American Public Health Association) (1989) Standard methods for examinations of water and wastewater, 17th edn. APHA, Washington DC
Arhonditsis GB, Paerl HW, Valdes-Weaver LM, Stow CA, Steinberg LJ, Reckhow KH (2007) Application of Bayesian structural equation modeling for examining phytoplankton dynamics in the Neuse River Estuary (North Carolina, USA). Estuar Coast Shelf Sci 72:63–80
Cabecinha E, Cortes R, Cabral JA, Ferreira T, Lourenço M, Pardal A (2009) Multi-scale approach using phytoplankton as a first step towards the definition of the ecological status of reservoirs. Ecol Indic 9:240–255
Cairns J Jr, Lanza GR, Parker BC (1972) Pollution related to structural and functional changes in aquatic communities with emphasis on freshwater algal and protozoa. Proc Acad Nat Sci Phila 124:79–127
Clarke KR, Gorley RN (2006) User manual/tutorial. PRIMER-E Ltd., Plymouth
Hu HJ, Wei YX (2006) The freshwater algae of China: systematics, taxonomy and ecology. Science Press, Beijing, pp 1–1023 (in Chinese)
Huang L, Jian W, Song X, Huang X, Liu S, Qian P, Yin K, Wu M (2004) Species diversity and distribution for phytoplankton of the Pearl River estuary during rainy and dry seasons. Mar Pollut Bull 49:588–596
Hutchins MG, Johnson AC, Deflander-Vlandas A, Comber S, Posen P, Boorman D (2010) Which offers more scope to suppress river phytoplankton blooms: reducing nutrient pollution or riparian shading? Sci Total Environ 408:5065–5077
Ismael AA, Dorgham MM (2003) Ecological indices as a tool for assessing pollution in El-Dekhaila Harbour (Alexandria, Egypt). Oceanologia 45:121–131
Jiang Y, Xu H, Warren A (2014) Insights into discriminating environmental quality status based on a simplified taxonomic pool of ciliated protozoa in marine ecosystems. Sci Total Environ 468–469:663–670
Joy CM, Balakrishnan KP, Joseph A (1990) Effect of industrial discharges on the ecology of phytoplankton production in the river periyar (India). Water Res 24:787–796
Pantle K, Buck H (1955) Die biologische Überwachung der Gewässer und die Darstellung der Ergebnisse. gwf-Wasser/Abwasser 96:609–620
Qiu D, Huang L, Zhang J, Lin S (2010) Phytoplankton dynamics in and near the highly eutrophic Pear River Estuary, South China Sea. Cont Shelf Res 30:177–186
Rolland A, Bertrand F, Maumy M, Jacquet S (2009) Assessing phytoplankton structure and spatio-temporal dynamics in a freshwater ecosystem using a powerful multiway statistical analysis. Water Res 43:3155–3168
Shi X, Liu X, Liu G, Sun Z, Xu H (2012a) Application of phytoplankton communities for monitoring water quality in the Hangzhou section of Jing-Hang Canal, southern China. Fundam Appl Limnol 180:1–11
Shi X, Liu X, Liu G, Sun Z, Xu H (2012b) An approach to analyze spatial patterns of protozoan communities for assessing water quality in the Hangzhou section of Jinghang Grant Canal in China. Environ Sci Pollut Res 19:739–747
Tan X, Shi X, Liu G, Xu H, Nie P (2010) An approach to analyzing taxonomic patterns of protozoan communities for monitoring water quality in Songhua River, northeast China. Hydrobiologia 638:193–201
Xu H, Warren A, AL-Rasheid KAS, Zhu M, Song W (2010a) Planktonic protist communities in semi-enclosed mariculture waters: temporal dynamics of functional groups and their responses to environmental conditions. Acta Oceanol Sin 29:106–115
Xu H, Min GS, Choi JK, Al-Rasheid KAS, Lin X, Zhu M (2010b) Temporal dynamics of phytoplankton communities in a semi-enclosed mariculture pond and their responses to environmental factor. Chin J Oceanol Limnol 28:295–303
Xu H, Zhang W, Jiang Y, Yang EJ (2014) Use of biofilm-dwelling ciliate communities to determine environmental quality status of coastal waters. Sci Total Environ 470–471:511–518
Young J, Watt A, Nowichi P (2005) Towards sustainable land use: identifying and managing the conflicts between human activities and biodiversity conservation Europe. Conserv Biol 14:1641–1661
Zelinka M, Marvan P (1961) Zur Prazisierung der biologischen Klassifikation des Reinheit fliessender Gewässer. Arch Hydrobiol 57:389–407
Acknowledgments
This work was supported by the National Natural Science Foundation of China (31272262, 31071880, and 41076089), Zhejiang Provincial Natural Science Foundation, and Zhejiang Key Scientific & Technological Innovation Team Project (Y3100128, 2010R50039-20), Hangzhou Key Laboratory for Animal Adaptation and Evolution (20100333T05), Hangzhou Normal University.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding authors
Additional information
Responsible editor: Philippe Garrigues
Electronic supplementary material
Below is the link to the electronic supplementary material.
Table S1
(DOC 661 kb)
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Shi, X., Sun, Z., Liu, G. et al. Insights into community-based discrimination of water quality status using an annual pool of phytoplankton in mid-subtropical canal systems. Environ Sci Pollut Res 22, 1199–1206 (2015). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11356-014-3391-9
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11356-014-3391-9