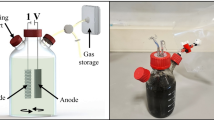
Abstract
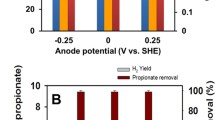
A methane-producing microbial electrolysis cell (MEC) was continuously fed at the anode with a synthetic solution of soluble organic compounds simulating the composition of the soluble fraction of a municipal wastewater. The MEC performance was assessed at different anode potentials in terms of chemical oxygen demand (COD) removal efficiency, methane production, and energy efficiency. As a main result, about 72–80 % of the removed substrate was converted into current at the anode, and about 84–86 % of the current was converted into methane at the cathode. Moreover, even though both COD removed and methane production slightly decreased as the applied anode potential decreased, the energy efficiency (i.e., the energy recovered as methane with respect to the energy input into the system) increased from 54 to 63 %. Denaturing gradient gel electrophoresis (DGGE) analyses revealed a high diversity in the anodic bacterial community with the presence of both fermentative (Proteiniphilum acetatigenes and Petrimonas sulphurifila) and aerobic (Rhodococcus qingshengii) microorganisms, whereas only two microorganisms (Methanobrevibacter arboriphilus and Methanosarcina mazei), both assignable to methanogens, were observed in the cathodic community.





Similar content being viewed by others
References
Agler MT, Wrenn BA, Zinder SH, Angenent LT (2011) Waste to bioproduct conversion with undefined mixed cultures: the carboxylate platform. Trends Biotechnol 29(2):70–78. doi:10.1016/j.tibtech.2010.11.006
Altschul SF, Madden TL, Schaffer AA, Zhang J, Zhang Z, Miller W, Lipman DJ (1997) Gapped BLAST and PSI-BLAST: a new generation of protein database search programs. Nucleic Acids Res 25(17):3389–3402
APHA (1995) Standard methods for the examination of water and wastewater. American public health association, Washington, DC
Aulenta F, Gossett JM, Papini MP, Rossetti S, Majone M (2005) Comparative study of methanol, butyrate, and hydrogen as electron donors for long-term dechlorination of tetrachloroethene in mixed anerobic cultures. Biotechnol Bioeng 91(6):743–753. doi:10.1002/bit.20569
Balch WE, Fox GE, Magrum LJ, Woese CR, Wolfe RS (1979) Methanogens: reevaluation of a unique biological group. Microbiol Rev 43(2):260–296
Chen S, Dong X (2005) Proteiniphilum acetatigenes gen. nov., sp. nov., from a UASB reactor treating brewery wastewater. Int J Syst Evol Microbiol 55(Pt 6):2257–2261. doi:10.1099/ijs.0.63807-0
Cheng S, Xing D, Call DF, Logan BE (2009) Direct biological conversion of electrical current into methane by electromethanogenesis. Environ Sci Technol 43(10):3953–3958
Di Fabio S, Lampis S, Zanetti L, Cecchi F, Fatone F (2013) Role and characteristics of problematic biofilms within the removal and mobility of trace metals in a pilot-scale membrane bioreactor. Process Biochem 48(11):1757–1766
Freguia S (2010) Organics oxidation. In: Rabaey K, Angenent L, Schroder U, Keller J (eds) Bioelectrochemical systems. IWA publishing, London, pp 228–231
Freguia S, Rabaey K, Yuan Z, Keller J (2008) Syntrophic processes drive the conversion of glucose in microbial fuel cell anodes. Environ Sci Technol 42(21):7937–7943
Grabowski A, Tindall BJ, Bardin V, Blanchet D, Jeanthon C (2005) Petrimonas sulfuriphila gen. nov., sp. nov., a mesophilic fermentative bacterium isolated from a biodegraded oil reservoir. Int J Syst Evol Microbiol 55(3):1113–1121
Green DW, Perry RH (2008) Perry’s chemical engineers’ handbook, eighth ed. McGraw-Hill
Grosskopf R, Janssen PH, Liesack W (1998) Diversity and structure of the methanogenic community in anoxic rice paddy soil microcosms as examined by cultivation and direct 16S rRNA gene sequence retrieval. Appl Environ Microbiol 64(3):960–969
Kelly PT, He Z (2014) Nutrients removal and recovery in bioelectrochemical systems: a review. Bioresour Technol 153:351–360. doi:10.1016/j.biortech.2013.12.046
Kropf S, Heuer H, Gruning M, Smalla K (2004) Significance test for comparing complex microbial community fingerprints using pairwise similarity measures. J Microbiol Methods 57(2):187–195. doi:10.1016/j.mimet.2004.01.002
Lane DJ (1991) 16S/23S rRNA sequencing. Nucleic Acid Techniques in Bacterial Systematics. Wiley, Chichester
Lovley DR (2011) Powering microbes with electricity: direct electron transfer from electrodes to microbes. Environ Microbiol Rep 3(1):27–35
Ney U, Macario AJL, Conway de Macario E, Aivasidis A, Schoberth SM, Sahm H (1990) Quantitative microbiological analysis of bacterial community shifts in a high-rate anaerobic bioreactor treating sulfite evaporator condensate. Appl Environ Microbiol 56(8):2389–2398
Pant D, Van Bogaert G, Diels L, Vanbroekhoven K (2010) A review of the substrates used in microbial fuel cells (MFCs) for sustainable energy production. Bioresour Technol 101(6):1533–1543. doi:10.1016/j.biortech.2009.10.017
Pant D, Singh A, Van Bogaert G, Irving Olsen S, Singh Nigam P, Dielsa L, Vanbroekhovena K (2012) Bioelectrochemical systems (BES) for sustainable energy production and product recovery from organic wastes and industrial wastewaters. RSC Adv 2:1248–1263
Roest K, Heilig HG, Smidt H, de Vos WM, Stams AJ, Akkermans AD (2005) Community analysis of a full-scale anaerobic bioreactor treating paper mill wastewater. Syst Appl Microbiol 28(2):175–185. doi:10.1016/j.syapm.2004.10.006
Rosenbaum M, Aulenta F, Villano M, Angenent LT (2011) Cathodes as electron donors for microbial metabolism: which extracellular electron transfer mechanisms are involved? Bioresour Technol 102(1):324–333
Tamura K, Peterson D, Peterson N, Stecher G, Nei M, Kumar S (2011) MEGA5: molecular evolutionary genetics analysis using maximum likelihood, evolutionary distance, and maximum parsimony methods. Mol Biol Evol 28(10):2731–2739. doi:10.1093/molbev/msr121
Thompson JD, Gibson TJ, Plewniak F, Jeanmougin F, Higgins DG (1997) The CLUSTAL_X windows interface: flexible strategies for multiple sequence alignment aided by quality analysis tools. Nucleic Acids Res 25(24):4876–4882
Villano M, Aulenta F, Giuliano A, Ciucci C, Ferri T, Majone M (2010) Bioelectrochemical reduction of CO2 to CH4 via direct and indirect extracellular electron transfer by a hydrogenophilic methanogenic culture. Bioresour Technol 101:3085–3090
Villano M, Monaco G, Aulenta F, Majone M (2011) Electrochemically assisted methane production in a biofilm reactor. J Power Sources 196(22):9467–9472. doi:10.1016/j.jpowsour.2011.07.016
Villano M, Scardala S, Aulenta F, Majone M (2013) Carbon and nitrogen removal and enhanced methane production in a microbial electrolysis cell. Bioresour Technol 130:366–371
Xu JL, He J, Wang ZC, Wang K, Li WJ, Tang SK, Li SP (2007) Rhodococcus qingshengii sp. nov., a carbendazim-degrading bacterium. Int J Syst Evol Microbiol 57(Pt 12):2754–2757. doi:10.1099/ijs.0.65095-0
Zeikus JG (1977) The biology of methanogenic bacteria. Bacteriol Rev 41(2):514–541
Acknowledgments
This work was supported by the EU Routes Project (Contract No. 265156, FP7 2007-2013, THEME [ENV.2010.3.1.1-2] Innovative system solutions for municipal sludge treatment and management). The authors also thank Dr. Claudia Ralo (Universidade Nova de Lisboa) and Gianluca De Santis (University of Rome Sapienza) for the skillful assistance with the experimental work.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Additional information
Responsible editor: Gerald Thouand
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Zeppilli, M., Villano, M., Aulenta, F. et al. Effect of the anode feeding composition on the performance of a continuous-flow methane-producing microbial electrolysis cell. Environ Sci Pollut Res 22, 7349–7360 (2015). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11356-014-3158-3
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11356-014-3158-3