Abstract
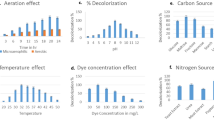
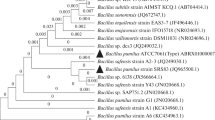
A new strain isolated from activated sludge and identified as Burkholderia vietnamiensis C09V was used to biodegrade crystal violet (CV) from aqueous solution. To understand the degradation pathways of CV, batch experiments showed that the degradation using B. vietnamiensis C09V significantly depended on conditions such as pH, initial dye concentration and media components, carbon and nitrogen sources. Acceleration in the biodegradation of CV was observed in presence of metal ions such as Cd and Mn. More than 98.86C of CV (30 mg l−1) was degraded within 42 h at pH 5 and 30 °C. The biodegradation kinetics of CV corresponded to the pseudo first-order rate model with a rate constant of 0.046 h−1. UV–visible and Fourier transform infrared spectroscopy (FTIR) were used to identify degradation metabolites. Which further confirmed by LC-MS analysis, indicating that CV was biodegraded to N,N-dimethylaminophenol and Michler’s ketone prior to these intermediates being further degraded. Finally, the ability of B. vietnamiensis C09V to remove CV in wastewater was demonstrated.







Similar content being viewed by others
References
Asad S, Amoozegar M, Pourbabaee A, Sarbolouki M, Dastgheib S (2007) Decolorization of textile azo dyes by newly isolated halophilic and halotolerant bacteria. Bioresour Technol 98:2082–2088
Ayed L, Chaieb K, Cheref A, Bakhrouf A (2010) Biodegradation and decolorization of triphenylmethane dyes by Staphylococcus epidermidis. Desalination 260:137–146
Bamforth S, Singleton I (2005) Bioremediation of polycyclic aromatic hydrocarbons: current knowledge and future directions. J Chem Technol Biotechnol 80:723–736
Cha C, Doerge D, Cerniglia C (2001) Biotransformation of malachite green by the fungus Cunninghamella elegans. Appl Environ Microbiol 67:4358–4365
Chen C, Kuo J, Cheng C, Huang Y, Ho I, Chung Y (2009) Biological decolorization of dye solution containing malachite green by Pandoraea pulmonicola YC32 using a batch and continuous system. J Hazard Mater 172:1439–1445
Chen CH, Chang CF, Ho CH, Tsai TL, Liu SM (2008) Biodegradation of crystalviolet by a Shewanella sp. NTOU1. Chemosphere 72:1712–1720
Clesceri LS., Greenberg AE, Eaton AD (eds.) (1999) Standard methods for the examination of water and wastewater, 20th edn. American Public Health Association, American Water Work Association, Water Environment Federation, Washington, DC. APHA-AWWA-WEF
Daneshvar N, Ayazloo M, Khataee A, Pourhassan M (2007) Biological decolorization of dye solution containing Malachite Green by microalgae Cosmarium sp. Bioresour Technol 98:1176–1182
Du LN, Zhao M, Li G, Xu FC, Chen WH, Zhao YH (2013) Biodegradation of malachite green by Micrococcus sp. strain BD15: biodegradation pathway and enzyme analysis. Int Biodeterior Biodegrad 78:108–116
Forgacs E, Cserha’ti T, Oros G (2004) Removal of synthetic dyes from wastewaters: a review. Environ Internl 30:953–971
Garg SK, Tripathi M, Singh SK, Tiwari JK (2012) Biodecolorization of textile dye effluent by Pseudomonas putida SKG-1 (MTCC 10510) under the conditions optimized for monoazo dye orange II color removal in simulated minimal salt medium Int. Biodet Biodegrad 74:24–35
Guo MR, Lin YM, Xu XP, Chen ZL (2010) Bioleaching of iron from kaolin using Fe(III)-reducing bacteria with various carbon nitrogen sources. Appl Clay Sci 48:379–383
Hatvani N, Mecs I (2002) Effect of the nutrient composition on dye decolorisation and extracellular enzyme production by Lentinus edodes on solid medium. Enzyme Microb Technol 30:381–386
Kapdan IK, Kargia F, McMullanb G, Marchant R (2000) Effect of environmental conditions on biological decolourization of textile dyestuff by C. versicolor. Enzyme Microb Technol 26:381–387
Kaushik P, Malik A (2009) Fungal dye decolourization: recent advances and future potential. Environ Int 35:127–141
Khehra MS, Saini HS, Sharma DK, Chadha BS, Chimni SS (2006) Biodegradation of azo dye CI acid red 88 by an anoxic–aerobic sequential bioreactor. Dyes Pigments 70:1–7
Kulkarni M, Chaudhari A (2007) Microbial remediation of nitro-aromatic compounds: an overview. J Environ Manage 85:496–512
Kumar A, Dewulf J, Luvsanjamba M, Langenhove HV (2008) Continuous operation of membrane bioreactor treating toluene vapors by Burkholderia vietnamiensis G4. Chem Eng J 140:193–200
Lin C, Gan L, Chen ZL (2010) Biodegradation of naphthalene by strain Bacillus fusiformis (BFN). J Hazard Mater 182:771–777
Margesin R, Schinner F (2001) Biodegradation and bioremediation of hydrocarbons in extreme environments. Appl Microbiol Biotechnol 56:650–663
Mellefont L, McMeekin T, Ross T (2008) Effect of relative inoculum concentration on Listeria monocytogenes growth in co-culture. Int J Food Microbiol 121:157–168
Mohan SV, Rao N, Sarma P (2007) Simulated acid azo dye (acid black 210) wastewater treatment by periodic discontinuous batch mode operation under anoxic–aerobic–anoxic microenvironment conditions. Ecol Eng 31:242–250
Murugesan K, Kim YM, Jeon JR, Chang YS (2009) Effect of metal ions on reactive dye decolorization by laccase from Ganoderma lucidum. J Hazard Mater 168:523–529
Nievas ML, Commendatore MG, Olivera NL, Esteves JL, Bucalá V (2006) Biodegradation of bilge waste from Patagonia with an indigenous microbial community. Bioresour Technol 97:2280–2290
Nostrand JV, Khijniak T, Neely B, Sattar M, Sowder A, Mills G, Bertsch P, Morris P (2007) Reduction of nickel and uranium toxicity and enhanced trichloroethylenedegradation to Burkholderia vietnamiensis PR1301 wit hydroxyapatite amendment. Environ Sci Technol 41:1877–1882
Noubactep C (2009) Characterizing the discoloration of methylene blue in Fe0/H2O systems. J Hazard Mater 166:79–87
Park K, Lee O, Jung H, Jeong J, Jeon Y, Hwang D, Lee C, Son H (2010) Rapid solubilization of insoluble phosphate by a novel environmental stress-tolerant Burkholderia vietnamiensis M6 isolated from ginseng rhizospheric soil. Appl Microbiol Biotechnol 86:947–955
Parshetti G, Kalme S, Saratale G, Govindwar S (2006) Biodegradation of malachite green by Kocuria rosea MTCC 1532. Acta Chim Slov 53:492–498
Sani RK, Peyton BM, Brown LT (2001) Copper induced inhibition of growth of Desulfovibrio desulfuricans G20: assessment of its toxicity and correlation with those of zinc and lead. Appl Environ Microbiol 67:4765–4772
Silveira E, Marques PP, Silva SS, Lima-Filho JL, Porto ALF, Tambourgi EB (2009) Selection of Pseudomonas for industrial textile dyes decolourization. Int Biodeterior Biodegrad 63:230–235
Telke A, Kalyani D, Jadhav J, Govindwar S (2008) Kinetics and mechanism of reactive red 141 degradation by a bacterial isolate Rhizobium radiobacter MTCC 8161. Acta Chim Slov 55:320–329
Yatome C, Yamada S, Ogawa T, Matsui M (1993) Degradation of crystal violet by Nocardia corallina. Appl Microbiol Biotechnol 38:565–569
Zavala ML, Funamizu N, Takakuwa T (2004) Temperature effect on aerobicbiodegradation of feces using sawdust as a matrix. Water Res 38:2406–2416
Acknowledgements
This research was supported by Fujian Provincial Development and Reform Commission.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Additional information
Responsible editor: Robert Duran
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Gan, L., Cheng, Y., Palanisami, T. et al. Pathways of reductive degradation of crystal violet in wastewater using free-strain Burkholderia vietnamiensis C09V. Environ Sci Pollut Res 21, 10339–10348 (2014). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11356-014-3037-y
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11356-014-3037-y