Abstract
Introduction
Meta-analyses across diverse independent studies provide improved confidence in results. However, within the context of metabolomic epidemiology, meta-analysis investigations are complicated by differences in study design, data acquisition, and other factors that may impact reproducibility.
Objective
The objective of this study was to identify maternal blood metabolites during pregnancy (> 24 gestational weeks) related to offspring body mass index (BMI) at age two years through a meta-analysis framework.
Methods
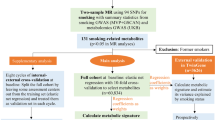
We used adjusted linear regression summary statistics from three cohorts (total N = 1012 mother–child pairs) participating in the NIH Environmental influences on Child Health Outcomes (ECHO) Program. We applied a random-effects meta-analysis framework to regression results and adjusted by false discovery rate (FDR) using the Benjamini–Hochberg procedure.
Results
Only 20 metabolites were detected in all three cohorts, with an additional 127 metabolites detected in two of three cohorts. Of these 147, 6 maternal metabolites were nominally associated (P < 0.05) with offspring BMI z-scores at age 2 years in a meta-analytic framework including at least two studies: arabinose (Coefmeta = 0.40 [95% CI 0.10,0.70], Pmeta = 9.7 × 10–3), guanidinoacetate (Coefmeta = − 0.28 [− 0.54, − 0.02], Pmeta = 0.033), 3-ureidopropionate (Coefmeta = 0.22 [0.017,0.41], Pmeta = 0.033), 1-methylhistidine (Coefmeta = − 0.18 [− 0.33, − 0.04], Pmeta = 0.011), serine (Coefmeta = − 0.18 [− 0.36, − 0.01], Pmeta = 0.034), and lysine (Coefmeta = − 0.16 [− 0.32, − 0.01], Pmeta = 0.044). No associations were robust to multiple testing correction.
Conclusions
Despite including three cohorts with large sample sizes (N > 100), we failed to identify significant metabolite associations after FDR correction. Our investigation demonstrates difficulties in applying epidemiological meta-analysis to clinical metabolomics, emphasizes challenges to reproducibility, and highlights the need for standardized best practices in metabolomic epidemiology.




Similar content being viewed by others
Data availability
Data sharing is not applicable in this study as no datasets were generated or analyzed during the current study. Only summary statistics were utilized.
References
Alemany, M. (2012). The problem of nitrogen disposal in the obese. Nutrition Research Reviews, 25, 18–28.
Barker, D. J. (2004). The developmental origins of adult disease. Journal of the American College of Nutrition, 23, 588S-595S.
Barton, M. (2012). Childhood obesity: A life-long health risk. Acta Pharmacologica Sinica, 33, 189–193.
Barupal, D. K., & Fiehn, O. (2017). Chemical Similarity Enrichment Analysis (ChemRICH) as alternative to biochemical pathway mapping for metabolomic datasets. Science and Reports, 7, 14567.
Benjamini, Y., & Hochberg, Y. (1995). Controlling the false discovery rate: A practical and powerful approach to multiple testing. Journal of the Royal Statistical Society: Series B (methodological), 57, 289–300.
Bianco, M. E., Vu, M. H., Bain, J. R., Muehlbauer, M. J., Ilkayeva, O. R., Scholtens, D. M., Josefson, J., & Lowe, W. L., Jr. (2023). Maternal and cord blood serum metabolite associations with childhood adiposity and body composition outcomes. Metabolites, 13(6), 749.
Bictash, M., Ebbels, T. M., Chan, Q., Loo, R. L., Yap, I. K., Brown, I. J., de Iorio, M., Daviglus, M. L., Holmes, E., Stamler, J., Nicholson, J. K., & Elliott, P. (2010). Opening up the “Black Box”: Metabolic phenotyping and metabolome-wide association studies in epidemiology. Journal of Clinical Epidemiology, 63, 970–979.
Bremer, P. L., Wohlgemuth, G., & Fiehn, O. (2023). The BinDiscover database: A biology-focused meta-analysis tool for 156,000 GC-TOF MS metabolome samples. J Cheminform, 15, 66.
Brennan, P. A., Dunlop, A. L., Smith, A. K., Kramer, M., Mulle, J., & Corwin, E. J. (2019). Protocol for the Emory University African American maternal stress and infant gut microbiome cohort study. BMC Pediatrics, 19, 246.
Brosnan, J. T., & Brosnan, M. E. (2010). Creatine metabolism and the urea cycle. Molecular Genetics and Metabolism, 100, S49–S52.
Casbas Pinto, F., Ravipati, S., Barrett, D. A., & Hodgman, T. C. (2017). A methodology for elucidating regulatory mechanisms leading to changes in lipid profiles. Metabolomics, 13, 81.
Chang, C. J., Barr, D. B., Ryan, P. B., Panuwet, P., Smarr, M. M., Liu, K., Kannan, K., Yakimavets, V., Tan, Y., Ly, V., Marsit, C. J., Jones, D. P., Corwin, E. J., Dunlop, A. L., & Liang, D. (2022). Per- and polyfluoroalkyl substance (PFAS) exposure, maternal metabolomic perturbation, and fetal growth in African American women: A meet-in-the-middle approach. Environment International, 158, 106964.
Cirulli, E. T., Guo, L., Leon Swisher, C., Shah, N., Huang, L., Napier, L. A., Kirkness, E. F., Spector, T. D., Caskey, C. T., Thorens, B., Venter, J. C., & Telenti, A. (2019). Profound Perturbation of the Metabolome in Obesity Is Associated with Health Risk. Cell Metabolism, 29(488–500), e2.
Corwin, E. J., Hogue, C. J., Pearce, B., Hill, C. C., Read, T. D., Mulle, J., & Dunlop, A. L. (2017). Protocol for the Emory University African American Vaginal, Oral, and Gut Microbiome in Pregnancy Cohort Study. BMC Pregnancy and Childbirth, 17, 161.
Daraki, V., Georgiou, V., Papavasiliou, S., Chalkiadaki, G., Karahaliou, M., Koinaki, S., Sarri, K., Vassilaki, M., Kogevinas, M., & Chatzi, L. (2015). Metabolic profile in early pregnancy is associated with offspring adiposity at 4 years of age: The Rhea pregnancy cohort Crete. Greece. Plos One, 10, e0126327.
Doherty, B. T., McRitchie, S. L., Pathmasiri, W. W., Stewart, D. A., Kirchner, D., Anderson, K. A., Gui, J., Madan, J. C., Hoen, A. G., Sumner, S. J., Karagas, M. R., & Romano, M. E. (2022). Chemical exposures assessed via silicone wristbands and endogenous plasma metabolomics during pregnancy. Journal of Exposure Science & Environmental Epidemiology, 32, 259–267.
Evans, A. M., DeHaven, C. D., Barrett, T., Mitchell, M., & Milgram, E. (2009). Integrated, nontargeted ultrahigh performance liquid chromatography/electrospray ionization tandem mass spectrometry platform for the identification and relative quantification of the small-molecule complement of biological systems. Analytical Chemistry, 81, 6656–6667.
Forrest, C. B., Blackwell, C. K., & Camargo, C. A., Jr. (2018). Advancing the science of children’s positive health in the national institutes of health environmental influences on child health outcomes (ECHO) research program. Journal of Pediatrics, 196, 298–300.
Gillman, M. W., & Blaisdell, C. J. (2018). Environmental influences on Child Health outcomes, a research program of the national institutes of health. Current Opinion in Pediatrics, 30, 260–262.
Goveia, J., Pircher, A., Conradi, L. C., Kalucka, J., Lagani, V., Dewerchin, M., Eelen, G., DeBerardinis, R. J., Wilson, I. D., & Carmeliet, P. (2016). Meta-analysis of clinical metabolic profiling studies in cancer: Challenges and opportunities. EMBO Molecular Medicine, 8, 1134–1142.
Guevarra, M.M.a.E. (2019) zscorer: Child Anthropometry z-Score Calculator.
Hagen, I. V., Helland, A., Bratlie, M., Midttun, O., McCann, A., Sveier, H., Rosenlund, G., Mellgren, G., Ueland, P. M., & Gudbrandsen, O. A. (2020). TMAO, creatine and 1-methylhistidine in serum and urine are potential biomarkers of cod and salmon intake: A randomised clinical trial in adults with overweight or obesity. European Journal of Nutrition, 59, 2249–2259.
Han, J. C., Lawlor, D. A., & Kimm, S. Y. (2010). Childhood obesity. Lancet, 375, 1737–1748.
Heinemann, J. (2019). Cluster analysis of untargeted metabolomic experiments. Methods in Molecular Biology, 1859, 275–285.
Hu, Z., Han, L., Liu, J., Fowke, J. H., Han, J. C., Kakhniashvili, D., LeWinn, K. Z., Bush, N. R., Mason, W. A., & Zhao, Q. (2022). Prenatal metabolomic profiles mediate the effect of maternal obesity on early childhood growth trajectories and obesity risk: The Conditions Affecting Neurocognitive Development and Learning in Early Childhood (CANDLE) Study. American Journal of Clinical Nutrition, 116, 1343–1353.
Huang, M., Kelly, R. S., Chu, S. H., Kachroo, P., Gürdeniz, G., Chawes, B. L., Bisgaard, H., Weiss, S. T., & Lasky-Su, J. (2021). Maternal metabolome in pregnancy and childhood asthma or recurrent wheeze in the Vitamin D antenatal asthma reduction trial. Metabolites, 11(2), 65.
Joshi, A. D., Rahnavard, A., Kachroo, P., Mendez, K. M., Lawrence, W., Julian-Serrano, S., Hua, X., Fuller, H., Sinnott-Armstrong, N., Tabung, F. K., Shutta, K. H., Raffield, L. M., Darst, B. F., Group, C.E.C.S.W. (2023). An epidemiological introduction to human metabolomic investigations. Trends Endocrinology Metabolism, 34, 505–525.
Karnovsky, A., & Li, S. (2020). Pathway Analysis for Targeted and Untargeted Metabolomics. In S. Li (Ed.), Computational Methods and Data Analysis for Metabolomics (pp. 387–400). Springer.
Kelly, R. S., Bayne, H., Spiro, A., 2nd., Vokonas, P., Sparrow, D., Weiss, S. T., Schwartz, J., Nassan, F. L., Lee-Sarwar, K., Huang, M., Kachroo, P., Chu, S. H., Litonjua, A. A., & Lasky-Su, J. A. (2020). Metabolomic signatures of lead exposure in the VA normative aging study. Environmental Research, 190, 110022.
Litonjua, A. A., Lange, N. E., Carey, V. J., Brown, S., Laranjo, N., Harshfield, B. J., O’Connor, G. T., Sandel, M., Strunk, R. C., Bacharier, L. B., Zeiger, R. S., Schatz, M., Hollis, B. W., & Weiss, S. T. (2014). The Vitamin D Antenatal Asthma Reduction Trial (VDAART): Rationale, design, and methods of a randomized, controlled trial of vitamin D supplementation in pregnancy for the primary prevention of asthma and allergies in children. Contemporary Clinical Trials, 38, 37–50.
Liu, Y., Wosu, A. C., Fleisch, A. F., Dunlop, A. L., Starling, A. P., Ferrara, A., Dabelea, D., Oken, E., Buckley, J. P., Chatzi, L., Karagas, M. R., Romano, M. E., Schantz, S., O’Connor, T. G., Woodruff, T. J., Zhu, Y., Hamra, G. B., Braun, J. M., & the program collaborators for Environmental influences on Child Health, O. (2023). Associations of gestational Perfluoroalkyl substances exposure with early childhood BMI z-scores and risk of overweight/obesity: results from the ECHO cohorts. Environmental Health Perspectives, 131, 67001.
Llambrich, M., Correig, E., Guma, J., Brezmes, J., & Cumeras, R. (2022). Amanida: An R package for meta-analysis of metabolomics non-integral data. Bioinformatics, 38, 583–585.
Louca, P., Nogal, A., Moskal, A., Goulding, N. J., Shipley, M. J., Alkis, T., Lindbohm, J. V., Hu, J., Kifer, D., Wang, N., Chawes, B., Rexrode, K. M., Ben-Shlomo, Y., Kivimaki, M., Murphy, R. A., Yu, B., Gunter, M. J., Suhre, K., Lawlor, D. A., … Menni, C. (2022). Cross-sectional blood metabolite markers of hypertension: A multicohort analysis of 44,306 individuals from the consortium of metabolomics studies. Metabolites, 12(7), 601.
Ludwig, D. S., & Currie, J. (2010). The association between pregnancy weight gain and birthweight: A within-family comparison. Lancet, 376, 984–990.
Marcus, C., Danielsson, P., & Hagman, E. (2022). Pediatric obesity—Long-term consequences and effect of weight loss. Journal of Internal Medicine, 292, 870–891.
Mitro, S. D., Wu, J., Rahman, M. L., Cao, Y., Zhu, Y., Chen, Z., Chen, L., Li, M., Hinkle, S. N., Bremer, A. A., Weir, N. L., Tsai, M. Y., Song, Y., Grantz, K. L., Gelaye, B., & Zhang, C. (2021). Longitudinal Plasma metabolomics profile in pregnancy-a study in an ethnically diverse U.S. pregnancy cohort. Nutrients, 13(9), 3080.
Newsholme, P., Stenson, L., Sulvucci, M., Sumayao, R., & Krause, M. (2011). 1.02 - Amino Acid Metabolism. In M. Moo-Young (Ed.), Comprehensive Biotechnology (pp. 3–14). Academic Press.
Nogal, A., Alkis, T., Lee, Y., Kifer, D., Hu, J., Murphy, R. A., Huang, Z., Wang-Sattler, R., Kastenmuler, G., Linkohr, B., Barrios, C., Crespo, M., Gieger, C., Peters, A., Price, J., Rexrode, K. M., Yu, B., & Menni, C. (2023). Predictive metabolites for incident myocardial infarction: a two-step meta-analysis of individual patient data from six cohorts comprising 7897 individuals from the the COnsortium of METabolomic Studies. Cardiovascular Research, 119(17), 2743–2754.
Nolin, S. L., Napoli, E., Flores, A., Hagerman, R. J., & Giulivi, C. (2021). Deficits in prenatal serine biosynthesis underlie the mitochondrial dysfunction associated with the autism-Linked FMR1 gene. International Journal of Molecular Sciences., 22(11), 5886.
Oken, E., Taveras, E. M., Kleinman, K. P., Rich-Edwards, J. W., & Gillman, M. W. (2007). Gestational weight gain and child adiposity at age 3 years. American Journal of Obstetrics and Gynecology, 196(322), e1-8.
Pan, X. F., Yang, J. J., Shu, X. O., Moore, S. C., Palmer, N. D., Guasch-Ferre, M., Herrington, D. M., Harada, S., Eliassen, H., Wang, T. J., Gerszten, R. E., Albanes, D., Tzoulaki, I., Karaman, I., Elliott, P., Zhu, H., Wagenknecht, L. E., Zheng, W., Cai, H., … Yu, D. (2021). Associations of circulating choline and its related metabolites with cardiometabolic biomarkers: An international pooled analysis. American Journal of Clinical Nutrition, 114, 893–906.
Pang, Z., Chong, J., Zhou, G., de Lima Morais, D. A., Chang, L., Barrette, M., Gauthier, C., Jacques, P. -É., Li, S., & Xia, J. (2021). MetaboAnalyst 5.0: Narrowing the gap between raw spectra and functional insights. Nucleic Acids Research, 49, W388–W396.
Perng, W., Gillman, M. W., Fleisch, A. F., Michalek, R. D., Watkins, S. M., Isganaitis, E., Patti, M. E., & Oken, E. (2014). Metabolomic profiles and childhood obesity. Obesity, 22, 2570–2578.
Prevention, C.f.D.C.a. (2023) Prevalence of Childhood Obesity in the United States, Overweight & Obesity.
Pulgaron, E. R. (2013). Childhood obesity: A review of increased risk for physical and psychological comorbidities. Clinical Therapeutics, 35, A18-32.
Romano, M. E., Heggeseth, B. C., Gallagher, L. G., Botelho, J. C., Calafat, A. M., Gilbert-Diamond, D., & Karagas, M. R. (2022). Gestational per- and polyfluoroalkyl substances exposure and infant body mass index trajectory in the New Hampshire Birth Cohort Study. Environmental Research, 215, 114418.
Romo, M., Lopez-Vicario, C., Perez-Romero, N., Casulleras, M., Martinez-Puchol, A. I., Sanchez, B., Flores-Costa, R., Alcaraz-Quiles, J., Duran-Guell, M., Ibarzabal, A., Espert, J. J., Claria, J., & Titos, E. (2022). Small fragments of hyaluronan are increased in individuals with obesity and contribute to low-grade inflammation through TLR-mediated activation of innate immune cells. International Journal of Obesity, 46, 1960–1969.
Roth, H. E., & Powers, R. (2022). Meta-Analysis reveals both the promises and the challenges of clinical metabolomics. Cancers (basel), 14(16), 3992.
Safi-Stibler, S., Thevenot, E. A., Jouneau, L., Jouin, M., Seyer, A., Jammes, H., Rousseau-Ralliard, D., Baly, C., & Gabory, A. (2020). Differential effects of post-weaning diet and maternal obesity on mouse liver and brain metabolomes. Nutrients, 12(6), 1572.
Sahoo, K., Sahoo, B., Choudhury, A. K., Sofi, N. Y., Kumar, R., & Bhadoria, A. S. (2015). Childhood obesity: Causes and consequences. J Family Med Prim Care, 4, 187–192.
Schwarzer, S.B.a.G.R.a.G. (2019) How to perform a meta-analysis with {R}: a practical tutorial.
Signes-Pastor, A. J., Martinez-Camblor, P., Baker, E., Madan, J., Guill, M. F., & Karagas, M. R. (2021). Prenatal exposure to arsenic and lung function in children from the New Hampshire Birth Cohort Study. Environment International, 155, 106673.
Tan, K. M., Tint, M. T., Kothandaraman, N., Michael, N., Sadananthan, S. A., Velan, S. S., Fortier, M. V., Yap, F., Tan, K. H., Gluckman, P. D., Chong, Y. S., Chong, M. F. F., Lee, Y. S., Godfrey, K. M., Eriksson, J. G., & Cameron-Smith, D. (2022). The Kynurenine pathway metabolites in cord blood positively correlate with early childhood adiposity. Journal of Clinical Endocrinology and Metabolism, 107, e2464–e2473.
Team, R.C. (2020) R: A language and environment for statistical computing, R Foundation or Statistical Computing, Vienna, Austria.
Temprosa, M., Moore, S. C., Zanetti, K. A., Appel, N., Ruggieri, D., Mazzilli, K. M., Chen, K. L., Kelly, R. S., Lasky-Su, J. A., Loftfield, E., McClain, K., Park, B., Trijsburg, L., Zeleznik, O. A., & Mathe, E. A. (2022). COMETS analytics: An online tool for analyzing and meta-analyzing metabolomics data in large research consortia. American Journal of Epidemiology, 191, 147–158.
Tolstikov, V., Moser, A. J., Sarangarajan, R., Narain, N. R., & Kiebish, M. A. (2020). Current status of metabolomic biomarker discovery: impact of study design and demographic characteristics. Metabolites, 10, 224.
Villar, J., Ochieng, R., Gunier, R. B., Papageorghiou, A. T., Rauch, S., McGready, R., Gauglitz, J. M., Barros, F. C., Vatish, M., Fernandes, M., Zammit, V., Carrara, V. I., Munim, S., Craik, R., Barsosio, H. C., Carvalho, M., Berkley, J. A., Ismail, L. I. C., Norris, S. A., … Kennedy, S. H. (2022). Association between fetal abdominal growth trajectories, maternal metabolite signatures early in pregnancy, and childhood growth and adiposity: Prospective observational multinational INTERBIO-21st fetal study. The Lancet Diabetes and Endocrinology, 10, 710–719.
Ward, Z. J., Long, M. W., Resch, S. C., Giles, C. M., Cradock, A. L., & Gortmaker, S. L. (2017). Simulation of growth trajectories of childhood obesity into adulthood. New England Journal of Medicine, 377, 2145–2153.
Xiao, J. F., Zhou, B., & Ressom, H. W. (2012). Metabolite identification and quantitation in LC-MS/MS-based metabolomics. TrAC Trends in Analytical Chemistry, 32, 1–14.
Yan, S., Chi, X., Chang, X., & Tian, M. (2020). Analysing the meta-interaction between pathways by gene set topological impact analysis. BMC Genomics, 21, 748.
Yang, J. J., Shu, X. O., Herrington, D. M., Moore, S. C., Meyer, K. A., Ose, J., Menni, C., Palmer, N. D., Eliassen, H., Harada, S., Tzoulaki, I., Zhu, H., Albanes, D., Wang, T. J., Zheng, W., Cai, H., Ulrich, C. M., Guasch-Ferre, M., Karaman, I., … Yu, D. (2021). Circulating trimethylamine N-oxide in association with diet and cardiometabolic biomarkers: An international pooled analysis. American Journal of Clinical Nutrition, 113, 1145–1156.
Yeum, D., Gilbert-Diamond, D., Doherty, B., Coker, M., Stewart, D., Kirchner, D., McRitchie, S., Sumner, S., Karagas, M. R., & Hoen, A. G. (2023). Associations of maternal plasma and umbilical cord plasma metabolomics profiles with birth anthropometric measures. Pediatric Research, 94, 135–142.
Yu, B., Zanetti, K. A., Temprosa, M., Albanes, D., Appel, N., Barrera, C. B., Ben-Shlomo, Y., Boerwinkle, E., Casas, J. P., Clish, C., Dale, C., Dehghan, A., Derkach, A., Eliassen, A. H., Elliott, P., Fahy, E., Gieger, C., Gunter, M. J., Harada, S., … Moore, S. C. (2019). The Consortium of Metabolomics Studies (COMETS): Metabolomics in 47 prospective cohort studies. American Journal of Epidemiology, 188, 991–1012.
Zhang, A., Sun, H., & Wang, X. (2017). Emerging role and recent applications of metabolomics biomarkers in obesity disease research. RSC Advances, 7, 14966–14973.
Zhao, Q., Hu, Z., Kocak, M., Liu, J., Fowke, J. H., Han, J. C., Kakhniashvili, D., Lewinn, K. Z., Bush, N. R., Mason, W. A., & Tylavsky, F. A. (2021). Associations of prenatal metabolomics profiles with early childhood growth trajectories and obesity risk in African Americans: The CANDLE study. International Journal of Obesity, 45, 1439–1447.
Acknowledgements
The authors wish to thank our ECHO Colleagues; the medical, nursing, and program staff; and the children and families participating in the ECHO cohorts. We also acknowledge the contribution of the following ECHO Program collaborators: ECHO Components—Coordinating Center: Duke Clinical Research Institute, Durham, North Carolina: Smith PB, Newby LK; Data Analysis Center: Johns Hopkins University Bloomberg School of Public Health, Baltimore, Maryland: Jacobson LP; Research Triangle Institute, Durham, North Carolina: Catellier DJ; Person-Reported Outcomes Core: Northwestern University, Evanston, Illinois: Gershon R, Cella D. ECHO Awardees and Cohorts—VDAART; AEC; NHBCS; MARBLES; PROTECT, Boston University Medical Center, Boston, MA: O’Connor G; Kaiser Permanente, Southern California, San Diego, CA: Zeiger R; Washington University of St. Louis, St Louis, MO: Bacharier L; AJ Drexel Autism Institute, Philadelphia, PA: Lyall K; John Hopkins Bloomberg School of Public Health, Baltimore, MD: Volk H. We also wish to thank the NIH Children's Health Exposure Analysis Resource (CHEAR) Program and the Human Health Exposure Analysis Resource (HHEAR) Program for their support.
Funding
The content is solely the responsibility of the authors and does not necessarily represent the official views of the National Institutes of Health. Research reported in this publication was supported by the Environmental influences on Child Health Outcomes (ECHO) Program, Office of the Director, National Institutes of Health, under Award Numbers U2COD023375 (Coordinating Center), U24OD023382 (Data Analysis Center), U24OD023319 with co-funding from the Office of Behavioral and Social Science Research (PRO Core), U2CES026544 RTI Children’s Health Exposure Analysis Resource (CHEAR) Exposure Assessment Untargeted Hub (NIEHS, Fennell, Sumner), U2CES03085 North Carolina Human Health Exposure Analysis Resource (HHEAR) Hub (NIEHS, Fennell, Sumner, Du), UH3OD023318 (Dunlop), UH3OD023275 (Karagas), UH3OD023268 (Weiss), UH3OD023342 (Lyall), R01HL141826 (Lasky-Su), R01HL123915 (Lasky-Su), K01 HL146980 (Kelly).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Contributions
NP and RSK: wrote the main manuscript text and conducted the meta-analysis. DL, YT, SB, and MSZ: conducted analysis in individual cohorts. AA, EEA, SAB, SHC, JFC, PC, ALD, DGD, CG, AGH, MRK, DK, AAL, JM, SM, JDM, WP, WP, RJS, DJW, STW, YZ, and JALS: provided cohort-specific information on demographics and details of study design, contributed to reporting of data collection procedures, assisted in design of statistical models, and critically reviewed the manuscript.
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Conflict of interest
The authors declare no competing interests that are directly or indirectly related to this work.
Additional information
Publisher's Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Submitted on behalf of program collaborators for Environmental influences on Child Health Outcomes; See Acknowledgments for full listing of collaborators.
Supplementary Information
Below is the link to the electronic supplementary material.
Rights and permissions
Springer Nature or its licensor (e.g. a society or other partner) holds exclusive rights to this article under a publishing agreement with the author(s) or other rightsholder(s); author self-archiving of the accepted manuscript version of this article is solely governed by the terms of such publishing agreement and applicable law.
About this article
Cite this article
Prince, N., Liang, D., Tan, Y. et al. Metabolomic data presents challenges for epidemiological meta-analysis: a case study of childhood body mass index from the ECHO consortium. Metabolomics 20, 16 (2024). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11306-023-02082-y
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11306-023-02082-y