Abstract
Introduction
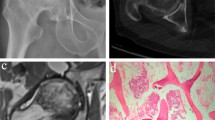
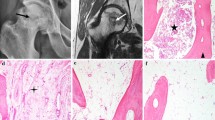
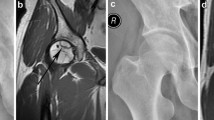
Osteonecrosis of the femoral head (ONFH) is a disorder that causes a collapse of the femoral head, requiring subsequent total hip replacement. However, the pathogenesis of ONFH remains largely unclear. Herein, exosome metabolomics analyses were conducted to explore the pathophysiology of ONFH.
Objectives
This study aimed to conduct metabolic profiling of bone-derived exosomes of ONFH.
Methods
30 ONFH patients and 30 femoral neck fracture (FNF) patients were included in this study. Exosomes were harvested from the femoral head by using ultracentrifugation. Ultraperformance liquid chromatography/tandem mass spectrometry (UPLC-MS/MS) was performed in combination with multivariate statistical analysis to reveal and provided new insight into identify the global metabolic profile of ONFH.
Results
The results of transmission electron microscope (TEM), nanoparticle tracking analysis (NTA), and Western blots indicated that the microvesicles isolated from the femoral head were exosomes. Several compounds were identified, including lipids and lipid-like molecules, amino acids, peptides, organooxygen compounds. 44 differential metabolites were screened between ONFH and FNF patients. The up-and down-regulation of Riboflavin metabolism, Pantothenate and CoA biosynthesis, Glycerophospholipid metabolism, and Sphingolipid metabolism were associated with ONFH pathophysiology.
Conclusion
Our results suggest that metabolomics has huge prospects for elucidating pathophysiology of ONFH.





Similar content being viewed by others
Data Availability
The metabolomics and metadata reported in this paper are available via study identifier MTBLS4920.
References
Adams, S., Setton, L., & Nettles, D. (2013). The role of metabolomics in osteoarthritis research. The Journal of the American Academy of Orthopaedic Surgeons, 21(1), 63–64. https://doi.org/10.5435/JAAOS-21-01-63.
Aldridge, J. M., & Urbaniak, J. R. (2004). Avascular necrosis of the femoral head: Etiology, pathophysiology, classification, and current treatment guidelines. American Journal of Orthopedics, 33(7), 327–332.
Andaloussi, S. E., Mager, I., Breakefield, X. O., & Wood, M. J. (2013). Extracellular vesicles: Biology and emerging therapeutic opportunities. Nature reviews Drug discovery, 12(5), 347–357. https://doi.org/10.1038/nrd3978.
Arbab, D., & Konig, D. P. (2016). Atraumatic femoral head necrosis in adults. Deutsches Arzteblatt international, 113(3), 31–38. https://doi.org/10.3238/arztebl.2016.0031.
Bai, H., Chen, T., Lu, Q., Zhu, W., & Zhang, J. (2019). Gene expression profiling of the bone trabecula in patients with osteonecrosis of the femoral head by RNA sequencing. Journal of biochemistry, 166(6), 475–484. https://doi.org/10.1093/jb/mvz060.
Chierico, L., Joseph, A. S., Lewis, A. L., & Battaglia, G. (2014). Live cell imaging of membrane/cytoskeleton interactions and membrane topology. Scientific Reports, 4, 6056. https://doi.org/10.1038/srep06056.
Clarke, M., Ward, M., Dickey, W., Hoey, L., Molloy, A. M., Waldron, L., & McNulty, H. (2015). B-vitamin status in relation to bone mineral density in treated celiac disease patients.Scandinavian Journal of Gastroenterology, 50(8),975–84. https://doi.org/10.3109/00365521.2015.1015603.
Doyle, L. M., & Wang, M. Z. (2019). Overview of Extracellular vesicles, their origin, composition, purpose, and methods for Exosome isolation and analysis. Cells, 8(7), 727. https://doi.org/10.3390/cells8070727.
Du, W., Zhang, K., Zhang, S., Wang, R., Nie, Y., Tao, H., & Li, Z. (2017). Enhanced proangiogenic potential of mesenchymal stem cell-derived exosomes stimulated by a nitric oxide releasing polymer.Biomaterials, 133,70–81. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.biomaterials.2017.04.030.
Fiehn, O. (2017). Metabolomics–the link between genotypes and phenotypes. Plant molecular biology, 48(1–2), 155–157.
Gao, M., Gao, W., Papadimitriou, J. M., Zhang, C., Gao, J., & Zheng, M. (2018). Exosomes-the enigmatic regulators of bone homeostasis. Bone research, 6, 36. https://doi.org/10.1038/s41413-018-0039-2.
Hu, G. W., Li, Q., Niu, X., Hu, B., Liu, J., & Zhou, S. M. (2015). Exosomes secreted by human-induced pluripotent stem cell-derived mesenchymal stem cells attenuate limb ischemia by promoting angiogenesis in mice. Stem Cell Research & Therapy, 6(1), 10. https://doi.org/10.1186/scrt546.
Jeppesen, D. K., Fenix, A. M., Franklin, J. L., Higginbotham, J. N., Zhang, Q., Zimmerman, L. J., & Coffey, R. J. (2019). Reassessment of Exosome Composition. Cell, 177(2), 428–445e18. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.cell.2019.02.029.
Kang, J., Ko, H., Han, G., Lee, S., Moon, J., & Kim, S. (2020). Dual role of phosphatidylserine and its receptors in osteoclastogenesis. Cell death & disease, 11(7), 497. https://doi.org/10.1038/s41419-020-2712-9.
Kanno, S., Hirano, S., Sakamoto, T., Furuyama, A., & Aoki, Y. (2020). Scavenger receptor MARCO contributes to cellular internalization of exosomes by dynamin-dependent endocytosis and macropinocytosis. Scientific Reports, 10(1), 21795. https://doi.org/10.1038/s41598-020-78464-2.
Kilpinen, L., Tigistu-Sahle, F., Oja, S., Greco, D., Parmar, A., & Laitinen, S. (2013). Aging bone marrow mesenchymal stromal cells have altered membrane glycerophospholipid composition and functionality. Journal of lipid research, 54(3), 622–635. https://doi.org/10.1194/jlr.M030650.
Kuang, M. J., Huang, Y., Zhao, X. G., Zhang, R., Ma, J. X., Wang, D. C., & Ma, X. L. (2019). Exosomes derived from Wharton’s jelly of human umbilical cord mesenchymal stem cells reduce osteocyte apoptosis in glucocorticoid-induced osteonecrosis of the femoral head in rats via the mir-21-PTEN-AKT signalling pathway. International journal of biological sciences, 15(9), 1861–1871. https://doi.org/10.7150/ijbs.32262.
Lai, R. C., Arslan, F., Lee, M. M., Sze, N. S., Choo, A., Chen, T. S., & Lim, S. K. (2010). Exosome secreted by MSC reduces myocardial ischemia/reperfusion injury. Stem cell research, 4(3), 214–222. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.scr.2009.12.003.
Liu, X., Li, Q., Niu, X., Hu, B., Chen, S., Song, W., & Wang, Y. (2017). Exosomes secreted from Human-Induced pluripotent stem cell-derived mesenchymal stem cells prevent osteonecrosis of the femoral head by promoting angiogenesis. International Journal of Biological Sciences, 13(2), 232–244. https://doi.org/10.7150/ijbs.16951.
Lu, X., Chen, Y., Wang, H., Bai, Y., Zhao, J., & Ma, T. (2019). Integrated Lipidomics and Transcriptomics characterization upon aging-related changes of lipid species and pathways in human bone marrow mesenchymal stem cells. Journal of proteome research, 18(5), 2065–2077. https://doi.org/10.1021/acs.jproteome.8b00936.
McNally, S., & O’Brien, C. J. (2014). Metabolomics/Proteomics strategies used to identify biomarkers for exfoliation glaucoma. Journal of Glaucoma, 23(8 Suppl 1), S51–S54. https://doi.org/10.1097/IJG.0000000000000117.
Mont, M. A., Zywiel, M. G., Marker, D. R., McGrath, M. S., & Delanois, R. E. (2010). The natural history of untreated asymptomatic osteonecrosis of the femoral head: A systematic literature review. The Journal of bone and joint surgery American volume, 92(12), 2165–2170. https://doi.org/10.2106/JBJS.I.00575.
Naquet, P., Kerr, E. W., Vickers, S. D., & Leonardi, R. (2020). Regulation of coenzyme A levels by degradation: The ‘ins and outs’. Progress in Lipid Research, 78, 101028. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.plipres.2020.101028.
Perumal, S. S., Shanthi, P., & Sachdanandam, P. (2005). Augmented efficacy of tamoxifen in rat breast tumorigenesis when gavaged along with riboflavin, niacin, and CoQ 10: Effects on lipid peroxidation and antioxidants in mitochondria. Chemico-Biological Interactions, 152(1), 49–58. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.cbi.2005.01.007.
Qiang, H., Liu, H., Ling, M., Wang, K., & Zhang, C. (2015). Early Steroid-Induced Osteonecrosis of Rabbit Femoral Head and Panax notoginseng Saponins: Mechanism and Protective Effects. Evidence-based complementary and alternative medicine, 2015, 719370. https://doi.org/10.1155/2015/719370.
Rhee, E. P., Cheng, S., Shi, X., Helenius, I. T., & O’Donnell, C. J. (2013). A genome-wide association study of the human metabolome in a community-based cohort. Cell Metabolism, 18(1), 130–143. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.cmet.2013.06.013.
Rodriguez-Cuenca, S., Pellegrinelli, V., Campbell, M., Oresic, M., & Vidal-Puig, A. (2017). Sphingolipids and glycerophospholipids - the “ying and yang” of lipotoxicity in metabolic diseases. Progress in lipid research, 66, 14–29. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.plipres.2017.01.002.
Sanches, S. C., Ramalho, L., Mendes-Braz, M., Terra, V. A., Cecchini, R., Augusto, M. J., & Ramalho, F. S. (2014). Riboflavin (vitamin B-2) reduces hepatocellular injury following liver ischaemia and reperfusion in mice. Food and chemical toxicology, 67, 65–71. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.fct.2014.02.013.
Schrimpe-Rutledge, A. C., Codreanu, S. G., Sherrod, S. D., & McLean, J. A. (2016). Untargeted Metabolomics Strategies-Challenges and emerging directions. Journal of the American Society for Mass Spectrometry, 27(12), 1897–1905. https://doi.org/10.1007/s13361-016-1469-y.
Sreekumar, A., Poisson, L. M., Rajendiran, T. M., Khan, A. P., Cao, Q., Yu, J., & Chinnaiyan, A. M. (2009). Metabolomic profiles delineate potential role for sarcosine in prostate cancer progression. Nature, 457(7231), 910–914. https://doi.org/10.1038/nature07762.
Sun, W., Wang, B., & Li, Z. (2011). Chinese specialist consensus on diagnosis and treatment of osteonecrosis of the femoral head. Orthopaedic surgery, 3(2), 131–137. https://doi.org/10.1111/j.1757-7861.2011.00127.x.
Suwannasom, N., Kao, I., Pru, A., Georgieva, R., & Bumler, H. (2020). Riboflavin: The Health benefits of a Forgotten Natural vitamin. International Journal of Molecular Sciences, 21(3), 950. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms21030950.
Thakur, K., Tomar, S. K., Singh, A. K., Mandal, S., & Arora, S. (2016). Riboflavin and health: A review of recent human research. Critical reviews in food science and nutrition, 57(17), 3650–3660. https://doi.org/10.1080/10408398.2016.1145104.
Tilton, G. B., Wedemeyer, W. J., Browse, J., & Ohlrogge, J. (2006). Plant coenzyme a biosynthesis: Characterization of two pantothenate kinases from Arabidopsis. Plant molecular biology, 61(4–5), 629–642. https://doi.org/10.1007/s11103-006-0037-4.
Todorova, D., Simoncini, S., Lacroix, R., Sabatier, F., & Dignat-George, F. (2017). Extracellular vesicles in Angiogenesis. Circulation research, 120(10), 1658–1673. https://doi.org/10.1161/CIRCRESAHA.117.309681.
Verma, S., Leikina, E., Melikov, K., Gebert, C., Kram, V., & Chernomordik, L. V. (2018). Cell-surface phosphatidylserine regulates osteoclast precursor fusion. The Journal of biological chemistry, 293(1), 254–270. https://doi.org/10.1074/jbc.M117.809681.
Wang, C. J., Cheng, J. H., Huang, C. C., Yip, H. K., & Russo, S. (2015). Extracorporeal shockwave therapy for avascular necrosis of femoral head. International journal of surgery (London England), 24(Pt B), 184–187. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ijsu.2015.06.080.
Wang, X., Xu, Y., Song, X., Jia, Q., Zhang, X., Qian, Y., & Qiu, J. (2019). Analysis of glycerophospholipid metabolism after exposure to PCB153 in PC12 cells through targeted lipidomics by UHPLC-MS/MS. Ecotoxicology and Environmental Safety, 169, 120–127. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ecoenv.2018.11.006.
Xu, T., Jin, H., Lao, Y., Wang, P., Zhang, S., Ruan, H., & Wu, C. (2017). Administration of erythropoietin prevents bone loss in osteonecrosis of the femoral head in mice. Molecular medicine reports, 16(6), 8755–8762. https://doi.org/10.3892/mmr.2017.7735.
Xu, Z., Xu, K., Ding, S., Luo, J., & Zhang, J. (2017). Serum metabolomic study for detecting biomarkers of nontraumatic osteonecrosis of the femoral head. Metabolomics, 13, 73. https://doi.org/10.1007/s11306-017-1208-9.
Yang, G., Zhao, G., Zhang, J., Gao, S., Chen, T., Ding, S., & Zhu, Y. (2019). Global urinary metabolic profiling of the osteonecrosis of the femoral head based on UPLC-QTOF/MS. Metabolomics, 15, 26. https://doi.org/10.1007/s11306-019-1491-8.
Yazdanpanah, N., Uitterlinden, A. G., Zillikens, M. C., Jhamai, M., & Meurs, J. (2010). Low dietary riboflavin but not folate predicts increased fracture risk in postmenopausal women homozygous for the MTHFR 677 T allele. Journal of Bone & Mineral Research, 23(1), 86–94. https://doi.org/10.1359/jbmr.070812.
Zhao, X., Wang, B., Xie, K., Liu, J., Zhang, Y., Wang, Y., & Wang, J. (2018). Development and comparison of HPLC-MS/MS and UPLC-MS/MS methods for determining eight coccidiostats in beef. Journal of Chromatography, 1087–1088, 98–107. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jchromb.2018.04.044.
Zhu, W., Chen, T., Ding, S., Yang, G., Xu, Z., Xu, K., & Zhang, J. (2016). Metabolomic study of the bone trabecula of osteonecrosis femoral head patients based on UPLC-MS/MS. Metabolomics, 12, 48. https://doi.org/10.1007/s11306-016-0965-1.
Zhu, W., Guo, M. K., Yang, W., Tang, M., Chen, T., Gan, D., & Zhang, J. (2020). CD41-deficient exosomes from non-traumatic femoral head necrosis tissues impair osteogenic differentiation and migration of mesenchymal stem cells. Cell Death & Disease, 11(4), 293. https://doi.org/10.1038/s41419-020-2496-y.
Funding
This work was supported by Chongqing Technology Innovation and Application Development Project (Grant No. cstc2019jscx-msxmX0245).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Contributions
GMK and ZJ designed study and performed clinical study and sampling. GMK conducted statistical analysis and wrote the manuscript. ZJ revised the manuscript. All authors have read and agreed to the published version of the manuscript.
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Conflict of interest
The authors declare that they have no conflict of interests.
Ethics
The study was conducted in accordance with the Declaration of Helsinki. All experiments were approved by the Research Ethics Committee of the First Affiliated Hospital of Chongqing Medical University. Written informed consent was obtained from each donor and approved by the Institutional Review of the First Affiliated Hospital of Chongqing Medical University.
Additional information
Publisher’s Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Electronic supplementary material
Below is the link to the electronic supplementary material.
Rights and permissions
Springer Nature or its licensor (e.g. a society or other partner) holds exclusive rights to this article under a publishing agreement with the author(s) or other rightsholder(s); author self-archiving of the accepted manuscript version of this article is solely governed by the terms of such publishing agreement and applicable law.
About this article
Cite this article
Guo, M., Zhang, J. Metabolomic analysis of bone-derived exosomes in osteonecrosis of the femoral head based on UPLC–MS/MS. Metabolomics 19, 34 (2023). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11306-023-01986-z
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11306-023-01986-z