Abstract
Introduction
Ocean temperatures have been consistently increasing due to climate change, and the frequency of heatwave events on shellfish quality is a growing concern worldwide. Typically, shellfish growing areas are in remote or difficult to access locations which makes in-field sampling and sample preservation of shellfish heat stress difficult. As such, there is a need to investigate in-field sampling approaches that facilitate the study of heat stress in shellfish.
Objectives
This study aims to apply a gas chromatography–mass spectrometry (GC–MS) based metabolomics approach to examine molecular mechanisms of heat stress responses in shellfish using abalone as a model, and compare the effects of different quenching protocols on abalone metabolic profiles.
Methods
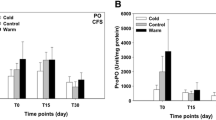
Twenty adult Haliotis iris abalone were exposed to two temperatures (14 °C and 24 °C) for 24 h. Then, haemolymph and muscle tissues of each animal were sampled and quenched with 4 different protocols (liquid nitrogen, dry ice, cold methanol solution and normal ice) which were analyzed via GC–MS for central carbon metabolites.
Results
The effects of different quenching protocols were only observed in muscle tissues in which the cold methanol solution and normal ice caused some changes in the observed metabolic profiles, compared to dry ice and liquid nitrogen. Abalone muscle tissues were less affected by thermal stress than haemolymph. There were 10 and 46 compounds significantly influenced by thermal stress in muscle and haemolymph, respectively. The changes of these metabolite signatures indicate oxidative damage, disturbance of amino acid and fatty acid metabolism, and a shift from aerobic metabolism to anaerobic pathways.
Conclusions
The study provided insights into the heat response of abalone, which could be useful for understanding the effects of marine heatwaves and summer mortality events on abalone. Dry ice appeared to be a suitable protocol, and safer in-field alternative to liquid nitrogen, for quenching of abalone tissues.






Similar content being viewed by others
Availability of data and material
Raw metabolite data of abalone haemolymph and muscle tissues are included in Supplementary File 2.
Code availability
Not applicable.
References
Alfaro, A. C, Nguyen, T. V., & Mellow, D. (2019a). A metabolomics approach to assess the effect of storage conditions on metabolic processes of New Zealand surf clam (Crassula aequilatera). Aquaculture, 498, 315–321. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.aquaculture.2018.08.065
Alfaro, A. C., Nguyen, T. V., Bayot, B., Rodriguez Leon, J. A., Domínguez-Borbor, C., & Sonnenholzner, S. (2021a). Metabolic responses of whiteleg shrimp to white spot syndrome virus (WSSV). Journal of Invertebrate Pathology, 180, 107545. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jip.2021.107545
Alfaro, A. C., Nguyen, T. V., Venter, L., Ericson, J. A., Sharma, S., et al. (2021b). The effects of live transport on metabolism and stress responses of abalone (Haliotis iris). Metabolites, 11, 748. https://doi.org/10.3390/metabo11110748
Alfaro, A. C., Nguyen, T. V., & Merien, F. (2019b). The complex interactions of Ostreid herpesvirus 1, Vibrio bacteria, environment and host factors in mass mortality outbreaks of Crassostrea gigas. Review in Aquaculture, 11, 1148–1168. https://doi.org/10.1111/raq.12284
Alfaro, A. C., & Young, T. (2018). Showcasing metabolomic applications in aquaculture: A review. Reviews in Aquaculture, 10, 135–152. https://doi.org/10.1111/raq.12152
Amaya, F., Izumi, Y., Matsudaand, M., & Sasaki, M. (2013). Tissue injury and related mediators of pain exacerbation. Current Neuropharmacology, 11, 592–597.
Bakker, J., Nijstenand, M. W. N., & Jansen, T. C. (2013). Clinical use of lactate monitoring in critically ill patients. Annals of Intensive Care, 3, 12–12. https://doi.org/10.1186/2110-5820-3-12
Beale, D. J., Pinu, F. R., Kouremenos, K. A., Poojary, M. M., Narayana, V. K., et al. (2018). Review of recent developments in GC–MS approaches to metabolomics-based research. Metabolomics, 14, 1–31.
Cappello, T. (2020). NMR-Based Metabolomics of Aquatic Organisms. In Harris, R. K., & Wasylishen, R. L. (Eds.), eMagRes (pp81–100).
Cappello, T., Maisano, M., Mauceriand, A., & Fasulo, S. (2017). 1H NMR-based metabolomics investigation on the effects of petrochemical contamination in posterior adductor muscles of caged mussel Mytilus galloprovincialis. Ecotoxicology and Environmental Safety, 142, 417–422. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ecoenv.2017.04.040
Caricato, R., Giordano, M. E., Schettino, T., Maisano, M., Mauceri, A., et al. (2019). Carbonic anhydrase integrated into a multimarker approach for the detection of the stress status induced by pollution exposure in Mytilus galloprovincialis: A field case study. Science of the Total Environment, 690, 140–150. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.scitotenv.2019.06.446
Chen, Y.-Q., Wang, J., Liao, M.-L., Liand, X.-X., & Dong, Y.-W. (2021). Temperature adaptations of the thermophilic snail Echinolittorina malaccana: insights from metabolomic analysis. Journal of Experimental Biology, 224, jeb238659.
de Zwaan, A., & Wijsman, T. C. M. (1976). Anaerobic metabolism in bivalvia (Mollusca). Characteristics of anaerobic metabolism. Comparative Biochemistry and Physiology Part b: Comparative Biochemistry, 54, 313–323. https://doi.org/10.1016/0305-0491(76)90247-9
Ding, J., Li, L., Wuand, F., & Zhang, G. (2016). Effect of chronic temperature exposure on the immunity of abalone, H aliotis discus hannai. Aquaculture Research, 47, 2861–2873.
Doney, S. C., Ruckelshaus, M., Duffy, J. E., Barry, J. P., Chan, F., et al. (2011). Climate change impacts on marine ecosystems. Annual Review of Marine Science, 4, 11–37.
Duan, Y., Zhang, Y., Dongand, H., & Zhang, J. (2016). Effect of desiccation on oxidative stress and antioxidant response of the black tiger shrimp Penaeus monodon. Fish & Shellfish Immunology, 58, 10–17.
Duncan, P. F. (2003). SHELLFISH | Commercially Important Molluscs. In B. Caballero (Ed.), Encyclopedia of food sciences and nutrition (2nd ed., pp. 5222–5228). Academic Press.
Dunphy, B. J., Wattsand, E., & Ragg, N. L. (2015). Identifying thermally-stressed adult green-lipped mussels (Perna canaliculus Gmelin, 1791) via metabolomic profiling. American Malacological Bulletin, 33, 127–135.
Duong, D. N., Qin, J. G., Harris, J. O., Hoang, T. H., Bansemer, M. S., et al. (2016). Effects of dietary grape seed extract, green tea extract, peanut extract and vitamin C supplementation on metabolism and survival of greenlip abalone (Haliotis laevigata Donovan) cultured at high temperature. Aquaculture, 464, 364–373. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.aquaculture.2016.07.011
Ellington, W. R. (1983). The recovery from anaerobic metabolism in invertebrates. Journal of Experimental Zoology, 228, 431–444.
Estes, J. A., Lindbergand, D. R., & Wray, C. (2005). Evolution of large body size in abalones (Haliotis): patterns and implications. Paleobiology, 31, 591–606.
FAO. (2021a). Global aquaculture production 1950–2019 (online query). FAO. Retrieved April 14, 2021, from http://www.fao.org/fishery/statistics/global-aquaculture-production/query/en.
FAO. (2021b). Global Capture Production 1950–2019 (online query). Retrieved April 14, 2021, from http://www.fao.org/fishery/statistics/global-capture-production/query/en
Farcy, E., Serpentini, A., Fiévetand, B., & Lebel, J.-M. (2007). Identification of cDNAs encoding HSP70 and HSP90 in the abalone Haliotis tuberculata: Transcriptional induction in response to thermal stress in hemocyte primary culture. Comparative Biochemistry and Physiology Part b: Biochemistry and Molecular Biology, 146, 540–550.
Frölicher, T. L., Fischer, E. M., & Gruber, N. (2018). Marine heatwaves under global warming. Nature, 560, 360–364. https://doi.org/10.1038/s41586-018-0383-9
Gattuso, J.-P., Magnan, A. K., Bopp, L., Cheung, W. W., Duarte, C. M., et al. (2018). Ocean solutions to address climate change and its effects on marine ecosystems. Frontiers in Marine Science, 5, 337.
Gilroy, A., & Edwards, S. J. (1998). Optimum temperature for growth of Australian abalone: Preferred temperature and critical thermal maximum for blacklip abalone, Haliotis rubra (Leach), and greenlip abalone, Haliotis laevigata (Leach). Aquaculture Research, 29, 481–485. https://doi.org/10.1046/j.1365-2109.1998.00241.x
González-Domínguez, R., González-Domínguez, Á., Sayagoand, A., & Fernández-Recamales, Á. (2020). Recommendations and best practices for standardizing the pre-analytical processing of blood and urine samples in metabolomics. Metabolites, 10, 229.
Gornati, R., Maisano, M., Pirrone, C., Cappello, T., Rossi, F., et al. (2019). Mesocosm system to evaluate BF-MBR efficacy in mitigating oily wastewater discharges: An integrated study on Mytilus galloprovincialis. Marine Biotechnology, 21, 773–790.
Grandiosa, R., Mérien, F., Young, T., Van Nguyen, T., Gutierrez, N., et al. (2018). Multi-strain probiotics enhance immune responsiveness and alters metabolic profiles in the New Zealand black-footed abalone (Haliotis iris). Fish & Shellfish Immunology, 82, 330–338. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.fsi.2018.08.034
Guo, G., McKenzie, E. J., Jones, M. B., Friesen, M., Zarate, E., et al. (2020). MassOmics: An R package of untargeted metabolomics Batch processing using the NIST Mass Spectral Library. The University of Auckland. Retrieved November 11, 2020, from https://htmlpreview.github.io/?https://github.com/MASHUOA/MassOmics/blob/master/README.html.
Gyawali, P., Karpe, A. V., Hillyer, K. E., Nguyen, T. V., Hewitt, J., et al. (2021). A multi-platform metabolomics approach to identify possible biomarkers for human faecal contamination in GreenshellTM mussels (Perna canaliculus). Science of the Total Environment. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.scitotenv.2021.145363
Hassel, B., Dahlberg, D., Mariussen, E., Goverud, I. L., Antal, E. A., et al. (2014). Brain infection with Staphylococcus aureus leads to high extracellular levels of glutamate, aspartate, γ-aminobutyric acid, and zinc. Journal of Neuroscience Research, 92, 1792–1800.
Hobday, A. J., Alexander, L. V., Perkins, S. E., Smale, D. A., Straub, S. C., et al. (2016). A hierarchical approach to defining marine heatwaves. Progress in Oceanography, 141, 227–238. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.pocean.2015.12.014
Huo, D., Sun, L., Zhang, L., Ru, X., Liu, S., et al. (2019). Metabolome responses of the sea cucumber Apostichopus japonicus to multiple environmental stresses: Heat and hypoxia. Marine Pollution Bulletin, 138, 407–420. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.marpolbul.2018.11.063
Hyotylainen, T., & Wiedmer, S. (2013). Chromatographic methods in metabolomics. Royal Society of Chemistry.
Jabs, T. (1999). Reactive oxygen intermediates as mediators of programmed cell death in plants and animals. Biochemical Pharmacology, 57, 231–245.
Jha, A. K., Huang, S.C.-C., Sergushichev, A., Lampropoulou, V., Ivanova, Y., et al. (2015). Network integration of parallel metabolic and transcriptional data reveals metabolic modules that regulate macrophage polarization. Immunity, 42, 419–430.
Jiang, Y., Jiao, H., Sun, P., Yinand, F., & Tang, B. (2020). Metabolic response of Scapharca subcrenata to heat stress using GC/MS-based metabolomics. PeerJ, 8, e8445.
Johnson, E. C. (2017). Aspartic acid reference module in biomedical sciences. Elsevier.
Kanehisa, M., & Goto, S. (2000). KEGG: Kyoto Encyclopedia of Genes and Genomes. Nucleic Acids Research, 28, 27–30.
Kang, H. Y., Lee, Y.-J., Song, W.-Y., Kim, T.-I., Lee, W.-C., et al. (2019). Physiological responses of the abalone Haliotis discus hannai to daily and seasonal temperature variations. Scientific Reports, 9, 8019. https://doi.org/10.1038/s41598-019-44526-3
Kyeong, D., Kim, J., Shin, Y., Subramaniyam, S., Kang, B.-C., et al. (2020). Expression of heat shock proteins in thermally challenged Pacific abalone Haliotis discus hannai. Genes. https://doi.org/10.3390/genes11010022
Liu, X., Ji, C., Zhao, J., Wang, Q., Li, F., et al. (2014). Metabolic profiling of the tissue-specific responses in mussel Mytilus galloprovincialis towards Vibrio harveyi challenge. Fish & Shellfish Immunology, 39, 372–377. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.fsi.2014.05.033
Lu, J., Shi, Y., Wang, S., Chen, H., Cai, S., et al. (2016). NMR-based metabolomic analysis of Haliotis diversicolor exposed to thermal and hypoxic stresses. Science of the Total Environment, 545, 280–288.
Mallet, A., Carverand, C., & Freeman, K. (1990). Summer mortality of the blue mussel in eastern Canada: Spatial, temporal, stock and age variation. Marine Ecology Progress Series, 67, 35–41.
MPI. (2019). Pāua stock assessments and status reports. Ministry of Primary Industries, Wellington, New Zealand. https://www.mpi.govt.nz/travel-and-recreation/fishing/fish-species/paua/. Accessed April 14 2021.
Nguyen, T. V., Alfaro, A., Arroyo, B. B., Leonand, J. A. R., & Sonnenholzner, S. (2021). Metabolic responses of penaeid shrimp to acute hepatopancreatic necrosis disease caused by Vibrio parahaemolyticus. Aquaculture, 533, 736174. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.aquaculture.2020.736174
Nguyen, T. V., & Alfaro, A. C. (2020). Metabolomics investigation of summer mortality in New Zealand Greenshell™ mussels (Perna canaliculus). Fish & Shellfish Immunology, 106, 789–791. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.fsi.2020.08.022
Nguyen, V. T. (2020). Metabolomics Applications in Immunological Studies of Marine Molluscs. PhD Thesis, Auckland University of Technology. https://doi.org/10.13140/RG.2.2.10327.21929
Nguyen, V. T., & Alfaro, A. (2019). Targeted metabolomics to investigate antimicrobial activity of itaconic acid in marine molluscs. Metabolomics, 15, 97. https://doi.org/10.1007/s11306-019-1556-8
Nguyen, V. T., Alfaro, A., Merien, F., Lulijwaand, R., & Young, T. (2018a). Copper-induced immunomodulation in mussel (Perna canaliculus) haemocytes. Metallomics, 10, 965–978. https://doi.org/10.1039/c8mt00092a
Nguyen, V. T., Alfaro, A., Merienand, F., & Young, T. (2019). In vitro study of apoptosis in mussel (Perna canaliculus) haemocytes induced by lipopolysaccharide. Aquaculture, 503, 8–15. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.aquaculture.2018.12.086
Nguyen, V. T., Alfaro, A., Youngand, T., & Merien, F. (2018b). Tissue-specific immune responses to Vibrio sp. infection in mussels (Perna canaliculus): A metabolomics approach. Aquaculture, 500, 118–125. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.aquaculture.2018.09.061
Nguyen, V. T., Alfaro, A., Young, T., Raviand, S., & Merien, F. (2018c). Metabolomics study of immune responses of New Zealand greenshell™ mussels (Perna canaliculus) infected with pathogenic Vibrio sp. Marine Biotechnology, 20, 396–409. https://doi.org/10.1007/s10126-018-9804-x
Nguyen, V. T., Ragg, N. L. C., Alfaroand, A., & Zamora, L. N. (2020). Physiological stress associated with mechanical harvesting and transport of cultured mussels (Perna canaliculus): A metabolomics approach. Aquaculture, 529, 735657. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.aquaculture.2020.735657
Nikiforova, V. J., & Willmitzer, L. (2007). Network visualization and network analysis. In S. Baginsky & A. R. Fernie (Eds.), Plant systems biology (pp. 245–275). Birkhäuser Basel.
Pang, Z., Chong, J., Zhou, G., de Lima Morais, D. A., Chang, L., et al. (2021). MetaboAnalyst 5.0: Narrowing the gap between raw spectra and functional insights. Nucleic Acids Research. https://doi.org/10.1093/nar/gkab382
Park, K., Lee, J. S., Kang, J.-C., Kimand, J. W., & Kwak, I.-S. (2015). Cascading effects from survival to physiological activities, and gene expression of heat shock protein 90 on the abalone Haliotis discus hannai responding to continuous thermal stress. Fish & Shellfish Immunology, 42, 233–240. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.fsi.2014.10.036
Pearce, A. F., & Feng, M. (2013). The rise and fall of the “marine heat wave” off Western Australia during the summer of 2010/2011. Journal of Marine Systems, 111, 139–156.
Pinu, F. R., Beale, D. J., Paten, A. M., Kouremenos, K., Swarup, S., et al. (2019). Systems biology and multi-omics integration: Viewpoints from the metabolomics research community. Metabolites, 9, 76.
Pörtner, H.-O. (2010). Oxygen-and capacity-limitation of thermal tolerance: A matrix for integrating climate-related stressor effects in marine ecosystems. Journal of Experimental Biology, 213, 881–893.
Rist, M. J., Muhle-Goll, C., Görling, B., Bub, A., Heissler, S., et al. (2013). Influence of freezing and storage procedure on human urine samples in NMR-based metabolomics. Metabolites, 3, 243–258.
Roberts, S. D., Van Ruth, P. D., Wilkinson, C., Bastianelloand, S. S., & Bansemer, M. S. (2019). Marine heatwave, harmful algae blooms and an extensive fish kill event during 2013 in South Australia. Frontiers in Marine Science, 6, 610.
Rogatzki, M. J., Ferguson, B. S., Goodwinand, M. L., & Gladden, L. B. (2015). Lactate is always the end product of glycolysis. Frontiers in neuroscience, 9, 1–7. https://doi.org/10.3389/fnins.2015.00022
Romo, Z. M., Re, A. D., Díazand, F., & Mena, A. (2010). Physiological responses of pink abalone Haliotis corrugata (Gray, 1828) exposed to different combinations of temperature and salinity. Aquaculture Research, 41, 953–960. https://doi.org/10.1111/j.1365-2109.2009.02377.x
Roodt-Wilding, R. (2007). Abalone ranching: A review on genetic considerations. Aquaculture Research, 38, 1229–1241.
Salinger, M. J., Renwick, J., Behrens, E., Mullan, A. B., Diamond, H. J., et al. (2019). The unprecedented coupled ocean-atmosphere summer heatwave in the New Zealand region 2017/18: drivers, mechanisms and impacts. Environmental Research Letters, 14, 044023.
Shiel, B. P., Cooke, I. R., Hall, N. E., Robinsonand, N. A., & Strugnell, J. M. (2020). Gene expression differences between abalone that are susceptible and resilient to a simulated heat wave event. Aquaculture, 526, 735317. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.aquaculture.2020.735317
Shiel, B. P., Hall, N. E., Cooke, I. R., Robinsonand, N. A., & Strugnell, J. M. (2015). De novo characterisation of the greenlip abalone transcriptome (Haliotis laevigata) with a focus on the heat shock protein 70 (HSP70) family. Marine Biotechnology, 17, 23–32.
Shiel, B. P., Hall, N. E., Cooke, I. R., & N. A. Robinsonand J. M. Strugnell,. (2017). Epipodial tentacle gene expression and predetermined resilience to summer mortality in the commercially important greenlip abalone, Haliotis laevigata. Marine Biotechnology, 19, 191–205.
Smart, K. F., Aggio, R. B., Van Houtteand, J. R., & Villas-Bôas, S. G. (2010). Analytical platform for metabolome analysis of microbial cells using methyl chloroformate derivatization followed by gas chromatography–mass spectrometry. Nature Protocols, 5, 1709.
Tannahill, G., Curtis, A., Adamik, J., Palsson-McDermott, E., McGettrick, A., et al. (2013). Succinate is an inflammatory signal that induces IL-1 [bgr] through HIF-1 [agr]. Nature, 496, 238–242.
Torreilles, J., Guérinand, M.-C., & Roch, P. (1996). Reactive oxygen species and defense mechanisms in marine bivalves. Comptes Rendus de L’academie des Sciences Serie III, Sciences de la vie, 319, 209–218.
Turban-Just, S., & Schramm, S. (1998). Stable carbon and nitrogen isotope ratios of individual amino acids give new insights into bone collagen degradation. Bulletin de la Société Géologique de France, 169, 109–114.
Vandepeer, M. (2006). Abalone Aquaculture Subprogram: Preventing summer mortality of abalone in aquaculture systems by understanding interactions between nutrition and water temperature. FRDC Final Report. Adelaide, Australia: SARDI Aquatic Sciences.
Venter, L., Mienie, L. J., van Rensburg, P. J. J., Mason, S., Vosloo, A., et al. (2018a). Uncovering the metabolic response of abalone (Haliotis midae) to environmental hypoxia through metabolomics. Metabolomics, 14, 49.
Venter, L., Mienie, L. J., Vosloo, A., Loots, D. T., Jansen van Rensburg, P., et al. (2019). Effect of proline-enriched abalone feed on selected metabolite levels of slow-growing adult Haliotis midae. Aquaculture Research, 50, 1057–1067.
Venter, L., Vosloo, A., Loots, D. T., Mienie, L. J., Jansen van Rensburg, P. J., et al. (2018b). Characterising the metabolic differences related to growth variation in farmed Haliotis midae. Aquaculture, 493, 144–152. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.aquaculture.2018.04.052
Venter, L., Young, T., Alfaroand, A. C., & Lindeque, J. Z. (2021). Establishing sampling confidence parameters: Effect of sampling and transport conditions on haemocyte and metabolite profiles of Greenshell mussels. Aquaculture, 538, 6538. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.aquaculture.2021.736538
Villas-Boas, S. G., Nielsen, J., Smedsgaard, J., Hansenand, M. A. E., & Roessner-Tunali, U. (2007). Metabolome analysis: An introduction. Wiley.
Vohmann, A., Borcherding, J., Kureck, A., Bij de Vaate, A., Arndt, H., et al. (2010). Strong body mass decrease of the invasive clam Corbicula fluminea during summer. Biological Invasions, 12, 53–64.
Wang, J., Dong, B., Yuand, Z.-X., & Yao, C.-L. (2018). The impact of acute thermal stress on green mussel Perna viridis: Oxidative damage and responses. Comparative Biochemistry and Physiology Part a: Molecular & Integrative Physiology, 222, 7–15. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.cbpa.2018.04.001
Wang, N., Whang, I., Leeand, J.-S., & Lee, J. (2011). Molecular characterization and expression analysis of a heat shock protein 90 gene from disk abalone (Haliotis discus). Molecular Biology Reports, 38, 3055–3060.
Xia, J., & Wishart, D. S. (2010). MetPA: A web-based metabolomics tool for pathway analysis and visualization. Bioinformatics, 26, 2342–2344.
Xiao, J., Ford, S. E., Yang, H., Zhang, G., Zhang, F., et al. (2005). Studies on mass summer mortality of cultured zhikong scallops (Chlamys farreri Jones et Preston) in China. Aquaculture, 250, 602–615. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.aquaculture.2005.05.002
Xin, L., Zhang, H., Du, X., Li, Y., Li, M., et al. (2016). The systematic regulation of oyster CgIL17-1 and CgIL17-5 in response to air exposure. Developmental & Comparative Immunology, 63, 144–155.
Xu, F., Gaoand, T., & Liu, X. (2020). Metabolomics adaptation of juvenile Pacific abalone Haliotis discus hannai to heat stress. Scientific Reports, 10, 6353. https://doi.org/10.1038/s41598-020-63122-4
You, W., Guo, Q., Fan, F., Ren, P., Luo, X., et al. (2015). Experimental hybridization and genetic identification of Pacific abalone Haliotis discus hannai and green abalone H. fulgens. Aquaculture, 448, 243–249. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.aquaculture.2015.05.043
Zhang, X., Li, Y., Sun, Y., Guo, M., Feng, J., et al. (2020). Regulatory effect of heat shock transcription factor-1 gene on heat shock proteins and its transcriptional regulation analysis in small abalone Haliotis diversicolor. BMC Molecular and Cell Biology, 21, 1–12.
Zurburg, W., & Ebberink, R. (1980). Flexibility in anaerobic metabolism in Mytilus edulis L.I organ specific differences in ATP-generating systems. In R. Gilles (Ed.), Animals and environmental fitness physiological and biochemical aspects of adaptation and ecology (pp. 55–56). Elsevier.
Acknowledgements
We are thankful to Nick Cameron and Jeremy Cooper for providing abalone samples from the Chatham Islands. We are grateful for the technical support of the Aquaculture Biotechnology Research Group members at the Auckland University of Technology.
Funding
This project was partly funded by a grant from the Tasmanian Government Abalone Industry Reinvestment Fund (2020/43) and the Aquaculture Biotechnology Research Group at the Auckland University of Technology, Auckland, New Zealand.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Contributions
TVN, CM and AA conceived and designed research. TVN and EF conducted experiments. TVN and DC analyzed samples. TVN and DB processed analyzed data. TVA wrote the manuscript. All authors edited and approved the manuscript.
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Conflict of interest
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
Ethical approval
This article does not contain any studies with human and/or animal participants performed by any of the authors.
Consent to participate
Informed consent was obtained from all individual participants included in the study.
Consent for publication
Not applicable.
Additional information
Publisher's Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Supplementary Information
Below is the link to the electronic supplementary material.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Nguyen, T.V., Alfaro, A., Frost, E. et al. Investigating the biochemical effects of heat stress and sample quenching approach on the metabolic profiling of abalone (Haliotis iris). Metabolomics 18, 7 (2022). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11306-021-01862-8
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11306-021-01862-8