Abstract
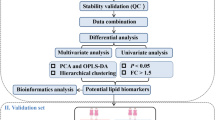
Biological requirements for tumor cell proliferation include the sustained increase of structural, energetic, signal transduction and biosynthetic precursors. Because lipids participate in the self-assembly of phospholipids to form biological membranes, they play important roles in membrane construction, energy storage, and cell signaling. We hypothesized that the differences in lipids between malignant ovarian carcinomas, benign ovarian tumors and normal controls could be reflected in the bio-fluids. A total of 215 pre-operative plasma samples were collected from 139 epithelial ovarian cancer (EOC), 38 benign ovarian tumor (BOT) and 38 uterine fibroid (UF) patients; these samples were then characterized by lipid profiling using ultra performance liquid chromatography/electrospray ionization mass spectrometry (UPLC–MS). The lipid profiles of the EOC and control samples (BOT/UF) as well as the different stages and histological subtypes of EOC were compared. Differentially expressed lipids were categorized as glycerophospholipids, sphingolipids and glyceroglycolipids and were found to be linked with three pathways. Almost all glycerophospholipids were down-regulated, especially phosphatidylcholine and phosphoethanolamine plasmalogens, whereas sphingolipids were up-regulated in the EOC patients compared to the controls. Lipids associated with pathological stage and histological subtype were also identified. We further identified five diagnostic lipids that were complementary to CA125. The predictive accuracy of five diagnostic lipids together with CA125 was higher than that of CA125 alone when distinguishing EOC and BOT/UF. In the future, the differential lipids identified may provide biologists with additional information regarding lipid metabolism and guide clinicians in making individualized therapeutic decisions if these results are confirmed in a larger study.




Similar content being viewed by others
References
Anderson, G. L., et al. (2010). Assessing lead time of selected ovarian cancer biomarkers: a nested case–control study. Journal of the National Cancer Institute, 102, 26–38. doi:10.1093/jnci/djp438.
Arana, L., Gangoiti, P., Ouro, A., Trueba, M., & Gomez-Munoz, A. (2010). Ceramide and ceramide 1-phosphate in health and disease. Lipids Health Dis, 9, 15. doi:10.1186/1476-511X-9-15.
Barber, M. N., et al. (2012). Plasma lysophosphatidylcholine levels are reduced in obesity and type 2 diabetes. PLoS One, 7, e41456. doi:10.1371/journal.pone.0041456.
Berkenblit, A., & Cannistra, S. A. (2005). Advances in the management of epithelial ovarian cancer. Journal of Reproductive Medicine, 50, 426–438.
Brautigam, C., et al. (1996). Plasmalogen phospholipids in plasma lipoproteins of normolipidemic donors and patients with hypercholesterolemia treated by LDL apheresis. Atherosclerosis, 119, 77–88.
Braverman, N. E., & Moser, A. B. (2012). Functions of plasmalogen lipids in health and disease. Biochimica et Biophysica Acta, 1822, 1442–1452. doi:10.1016/j.bbadis.2012.05.008.
Chen, S., et al. (2013). Serum lipid profiling of patients with chronic hepatitis B, cirrhosis, and hepatocellular carcinoma by ultra fast LC/IT-TOF MS. Electrophoresis, 34, 2848–2856.
Dutta, S., Wang, F. Q., Phalen, A., & Fishman, D. A. (2010). Biomarkers for ovarian cancer detection and therapy. Cancer Biology & Therapy, 9, 668–677.
Fan, L. J., et al. (2012). Identification of metabolic biomarkers to diagnose epithelial ovarian cancer using a UPLC/QTOF/MS platform. Acta Oncologica, 51, 473–479. doi:10.3109/0284186x.2011.648338.
Fhaner, C. J., Liu, S., Ji, H., Simpson, R. J., & Reid, G. E. (2012). Comprehensive lipidome profiling of isogenic primary and metastatic colon adenocarcinoma cell lines. Analytical Chemistry, 84, 8917–8926. doi:10.1021/ac302154g.
Gorke, R., Meyer-Base, A., Wagner, D., He, H. A., Emmett, M. R., & Conrad, C. A. (2010). Determining and interpreting correlations in lipidomic networks found in glioblastoma cells. BMC Systems Biology, 4(1), 126. doi:10.1186/1752-0509-4-126.
Guo, S., Wang, Y. M., Zhou, D., & Li, Z. L. (2014a). Significantly increased monounsaturated lipids relative to polyunsaturated lipids in six types of cancer microenvironment are observed by mass spectrometry imaging. Scientific Reports, 4, 5959. doi:10.1038/Srep05959.
Guo, S., et al. (2014b). Tissue imaging and serum lipidomic profiling for screening potential biomarkers of thyroid tumors by matrix-assisted laser desorption/ionization-Fourier transform ion cyclotron resonance mass spectrometry. Analytical and Bioanalytical Chemistry, 406, 4357–4370. doi:10.1007/s00216-014-7846-0.
Jemal, A., Bray, F., Center, M. M., Ferlay, J., Ward, E., & Forman, D. (2011). Global Cancer Statistics. CA: A Cancer Journal for Clinicians, 61, 69–90.
Jemal, A., Siegel, R., Xu, J., & Ward, E. (2010). Cancer statistics, 2010. CA: A Cancer Journal for Clinicians, 60, 277–300. doi:10.3322/caac.20073.
Jove, M., et al. (2013). Lipidomic and metabolomic analyses reveal potential plasma biomarkers of early atheromatous plaque formation in hamsters. Cardiovascular Research, 97, 642–652. doi:10.1093/cvr/cvs368.
Kang, S., et al. (2011). Alteration in lipid and protein profiles of ovarian cancer: similarity to breast cancer. International Journal of Gynecological Cancer, 21, 1566–1572. doi:10.1097/IGC.0b013e318226c5f5.
Ke, C., et al. (2015). Large-scale profiling of metabolic dysregulation in ovarian cancer. International Journal of Cancer, 136, 516–526. doi:10.1002/ijc.29010.
Kishi, Y., et al. (2006). Autotaxin is overexpressed in glioblastoma multiforme and contributes to cell motility of glioblastoma by converting lysophosphatidylcholine to lysophosphatidic acid. Journal of Biological Chemistry, 281, 17492–17500. doi:10.1074/jbc.M601803200.
Koybasi, S., et al. (2004). Defects in cell growth regulation by C18:0-ceramide and longevity assurance gene 1 in human head and neck squamous cell carcinomas. Journal of Biological Chemistry, 279, 44311–44319. doi:10.1074/jbc.M406920200.
Kurian, A. W., Balise, R. R., McGuire, V., & Whittemore, A. S. (2005). Histologic types of epithelial ovarian cancer: have they different risk factors? Gynecologic Oncology, 96, 520–530. doi:10.1016/j.gygno.2004.10.037.
Lahiri, S., & Futerman, A. H. (2007). The metabolism and function of sphingolipids and glycosphingolipids. Cellular and Molecular Life Sciences, 64, 2270–2284. doi:10.1007/s00018-007-7076-0.
Lengyel, E. (2010). Ovarian cancer development and metastasis. American Journal of Pathology, 177, 1053–1064. doi:10.2353/ajpath.2010.100105.
Liu, D., Nagan, N., Just, W. W., Rodemer, C., Thai, T. P., & Zoeller, R. A. (2005). Role of dihydroxyacetonephosphate acyltransferase in the biosynthesis of plasmalogens and nonether glycerolipids. Journal of Lipid Research, 46, 727–735. doi:10.1194/jlr.M400364-JLR200.
Liu, S., et al. (2009). Expression of autotaxin and lysophosphatidic acid receptors increases mammary tumorigenesis, invasion, and metastases. Cancer Cell, 15, 539–550. doi:10.1016/j.ccr.2009.03.027.
Mansilla, M. C., Cybulski, L. E., Albanesi, D., & de Mendoza, D. (2004). Control of membrane lipid fluidity by molecular thermosensors. Journal of Bacteriology, 186, 6681–6688. doi:10.1128/JB.186.20.6681-6688.2004.
McCluggage, W. G. (2011). Morphological subtypes of ovarian carcinoma: a review with emphasis on new developments and pathogenesis. Pathology, 43, 420–432. doi:10.1097/PAT.0b013e328348a6e7.
Memarzadeh, S., & Berek, J. S. (2001). Advances in the management of epithelial ovarian cancer. Journal of Reproductive Medicine, 46, 621–629. discussion 629-30.
Min, H. K., Lim, S., Chung, B. C., & Moon, M. H. (2011). Shotgun lipidomics for candidate biomarkers of urinary phospholipids in prostate cancer. Analytical and Bioanalytical Chemistry, 399, 823–830. doi:10.1007/s00216-010-4290-7.
Moyer, V. A., & Force, U. S. P. S. T. (2012). Screening for ovarian cancer: U.S. Preventive Services Task Force reaffirmation recommendation statement. Annals of Internal Medicine, 157, 900–904. doi:10.7326/0003-4819-157-11-201212040-00539.
Nosov, V., et al. (2009). Validation of serum biomarkers for detection of early-stage ovarian cancer. American Journal of Obstetrics and Gynecology, 200(639), e1–e5. doi:10.1016/j.ajog.2008.12.042.
Partridge, E., et al. (2009). Results from four rounds of ovarian cancer screening in a randomized trial. Obstetrics and Gynecology, 113, 775–782. doi:10.1097/AOG.0b013e31819cda77.
Piver, M. S., Malfetano, J., Baker, T. R., & Hempling, R. E. (1992). Five-year survival for stage IC or stage I grade 3 epithelial ovarian cancer treated with cisplatin-based chemotherapy. Gynecologic Oncology, 46, 357–360.
Ponnusamy, S., et al. (2010). Sphingolipids and cancer: ceramide and sphingosine-1-phosphate in the regulation of cell death and drug resistance. Future Oncology, 6, 1603–1624. doi:10.2217/fon.10.116.
Roberg-Larsen, H., et al. (2014). Highly automated nano-LC/MS-based approach for thousand cell-scale quantification of side chain-hydroxylated oxysterols. Journal of Lipid Research, 55, 1531–1536. doi:10.1194/jlr.D048801.
Schiffmann, S., et al. (2009). Ceramide synthases and ceramide levels are increased in breast cancer tissue. Carcinogenesis, 30, 745–752. doi:10.1093/carcin/bgp061.
Siti, H. N., Kamisah, Y., & Kamsiah, J. (2015). The role of oxidative stress, antioxidants and vascular inflammation in cardiovascular disease (a review). Vascular Pharmacology. doi:10.1016/j.vph.2015.03.005.
So, J., Navari, J., Wang, F. Q., & Fishman, D. A. (2004). Lysophosphatidic acid enhances epithelial ovarian carcinoma invasion through the increased expression of interleukin-8. Gynecologic Oncology, 95, 314–322. doi:10.1016/j.ygyno.2004.08.001.
Sutphen, R., et al. (2004). Lysophospholipids are potential biomarkers of ovarian cancer. Cancer Epidemiology Biomarkers & Prevention, 13, 1185–1191.
Tepper, A. D., Ruurs, P., Wiedmer, T., Sims, P. J., Borst, J., & van Blitterswijk, W. J. (2000). Sphingomyelin hydrolysis to ceramide during the execution phase of apoptosis results from phospholipid scrambling and alters cell-surface morphology. Journal of Cell Biology, 150, 155–164.
Tessitore, L., Cui, Z., & Vance, D. E. (1997). Transient inactivation of phosphatidylethanolamine N-methyltransferase-2 and activation of cytidine triphosphate: phosphocholine cytidylyltransferase during non-neoplastic liver growth. Biochemical Journal, 322(Pt 1), 151–154.
Tessitore, L., et al. (2003). Expression of phosphatidylethanolamine N-methyltransferase in human hepatocellular carcinomas. Oncology, 65, 152–158.
Urbanczyk-Wochniak, E., et al. (2003). Parallel analysis of transcript and metabolic profiles: a new approach in systems biology. EMBO Reports, 4, 989–993. doi:10.1038/sj.embor.embor944.
Vance, D. E., Walkey, C. J., & Cui, Z. (1997). Phosphatidylethanolamine N-methyltransferase from liver. Biochimica et Biophysica Acta, 1348, 142–150.
Wu, J. M., et al. (2010). Autotaxin expression and its connection with the TNF-α-NF-κB axis in human hepatocellular carcinoma. Molecular Cancer, 9, 71. doi:10.1186/1476-4598-9-71.
Zhang, T., et al. (2012). Discrimination between malignant and benign ovarian tumors by plasma metabolomic profiling using ultra performance liquid chromatography/mass spectrometry. Clinica Chimica Acta, 413, 861–868. doi:10.1016/j.cca.2012.01.026.
Zhou, X. C., Mao, J. H., He, Z., & Henegar, J. (2010). Lipidomics in identifying lipid biomarkers of prostate cancer. The FASEB Journal, 24, 354–356.
Zhou, X., et al. (2012). Identification of plasma lipid biomarkers for prostate cancer by lipidomics and bioinformatics. PLoS One, 7, e48889. doi:10.1371/journal.pone.0048889.
Acknowlegments
This work has received financial support from the National Natural Science Foundation of China (81473072), National Natural Science Foundation of Heilonglong Jiang Province (QC2015098) and Wu LianDe Youth Innovation Fund (WLD-QN1105).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding authors
Ethics declarations
Conflict of interest
No potential conflict of interest.
Ethical approval
All procedures performed in studies involving human participants were in accordance with the ethical standards of the institutional and/or national research committee and with the 1964 Helsinki declaration and its later amendments or comparable ethical standards.
Additional information
Yan Hou and Junnan Li have contributed equally to this work.
Kang Li is the first corresponding author and Ge Lou is the second corresponding author.
Electronic supplementary material
Below is the link to the electronic supplementary material.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Hou, Y., Li, J., Xie, H. et al. Differential plasma lipids profiling and lipid signatures as biomarkers in the early diagnosis of ovarian carcinoma using UPLC-MS. Metabolomics 12, 18 (2016). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11306-015-0891-7
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11306-015-0891-7