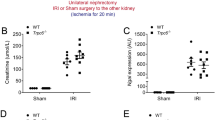
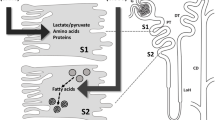
Abstract
Acute kidney injury (AKI) is a critical health issue with high mortality and morbidity rates in hospitalized individuals. The complex pathophysiology and underlying health conditions further complicate AKI management. Growing evidence suggests the pivotal role of ion channels in AKI progression, through promoting tubular cell death and altering immune cell functions. Among these channels, P2X purinergic receptors emerge as key players in AKI pathophysiology. P2X receptors gated by adenosine triphosphate (ATP), exhibit increased extracellular levels of ATP during AKI episodes. More importantly, certain P2X receptor subtypes upon activation exacerbate the situation by promoting the release of extracellular ATP. While therapeutic investigations have primarily focused on P2X4 and P2X7 subtypes in the context of AKI, while understanding about other subtypes still remains limited. Whilst some P2X antagonists show promising results against different types of kidney diseases, their role in managing AKI remains unexplored. Henceforth, understanding the intricate interplay between P2X receptors and AKI is crucial for developing targeted interventions. This review elucidates the functional alterations of all P2X receptors during normal kidney function and AKI, offering insights into their involvement in AKI. Notably, we have highlighted the current knowledge of P2X receptor antagonists and the possibilities to use them against AKI in the future. Furthermore, the review delves into the pathways influenced by activated P2X receptors during AKI, presenting potential targets for future therapeutic interventions against this critical condition.

Similar content being viewed by others
Data availability
No datasets were generated or analysed during the current study.
References
Mehta RL et al (2015) International society of nephrology’s 0by25 initiative for acute kidney injury (zero preventable deaths by 2025): a human rights case for nephrology. The Lancet 385(9987):2616–2643
Wilhelm K et al (2010) Graft-versus-host disease is enhanced by extracellular ATP activating P2X7R. Nat Med 16(12):1434–1438
Sluyter R et al (2023) Purinergic signalling in graft-versus-host disease. Curr Opin Pharmacol 68:102346
Bailey MA, Unwin RJ, Shirley DG (2012) P2X receptors and kidney function. Wiley Interdisciplinary Reviews: Membrane Transport and Signaling 1(4):503–511
Zhang W et al (2022) The role of the superior cervical sympathetic ganglion in ischemia reperfusion-induced acute kidney injury in rats. Front Med 9:792000
Han SJ et al (2020) P2X4 receptor exacerbates ischemic AKI and induces renal proximal tubular NLRP3 inflammasome signaling. FASEB J 34(4):5465–5482
Qian Y et al (2021) P2X7 receptor signaling promotes inflammation in renal parenchymal cells suffering from ischemia-reperfusion injury. Cell Death Dis 12(1):132
Burnstock G, Knight GE (2018) The potential of P2X7 receptors as a therapeutic target, including inflammation and tumour progression. Purinergic Signalling 14(1):1–18
Pichler R et al (2017) Immunity and inflammation in diabetic kidney disease: translating mechanisms to biomarkers and treatment targets. Am J Physiol Renal Physiol 312(4):F716–F731
Mahmood A, Iqbal J (2022) Purinergic receptors modulators: an emerging pharmacological tool for disease management. Med Res Rev 42(4):1661–1703
Illes P et al (2021) Update of P2X receptor properties and their pharmacology: IUPHAR review 30. Br J Pharmacol 178(3):489–514
Osmond DA, Inscho EW (2010) P2X(1) receptor blockade inhibits whole kidney autoregulation of renal blood flow in vivo. Am J Physiol Renal Physiol 298(6):F1360–F1368
Franco M et al (2017) Physiopathological implications of P2X1 and P2X7 receptors in regulation of glomerular hemodynamics in angiotensin II-induced hypertension. Am J Physiology-Renal Physiol 313(1):F9–F19
Rettinger J, Schmalzing G (2004) Desensitization masks nanomolar potency of ATP for the P2X1 receptor. J Biol Chem 279(8):6426–6433
Ennion SJ, Evans RJ (2001) Agonist-stimulated internalisation of the ligand‐gated ion channel P2X1 in rat vas deferens. FEBS Lett 489(2–3):154–158
Bennetts FM et al (2022) The P2X1 receptor as a therapeutic target. Purinergic Signalling 18(4):421–433
Vial C, Evans RJ (2002) P2X1 receptor-deficient mice establish the native P2X receptor and a P2Y6-like receptor in arteries. Mol Pharmacol 62(6):1438–1445
Billaud M et al (2011) Pannexin1 regulates α1-adrenergic receptor– mediated vasoconstriction. Circul Res 109(1):80–85
Kluess HA et al (2005) Acidosis attenuates P2X purinergic vasoconstriction in skeletal muscle arteries. Am J Physiol Heart Circ Physiol 288(1):H129–H132
Mancinelli R et al (2014) Extracellular GTP is a potent water-transport regulator via aquaporin 5 plasma-membrane insertion in M1-CCD epithelial cortical collecting duct cells. Cell Physiol Biochem 33(3):731–746
Kuczeriszka M et al (2016) Influence of P2X receptors on renal medullary circulation is not altered by angiotensin II pretreatment. Pharmacol Rep 68:1230–1236
Wildman SS et al (2009) Nucleotides downregulate aquaporin 2 via activation of apical P2 receptors. J Am Soc Nephrol 20(7):1480–1490
Craigie E et al (2018) The renal and blood pressure response to low sodium diet in P2X4 receptor knockout mice. Physiological Rep 6(20):e13899
Burnstock G, M.A. Evans Lc Fau - Bailey, and Bailey MA (1573–9546 (Electronic)) Purinergic signalling in the kidney in health and disease.
Kim H et al (2017) The purinergic receptor P2X5 regulates inflammasome activity and hyper-multinucleation of murine osteoclasts. Sci Rep 7(1):196
Kim H et al (2018) The purinergic receptor P2X5 contributes to bone loss in experimental periodontitis. BMB Rep 51(9):468–473
Turner CM et al (2003) The pattern of distribution of selected ATP-sensitive P2 receptor subtypes in normal rat kidney: an immunohistological study. Cells Tissues Organs 175(2):105–117
Vallon V et al (2020) Extracellular nucleotides and P2 receptors in renal function. Physiol Rev 100(1):211–269
de Baaij JHF et al (2016) P2X6 knockout mice exhibit normal electrolyte homeostasis. PLoS ONE 11(6):e0156803
Hillman KA, Burnstock G, Unwin RJ (2005) The P2X7 ATP receptor in the kidney: a matter of life or death? Nephron Experimental Nephrology 101(1):e24–e30
Jiang L-H et al (2021) Structural basis for the functional properties of the P2X7 receptor for extracellular ATP. Purinergic Signalling 17(3):331–344
Di Virgilio F, Schmalzing G, Markwardt F (2018) The elusive P2X7 macropore. Trends Cell Biol 28(5):392–404
Serife C-S, Kemal S, Mehmet U (2009) P2X7 receptor activates multiple selective dye-permeation pathways in RAW 264.7 and human embryonic kidney 293 cells. Mol Pharmacol 76(6):1323
Gonçalves RG et al (2006) The role of purinergic P2X7 receptors in the inflammation and fibrosis of unilateral ureteral obstruction in mice. Kidney Int 70(9):1599–1606
Menzies RI et al (2013) Effect of P2X4 and P2X7 receptor antagonism on the pressure diuresis relationship in rats. Front Physiol 4:305
Feng W et al (2021) Restoration of afferent arteriolar autoregulatory behavior in ischemia-reperfusion injury in rat kidneys. Am J Physiology-Renal Physiol 320(3):F429–F441
Guan Z et al (2023) Mitochondria and renal microvascular dysfunction following ischemia-reperfusion in rats. Physiology 38(S1):5729680
Inscho EW et al (2003) Physiological role for P2X 1 receptors in renal microvascular autoregulatory behavior. J Clin Investig 112(12):1895–1905
Inscho EW et al (2004) Renal autoregulation in P2X1 knockout mice. Acta Physiol Scand 181(4):445–453
Menzies RI et al (2017) Purinergic signaling in kidney disease. Kidney Int 91(2):315–323
Davenport AJ et al (2021) Eliapixant is a selective P2X3 receptor antagonist for the treatment of disorders associated with hypersensitive nerve fibers. Sci Rep 11(1):19877
Gao L et al (2023) The ethanol extract of scutellaria baicalensis georgi attenuates complete Freund’s adjuvant (CFA)-induced inflammatory pain by suppression of P2X3 receptor. J Ethnopharmacol 116762.
Cao W et al (2016) Reno-cerebral reflex activates the renin-angiotensin system, promoting oxidative stress and renal damage after ischemia-reperfusion injury. Antioxid Redox Signal 27(7):415–432
Grisk O (2020) The sympathetic nervous system in acute kidney injury. Acta Physiol 228(2):e13404
Cui W-W et al (2022) P2X3-selective mechanism of gefapixant, a drug candidate for the treatment of refractory chronic cough. Comput Struct Biotechnol J 20:1642–1653
Richards D et al (2019) Action of MK-7264 (gefapixant) at human P2X3 and P2X2/3 receptors and in vivo efficacy in models of sensitisation. Br J Pharmacol 176(13):2279–2291
Birring SS et al (2021) P60 patient-reported improvements with gefapixant, a P2X3-receptor antagonist, over 52 weeks in two phase 3 clinical trials for refractory or unexplained chronic cough. BMJ Publishing Group Ltd.
Wei Y-z et al (2023) Gefapixant, a novel P2X3 antagonist, protects against post myocardial infarction cardiac dysfunction and remodeling via suppressing NLRP3 inflammasome. Curr Med Sci 43(1):58–68
Thomas D, Gibson PG (2022) Gefapixant for chronic cough. The Lancet 399(10328):886–887
Nussbaum JC et al (2022) Effects of renal impairment on the pharmacokinetics of gefapixant, a P2X3 receptor antagonist. J Clin Pharmacol 62(11):1435–1444
Martinez FJ et al (2021) Treatment of persistent cough in subjects with idiopathic pulmonary fibrosis (IPF) with gefapixant, a P2X3 antagonist, in a randomized, placebo-controlled clinical trial. Pulmonary Therapy 7(2):471–486
Abu-Zaid A et al (2021) Safety and efficacy of gefapixant, a novel drug for the treatment of chronic cough: a systematic review and meta-analysis of randomized controlled trials. Annals of Thoracic Medicine 16(2):127
Morice A et al (2021) Eliapixant (BAY 1817080), a P2X3 receptor antagonist, in refractory chronic cough: a randomised, placebo-controlled, crossover phase 2a study. Eur Respir J 58(5)
Klein S et al (2022) First-in‐human study of eliapixant (BAY 1817080), a highly selective P2X3 receptor antagonist: tolerability, safety and pharmacokinetics. Br J Clin Pharmacol 88(10):4552–4564
Friedrich C et al (2023) The P2X3 receptor antagonist filapixant in patients with refractory chronic cough: a randomized controlled trial. Respir Res 24(1):109
Chauret N et al (2023) Model-based dose selection for phase 3 trials of the selective P2X3 antagonist camlipixant in refractory chronic cough, in B69. Airway Injury and Repair: Mechanisms and Treatment. American Thoracic Society. A4058-A4058
McGarvey L et al (2023) Response in patient-reported cough severity in soothe, a phase 2b trial of camlipixant in refractory chronic cough, in A99. Clinical Trials in Chronic Lung Disease. American Thoracic Society. A2533-A2533
Kim MJ et al (2014) Exaggerated renal fibrosis in P2X4 receptor-deficient mice following unilateral ureteric obstruction. Nephrol Dialysis Transplantation 29(7):1350–1361
Chen K et al (2013) ATP-P2X4 signaling mediates NLRP3 inflammasome activation: a novel pathway of diabetic nephropathy. Int J Biochem Cell Biol 45(5):932–943
Coddou C et al (2019) Characterization of the antagonist actions of 5-BDBD at the rat P2X4 receptor. Neurosci Lett 690:219–224
D’Antongiovanni V et al (2022) Anti-inflammatory effects of novel P2X4 receptor antagonists, NC-2600 and NP-1815-PX, in a murine model of colitis. Inflammation 45(4):1829–1847
Teixeira JM et al (2019) Diabetes-induced neuropathic mechanical hyperalgesia depends on P2X4 receptor activation in dorsal root ganglia. Neuroscience 398:158–170
Koo TY et al (2017) The P2X7 receptor antagonist, oxidized adenosine triphosphate, ameliorates renal ischemia-reperfusion injury by expansion of regulatory T cells. Kidney Int 92(2):415–431
Rabadi M et al (2018) ATP induces PAD4 in renal proximal tubule cells via P2X7 receptor activation to exacerbate ischemic AKI. Am J Physiology-Renal Physiol 314(2):F293–F305
Arulkumaran N et al (2018) P2X7 receptor antagonism ameliorates renal dysfunction in a rat model of sepsis. Physiological Rep 6(5):e13622
El-Maadawy WH et al (2022) Probenecid induces the recovery of renal ischemia/reperfusion injury via the blockade of pannexin 1/P2X7 receptor axis. Life Sciences 308:120933
Thakur A et al (2023) Effect of probenecid on blood levels and renal elimination of furosemide and endogenous compounds in rats: discovery of putative organic anion transporter biomarkers. Biochem Pharmacol 218:115867
Doǧan E et al (2020) The role of NMDA receptors in the effect of purinergic P2X7 receptor on spontaneous seizure activity in WAG/Rij rats with genetic absence epilepsy. Front Neurosci-Switz 14
Marotta G et al (2020) Memantine derivatives as multitarget agents in Alzheimer’s disease. Molecules 25. https://doi.org/10.3390/molecules25174005
Jeong YH et al (2020) Mice lacking the purinergic receptor P2X5 exhibit defective inflammasome activation and early susceptibility to listeria monocytogenes. J Immunol 205(3):760–766
Kim H et al (2020) Methylosome protein 50 associates with the purinergic receptor P2X5 and is involved in osteoclast maturation. FEBS Lett 594(1):144–152
Dietrich F et al (2022) High P2X6 receptor expression in human bladder cancer predicts good survival prognosis. Mol Cell Biochem 477(8):2047–2057
Alvarez CL, Troncoso MF, Espelt MV (2022) Extracellular ATP and adenosine in tumor microenvironment: roles in epithelial–mesenchymal transition, cell migration, and invasion. J Cell Physiol 237(1):389–400
Collier JB, Schnellmann RG (2018) ERK1/2 regulates NAD + metabolism during acute kidney injury through microRNA-34a‐mediated NAMPT expression. FASEB J 32:562–565
Acknowledgements
ABG sincerely acknowledges the financial support provided by the Birla Institute of Technology and Science-Pilani, Pilani, for carrying out this work.
Funding
Not applicable.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Contributions
Swati Mishra: conducted literature research and wrote the manuscript. Vishwadeep Shelke: conceptualized, conducted literature research and co-wrote the manuscript. Neha Dagar: conducted literature research and co-wrote the manuscript. Maciej Lech: participated in designing the manuscript, edited, and prepared it for submission. Anil Bhanudas Gaikwad: conceptualized, designed and drafted the manuscript. All authors read and approved the final manuscript.
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Ethical approval
Not applicable.
Clinical trial number
Not applicable.
Competing interests
The authors declare no competing interests.
Additional information
Publisher’s Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Rights and permissions
Springer Nature or its licensor (e.g. a society or other partner) holds exclusive rights to this article under a publishing agreement with the author(s) or other rightsholder(s); author self-archiving of the accepted manuscript version of this article is solely governed by the terms of such publishing agreement and applicable law.
About this article
Cite this article
Mishra, S., Shelke, V., Dagar, N. et al. Molecular insights into P2X signalling cascades in acute kidney injury. Purinergic Signalling (2024). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11302-024-09987-w
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11302-024-09987-w