Abstract
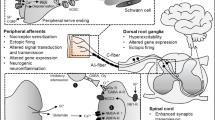
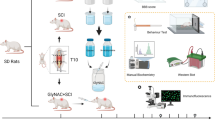
Diabetic neuropathic pain (DNP) is a common and destructive complication of diabetes mellitus. The discovery of effective therapeutic methods for DNP is vitally imperative because of the lack of effective treatments. Although 2 Hz electroacupuncture (EA) was a successful approach for relieving DNP, the mechanism underlying the effect of EA on DNP is still poorly understood. Here, we established a rat model of DNP that was induced by streptozotocin (STZ) injection. P2X4R was upregulated in the spinal cord after STZ-injection. The upregulation of P2X4R was mainly expressed on activated microglia. Intrathecal injection of a P2X4R antagonist or microglia inhibitor attenuated STZ-induced nociceptive thermal hyperalgesia and reduced the overexpression of brain-derived neurotrophic factor (BDNF), interleukin-1β (IL-1β) and tumor necrosis factor-α (TNF-α) in the spinal cord. We also assessed the effects of EA treatment on the pain hypersensitivities of DNP rats, and further investigated the possible mechanism underlying the analgesic effect of EA. EA relieved the hyperalgesia of DNP. In terms of mechanism, EA reduced the upregulation of P2X4R on activated microglia and decreased BDNF, IL-1β and TNF-α in the spinal cord. Mechanistic research of EA's analgesic impact would be beneficial in ensuring its prospective therapeutic effect on DNP as well as in extending EA's applicability.









Similar content being viewed by others
Data availability
The datasets generated during and/or analyzed during the current study are available from the corresponding author on reasonable request.
References
Fan W (2017) Epidemiology in diabetes mellitus and cardiovascular disease. Cardiovasc Endocrinol 6(1):8–16. https://doi.org/10.1097/XCE.0000000000000116
Abbott CA, Malik RA, van Ross ERE, Kulkarni J, Boulton AJM (2011) Prevalence and characteristics of painful diabetic neuropathy in a large community-based diabetic population in the U.K. Diabetes Care 34(10):2220–2224. https://doi.org/10.2337/dc11-1108
Deng Z, Li C, Liu C, Du E, Xu C (2018) Catestatin is involved in neuropathic pain mediated by purinergic receptor P2X4 in the spinal microglia of rats. Brain Res Bull 142:138–146. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.brainresbull.2018.07.003
Teng Y, Zhang Y, Yue S, Du E, Xu C (2019) Intrathecal injection of bone marrow stromal cells attenuates neuropathic pain via inhibition of P2X4R in spinal cord microglia. J Neuroinflammation 16(1):271. https://doi.org/10.1186/s12974-019-1631-0
Yan Y, Liang Y, Ding T, Chu H (2019) PI3K/Akt signaling pathway may be involved in MCP-1-induced P2X4R expression in cultured microglia and cancer-induced bone pain rats. Neurosci Lett 701:100–105. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.neulet.2019.02.024
Tsuda M (2016) Microglia in the spinal cord and neuropathic pain. J Diabetes Investig 7(1):17–26. https://doi.org/10.1111/jdi.12379
Tsuda M, Masuda T, Tozaki-Saitoh H, Inoue K (2013) Microglial regulation of neuropathic pain. J Pharmacol Sci 121(2):89–94. https://doi.org/10.1254/jphs.12r14cp
Tsuda M, Inoue K (2016) Neuron-microglia interaction by purinergic signaling in neuropathic pain following neurodegeneration. Neuropharmacology 104:76–81. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.neuropharm.2015.08.042
Ginhoux F, Lim S, Hoeffel G, Low D, Huber T (2013) Origin and differentiation of microglia. Front Cell Neurosci 7:45. https://doi.org/10.3389/fncel.2013.00045
Kim C, Lee JH, Kim W, Li D, Kim Y, Lee K, Kim SK (2016) The Suppressive Effects of Cinnamomi Cortex and Its Phytocompound Coumarin on Oxaliplatin-Induced Neuropathic Cold Allodynia in Rats. Molecules 21(9):1253. https://doi.org/10.3390/molecules21091253
Li J, Li X, Jiang X, Yang M, Yang R, Burnstock G, Xiang ZH, Yuan HB (2017) Microvesicles shed from microglia activated by the P2X7-p38 pathway are involved in neuropathic pain induced by spinal nerve ligation in rats. Purinergic Signal 13(1):13–26. https://doi.org/10.1007/s11302-016-9537-0
Ji RR, Xu ZZ, Gao YJ (2014) Emerging targets in neuroinflammation-driven chronic pain. Nat Rev Drug Discov 13(7):533–548. https://doi.org/10.1038/nrd4334
Inoue K, Tsuda M (2018) Microglia in neuropathic pain: cellular and molecular mechanisms and therapeutic potential. Nat Rev Neurosci 19(3):138–152. https://doi.org/10.1038/nrn.2018.2
Peltier A, Goutman SA, Callaghan BC (2014) Painful diabetic neuropathy. BMJ 348:1799. https://doi.org/10.1136/bmj.g1799
Snyder MJ, Gibbs LM, Lindsay TJ (2016) Treating Painful Diabetic Peripheral Neuropathy: An Update. Am Fam Physician 94(3):227–234
Lv ZT, Shen LL, Zhu B, Zhang ZQ, Ma CY, Huang GF, Yin J, Yu LL, Yu SY, Ding MQ, Li J, Yuan XC, He W, Jing XH, Li M (2019) Effects of intensity of electroacupuncture on chronic pain in patients with knee osteoarthritis: a randomized controlled trial. Arthritis Res Ther 21(1):120. https://doi.org/10.1186/s13075-019-1899-6
Seo SY, Lee KB, Shin JS, Lee J, Kim MR, Ha IH, Ko Y, Lee YJ (2017) Effectiveness of Acupuncture and Electroacupuncture for Chronic Neck Pain: A Systematic Review and Meta-Analysis. Am J Chin Med 45(8):1573–1595. https://doi.org/10.1142/S0192415X17500859
He XF, Wei JJ, Shou SY, Fang JQ, Jiang YL (2017) Effects of electroacupuncture at 2 and 100 Hz on rat type 2 diabetic neuropathic pain and hyperalgesia-related protein expression in the dorsal root ganglion. J Zhejiang Univ Sci B 18(3):239–248. https://doi.org/10.1631/jzus.B1600247
Shin KM, Lee S, Lee EY, Kim CH, Kang JW, Lee CK, Seo BN, Kim AR, Jung SY, Kwon O, Choi SM (2018) Electroacupuncture for Painful Diabetic Peripheral Neuropathy: A Multicenter, Randomized, Assessor-Blinded. Controlled Trial Diabetes Care 41(10):141–142. https://doi.org/10.2337/dc18-1254
Wang F, Ma J, Han F, Guo X, Meng L, Sun Y, Jin C, Duan H, Li H, Peng Y (2016) DL-3-n-butylphthalide delays the onset and progression of diabetic cataract by inhibiting oxidative stress in rat diabetic model. Sci Rep 6:19396. https://doi.org/10.1038/srep19396
Zhou R, Xu T, Liu X, Chen Y, Kong D, Tian H, Yue M, Huang D, Zeng J (2018) Activation of spinal dorsal horn P2Y13 receptors can promote the expression of IL-1β and IL-6 in rats with diabetic neuropathic pain. J Pain Res 11:615–628. https://doi.org/10.2147/JPR.S154437
Erbaş O, Oltulu F, Yılmaz M, Yavaşoğlu A, Taşkıran D (2016) Neuroprotective effects of chronic administration of levetiracetam in a rat model of diabetic neuropathy. Diabetes Res Clin Pract 114:106–116. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.diabres.2015.12.016
Manitz MP, Plümper J, Demir S, Ahrens M, Eßlinger M, Wachholz S, Eisenacher M, Juckel G, Friebe A (2016) Flow cytometric characterization of microglia in the offspring of PolyI: C treated mice. Brain Res 1636:172–182. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.brainres.2016.02.004
Hao L, Mi J, Song L, Guo Y, Li Y, Yin Y, Zhang C (2021) SLC40A1 Mediates Ferroptosis and Cognitive Dysfunction in Type 1 Diabetes. Neuroscience 463:216–226. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.neuroscience.2021.03.009
El-Hossary N, Hassanein H, El-Ghareeb AW, Issa H (2016) Intravenous vs intraperitoneal transplantation of umbilical cord mesenchymal stem cells from Wharton’s jelly in the treatment of streptozotocin-induced diabetic rats. Diabetes Res Clin Pract 121:102–111. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.diabres.2016.09.008
Qin Z, Wang L, Li G, Qian X, Zhang J, Guo Y, Liu G (2020) Analysis of the analgesic effects of tricyclic antidepressants on neuropathic pain, diabetic neuropathic pain, and fibromyalgia in rat models. Saudi J Biol Sci 27(9):2485–2490. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.sjbs.2020.05.043
Szkudelski T (2001) The mechanism of alloxan and streptozotocin action in B cells of the rat pancreas. Physiol Res 50(6):537–546
Morrow TJ (2004) Animal models of painful diabetic neuropathy: the STZ rat model. Curr Protoc Neurosci Chapter 9:Unit 9.18 https://doi.org/10.1002/0471142301.ns0918s29
Cheng KI, Wang HC, Chuang YT, Chou CW, Tu HP, Yu YC, Chang LL, Lai CS (2014) Persistent mechanical allodynia positively correlates with an increase in activated microglia and increased P-p38 mitogen-activated protein kinase activation in streptozotocin-induced diabetic rats. Eur J Pain 18(2):162–173. https://doi.org/10.1002/j.1532-2149.2013.00356.x
Sun JS, Yang YJ, Zhang YZ, Huang W, Li ZS, Zhang Y (2015) Minocycline attenuates pain by inhibiting spinal microglia activation in diabetic rats. Mol Med Rep 12(2):2677–2682. https://doi.org/10.3892/mmr.2015.3735
Colburn RW, DeLeo JA, Rickman AJ, Yeager MP, Kwon P, Hickey WF (1997) Dissociation of microglial activation and neuropathic pain behaviors following peripheral nerve injury in the rat. J Neuroimmunol 79(2):163–175. https://doi.org/10.1016/s0165-5728(97)00119-7
Schwab JM, Guo L, Schluesener HJ (2005) Spinal cord injury induces early and persistent lesional P2X4 receptor expression. J Neuroimmunol 163(1–2):185–189. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jneuroim.2005.02.016
Vázquez-Villoldo N, Domercq M, Martín A, Llop J, Gómez-Vallejo V, Matute C (2014) P2X4 receptors control the fate and survival of activated microglia. Glia 62(2):171–184. https://doi.org/10.1002/glia.22596
Zabala A, Vazquez-Villoldo N, Rissiek B, Gejo J, Martin A, Palomino A, Perez-Samartín A, Pulagam KR, Lukowiak M, Capetillo-Zarate E, Llop J, Magnus T, Koch-Nolte F, Rassendren F, Matute C, Domercq M (2018) P2X4 receptor controls microglia activation and favors remyelination in autoimmune encephalitis. EMBO Mol Med 10(8):8743. https://doi.org/10.15252/emmm.201708743
Zhang Z, Zhang ZY, Fauser U, Schluesener HJ (2008) Mechanical allodynia and spinal up-regulation of P2X4 receptor in experimental autoimmune neuritis rats. Neuroscience 152(2):495–501. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.neuroscience.2007.12.042
Butovsky O, Weiner HL (2018) Microglial signatures and their role in health and disease. Nat Rev Neurosci 19(10):622–635. https://doi.org/10.1038/s41583-018-0057-5
Salter MW, Stevens B (2017) Microglia emerge as central players in brain disease. Nat Med 23(9):1018–1027. https://doi.org/10.1038/nm.4397
Zhang J, Yi S, Xiao C, Li Y, Liu C, Jiang W, Yang C, Zhou T (2020) Asperosaponin VI inhibits LPS-induced inflammatory response by activating PPAR-γ pathway in primary microglia. Saudi J Biol Sci 27(11):3138–3144. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.sjbs.2020.07.013
Burnstock G (2008) Purinergic signalling and disorders of the central nervous system. Nat Rev Drug Discov 7(7):575–590. https://doi.org/10.1038/nrd2605
Khakh BS, North RA (2012) Neuromodulation by extracellular ATP and P2X receptors in the CNS. Neuron 76(1):51–69. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.neuron.2012.09.024
Inoue K (2021) Nociceptive signaling of P2X receptors in chronic pain states. Purinergic Signalling 17(1):41–47. https://doi.org/10.1007/s11302-020-09743-w
Tsuda M, Shigemoto-Mogami Y, Koizumi S, Mizokoshi A, Kohsaka S, Salter MW, Inoue K (2003) P2X4 receptors induced in spinal microglia gate tactile allodynia after nerve injury. Nature 424(6950):778–783. https://doi.org/10.1038/nature01786
Tsuda M, Kuboyama K, Inoue T, Nagata K, Tozaki-Saitoh H, Inoue K (2009) Behavioral phenotypes of mice lacking purinergic P2X4 receptors in acute and chronic pain assays. Mol Pain 5:28. https://doi.org/10.1186/1744-8069-5-28
Ulmann L, Hatcher JP, Hughes JP, Chaumont S, Green PJ, Conquet F, Buell GN, Reeve AJ, Chessell IP, Rassendren F (2008) Up-regulation of P2X4 receptors in spinal microglia after peripheral nerve injury mediates BDNF release and neuropathic pain. J Neurosci 28(44):11263–11268. https://doi.org/10.1523/JNEUROSCI.2308-08.2008
Tozaki-Saitoh H, Masuda J, Kawada R, Kojima C, Yoneda S, Masuda T, Inoue K, Tsuda M (2019) Transcription factor MafB contributes to the activation of spinal microglia underlying neuropathic pain development. Glia 67(4):729–740. https://doi.org/10.1002/glia.23570
Miao J, Ding M, Zhang A, Xiao Z, Qi W, Luo N, Di W, Tao Y, Fang Y (2012) Pleiotrophin promotes microglia proliferation and secretion of neurotrophic factors by activating extracellular signal-regulated kinase 1/2 pathway. Neurosci Res 74(3–4):269–276. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.neures.2012.09.001
Smith PA (2014) BDNF: no gain without pain? Neuroscience 283:107–123. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.neuroscience.2014.05.044
Trang T, Beggs S, Wan X, Salter MW (2009) P2X4-receptor-mediated synthesis and release of brain-derived neurotrophic factor in microglia is dependent on calcium and p38-mitogen-activated protein kinase activation. J Neurosci 29(11):3518–3528. https://doi.org/10.1523/JNEUROSCI.5714-08.2009
Ji RR, Nackley A, Huh Y, Terrando N, Maixner W (2018) Neuroinflammation and Central Sensitization in Chronic and Widespread Pain. Anesthesiology 129(2):343–366. https://doi.org/10.1097/ALN.0000000000002130
Gu Y, Chen S, Mo Y, Tu Y, Chen N, Zhao X, Li S, Yu Q, Dai Q, Wang J (2020) Electroacupuncture Attenuates CFA-Induced Inflammatory Pain by Regulating CaMKII. Neural Plast 2020:8861994. https://doi.org/10.1155/2020/8861994
Zhang RY, Zhu BF, Wang LK, Song Y, Zhao JG, Guo Y, Zhao L, Chen S (2020) Electroacupuncture alleviates inflammatory pain via adenosine suppression and its mediated substance P expression. Arq Neuropsiquiatr 78(10):617–623. https://doi.org/10.1590/0004-282X20200078
Zhao X, Liu L, Wang Y, Wang G, Zhao Y, Zhang Y (2019) Electroacupuncture enhances antioxidative signal pathway and attenuates neuropathic pain induced by chemotherapeutic paclitaxel. Physiol Res 68(3):501–510. https://doi.org/10.33549/physiolres.934084
Hu QQ, He XF, Ma YQ, Ma LQ, Qu SY, Wang HZ, Kang YR, Chen LH, Li X, Liu BY, Shao XM, Fang JF, Liang Y, Fang JQ, Jiang YL (2023) Dorsal root ganglia P2X4 and P2X7 receptors contribute to diabetes-induced hyperalgesia and the downregulation of electroacupuncture on P2X4 and P2X7. Purinergic Signal 19(1):29–41. https://doi.org/10.1007/s11302-022-09844-8
Lee JY, Choi HY, Park CS, Pyo MK, Yune TY, Kim GW, Chung SH (2019) GS-KG9 ameliorates diabetic neuropathic pain induced by streptozotocin in rats. J Ginseng Res 43(1):58–67. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jgr.2017.08.004
Chen XM, Xu J, Song JG, Zheng BJ, Wang XR (2015) Electroacupuncture inhibits excessive interferon-γ evoked up-regulation of P2X4 receptor in spinal microglia in a CCI rat model for neuropathic pain. Br J Anaesth 114(1):150–157. https://doi.org/10.1093/bja/aeu199
Funding
This research was supported by the National Natural Science Foundation of China (81804181 to X.F.H. and 81774389 to Y.L.J.), the Natural Science Foundation of Zhejiang Province of China (LY22H270006 to Y.L.J.), the Research Fund for Zhejiang Traditional Chinese Medicine University Affiliated Hospital (2022FSYYZZ09 to Y.L.J.), and the Key Laboratory of Acupuncture and Neurology of Zhejiang Province (2019E10011).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Contributions
X.H., J.F. and Y.J. conceived and designed the experiments. S.Q., H.W., Q.H., Y.K., X.L., L.C. and L.M. performed animal experiments. Q.H., Y.M., and L.M. performed western blotting experiments. S.Q. and H.W. performed immunofluorescence labeling experiments. B.L. and H.Z. performed data analysis. X.H., S.Q. and H.W. wrote the manuscript. X.S., Y.L., J.D. and B.L. performed revising. All authors reviewed and revised this manuscript and reviewed the final version of the manuscript.
Corresponding authors
Ethics declarations
Ethical approval
This study was permitted by The Animal Welfare Committee of Zhejiang Chinese Medical University (Approval number: IACUC-20190805-04). The institution agreed to participate and agreed to publish.
Competing interests
The authors declare no competing interests.
Additional information
Publisher's Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
The article has been submitted in preprint (https://doi.org/10.21203/rs.3.rs-1613857/v1).
Rights and permissions
Springer Nature or its licensor (e.g. a society or other partner) holds exclusive rights to this article under a publishing agreement with the author(s) or other rightsholder(s); author self-archiving of the accepted manuscript version of this article is solely governed by the terms of such publishing agreement and applicable law.
About this article
Cite this article
Qu, Sy., Wang, Hz., Hu, Qq. et al. Electroacupuncture may alleviate diabetic neuropathic pain by inhibiting the microglia P2X4R and neuroinflammation. Purinergic Signalling (2023). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11302-023-09972-9
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11302-023-09972-9