Abstract
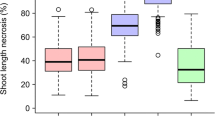
Fire blight, a bacterial disease caused by Erwinia amylovora, is the most devastating disease of apples and a major threat to apple production. Most commercial apple cultivars are susceptible to fire blight, driving the need to develop fire-blight-resistant cultivars. Although several major fire blight resistance QTLs have been identified from wild species of Malus, the challenges of breeding apples due to long juvenile phase and heterozygosity greatly limit their use. M. sieversii, the primary progenitor of domesticated apples, is one of the wild Malus species that is sexually compatible with M. domestica and has some favorable fruit quality traits. In this study, we performed QTL analysis on two F1 apple populations of M. domestica cv. “Royal Gala” × M. sieversii (GMAL4591 and GMAL4592) to identify fire blight resistance QTL. Parental linkage maps were constructed for each family using marker sets of approximately 20K GBS-SNPs. Phenotype data was collected from parents and progeny through controlled fire blight inoculations in the greenhouse for two subsequent years. A significant (P < 0.0001) moderate-effect fire blight resistance QTL on linkage group 7 of GMAL4591 was identified from the paternal parent M. sieversii “KAZ 95 17-14” (Msv_FB7). Msv_FB7 explains about 48–53% of the phenotyping variance across multiple years and time points. Additionally, a significant (P < 0.001) minor effect QTL explaining 18% of the phenotypic variance was identified in population GMAL4592 on LG10 from “Royal Gala.” We developed diagnostic SSR markers flanking the Msv_FB7 QTL to use in apple breeding. These findings have the potential to accelerate the development of fire-blight-resistant cultivars.




Similar content being viewed by others
Data availability
The genotype by sequencing SNP data sets for GMAL4591 and GMAL4592 to construct genetic maps are made available on the Dryad database (10.5061/dryad.15dv41p3c).
References
Antanaviciute L, Fernández-Fernández F, Jansen J et al (2012) Development of a dense SNP-based linkage map of an apple rootstock progeny using the Malus Infinium whole genome genotyping array. BMC Genomics 13:1–10. https://doi.org/10.1186/1471-2164-13-203
Baumgartner IO, Patocchi A, Franck L et al (2011) Fire blight resistance from “Evereste” and malus sieversii used in breeding for new high quality apple cultivars: strategies and results. Acta Hortic 896:391–398 https://www.ishs.org/ishs-article/896_56
Brachi B, Morris GP, Borevitz JO (2011) Genome-wide association studies in plants: the missing heritability is in the field. Genome Biol 12:1–8. https://doi.org/10.1186/gb-2011-12-10-232
Bradbury PJ, Zhang Z, Kroon DE et al (2007) TASSEL: software for association mapping of complex traits in diverse samples. Bioinformatics. https://doi.org/10.1093/bioinformatics/btm308
Broman KW, Wu H, Sen Ś, Churchill GA (2003) R/qtl: QTL mapping in experimental crosses. Bioinformatics 19:889–890. https://doi.org/10.1093/bioinformatics/btg112
Brown S (2012) Apple. Fruit Breed 329–367. https://doi.org/10.1007/978-1-4419-0763-9_10
Bus V, Ranatunga C, Gardiner S, Bassett H, Rikkerink E (2000) Marker assisted selection for pest and disease resistance in the New Zealand apple breeding programme. Actahort. https://www.actahort.org/books/538/538_95.htm
Bus VGM, Laurens FND, Van De Weg WE et al (2005) The Vh8 locus of a new gene-for-gene interaction between Venturia inaequalis and the wild apple Malus sieversii is closely linked to the Vh2 locus in Malus pumila R12740-7A. New Phytol 166:1035–1049. https://doi.org/10.1111/J.1469-8137.2005.01395.X
Calenge F, Drouet D, Denancé C et al (2005) Identification of a major QTL together with several minor additive or epistatic QTLs for resistance to fire blight in apple in two related progenies. Theor Appl Genet 111:128–135. https://doi.org/10.1007/S00122-005-2002-Z
Calenge F, Faure A, Goerre M et al (2004) Genetics and resistance quantitative trait loci (QTL) analysis reveals both broad-spectrum and isolate-specific QTL for scab resistance in an apple progeny challenged with eight isolates of Venturia inaequalis. APS Phytopathol. https://doi.org/10.1094/phyto.2004.94.4.370
Camacho C, Coulouris G, Avagyan V et al (2009) BLAST+: architecture and applications. BMC Bioinformatics 10:1–9. https://doi.org/10.1186/1471-2105-10-421
Cornille A, Giraud T, Smulders MJM et al (2014) The domestication and evolutionary ecology of apples. Trends Genet 30:57–65. https://doi.org/10.1016/J.TIG.2013.10.002
Cornille A, Gladieux P, Smulders MJM et al (2012) New insight into the history of domesticated apple: secondary contribution of the European wild apple to the genome of cultivated varieties. PLoS Genet 8:e1002703. https://doi.org/10.1371/JOURNAL.PGEN.1002703
Crosby JA, Janick J, Pecknold PC et al (1992) Breeding apples for scab resistance: 1945 – 1990. Acta Hortic:43–70. https://doi.org/10.17660/ACTAHORTIC.1992.317.5
Daccord N, Celton JM, Linsmith G et al (2017a) High-quality de novo assembly of the apple genome and methylome dynamics of early fruit development. Nat Genet. https://doi.org/10.1038/ng.3886
Daccord N, Celton JM, Linsmith G et al (2017b) High-quality de novo assembly of the apple genome and methylome dynamics of early fruit development. Nat Genet 497(49):1099–1106. https://doi.org/10.1038/ng.3886
Davies T, Watts S, McClure K et al (2022) Phenotypic divergence between the cultivated apple (Malus domestica) and its primary wild progenitor (Malus sieversii). PLoS One 17. https://doi.org/10.1371/journal.pone.0250751
Desnoues E, Norelli JL, Aldwinckle HS et al (2018a) Identification of novel strain-specific and environment-dependent minor QTLs linked to fire blight resistance in apples. Plant Mol Biol Report. https://doi.org/10.1007/s11105-018-1076-0
Desnoues E, Norelli JL, Aldwinckle HS et al (2018b) Identification of novel strain-specific and environment-dependent minor QTLs linked to fire blight resistance in apples. Plant Mol Biol Report 36:247–256. https://doi.org/10.1007/S11105-018-1076-0
Dougherty L, Wallis A, Cox K et al (2021) Phenotypic evaluation of fire blight outbreak in the USDA Malus Collection. Agron 11(144). https://doi.org/10.3390/AGRONOMY11010144
Duan N, Bai Y, Sun H et al (2017) (2017) Genome re-sequencing reveals the history of apple and supports a two-stage model for fruit enlargement. Nat Commun 81(8):1–11. https://doi.org/10.1038/s41467-017-00336-7
Durel CE, Denancé C, Brisset MN (2009) Two distinct major QTL for resistance to fire blight co-localize on linkage group 12 in apple genotypes “Evereste” and Malus floribunda clone 821. Genome. https://doi.org/10.1139/G08-111
Emeriewen O, Richter K, Kilian A et al (2014) Identification of a major quantitative trait locus for resistance to fire blight in the wild apple species Malus fusca. Mol Breed. https://doi.org/10.1007/s11032-014-0043-1
Elshire RJ, Glaubitz JC, Sun Q, Poland JA, Kawamoto K, Buckler ES, Mitchell SE (2011) A robust, simple genotyping-by-sequencing (GBS) approach for high diversity species. PloS One 6(5):e19379. https://doi.org/10.1371/journal.pone.0019379
Emeriewen OF, Peil A, Richter K et al (2017) Fire blight resistance of Malus ×arnoldiana is controlled by a quantitative trait locus located at the distal end of linkage group 12. Eur J Plant Pathol. https://doi.org/10.1007/s10658-017-1152-6
Emeriewen OF, Richter K, Flachowsky H et al (2021) Genetic analysis and fine mapping of the fire blight resistance locus of Malus ×arnoldiana on linkage group 12 reveal first candidate genes. Front Plant Sci 12:663. https://doi.org/10.3389/FPLS.2021.667133
Emeriewen OF, Richter K, Hanke MV et al (2015) The fire blight resistance QTL of Malus fusca (Mfu10) is affected but not broken down by the highly virulent Canadian Erwinia amylovora strain E2002A. Eur J Plant Pathol 141:631–635. https://doi.org/10.1007/s10658-014-0565-8
Emeriewen OF, Wöhner T, Flachowsky H, Peil A (2019) Malus hosts–Erwinia amylovora interactions: strain pathogenicity and resistance mechanisms. Front Plant Sci 10:551. https://doi.org/10.3389/FPLS.2019.00551
FAOSTAT (2020) Food and Agriculture Organization of the United Nations. FAOSTAT Stat Database. https://www.fao.org/faostat/en/
Fazio G (2021) Genetics, breeding, and genomics of apple rootstocks. Compendium of Plant Genomes. Springer International Publishing, pp 105–130. https://doi.org/10.1007/978-3-030-74682-7_6
Fazio G, Robinson TL, Aldwinckle HS (2015) The Geneva apple rootstock breeding program. Plant Breed Rev 39:379–424. https://doi.org/10.1002/9781119107743.CH8
Forsline PL, Aldwinckle HS (2004) Evaluation of Malus sieversii seedling populations for disease resistance and horticultural traits. Acta Hortic 663:529–534. https://doi.org/10.17660/ActaHortic.2004.663.92
Forsline PL, Luby JJ, Aldwinckle HS (2008) Fire blight incidence on Malus sieversii grown in New York and Minnesota. Acta Hortic 793:345–350. https://doi.org/10.17660/ACTAHORTIC.2008.793.51
Hanke M-V, Flachowsky H, Peil A, Hättasch C (2007) No flower no fruit – genetic potentials to trigger flowering in fruit trees. Global Science Books. https://www.semanticscholar.org/paper/No-Flower-no-Fruit-Genetic-Potentials-to-Trigger-in-Hanke/3f8b8c087eb9ea95902769867ea9dec37815a2d
Harshman JM, Evans KM, Allen H et al (2017) Fire blight resistance in wild accessions of Malus sieversii. Plant Dis 101. https://doi.org/10.1094/PDIS-01-17-0077-RE
Hokanson SC, McFerson JR, Forsline PL et al (1997) Collecting and managing wild Malus germplasm in its center of diversity. HortScience 32:173–176. https://doi.org/10.21273/HORTSCI.32.2.173
Hulce D, Li X, Snyder-Leiby T, Liu CSJ (2011) GeneMarker® genotyping software: tools to increase the statistical power of DNA fragment analysis. J Biomol Tech 22:S35
Janick J (2006) The PRI apple breeding program. HortScience 41:8–10. https://doi.org/10.21273/hortsci.41.1.8
Khan A, Gutierrez B, Chao CT, Singh J (2021) Origin of the domesticated apples. Compend Plant Genomes 383–394. https://doi.org/10.1007/978-3-030-74682-7_17
Khan A, Korban SS (2022) Breeding and genetics of disease resistance in temperate fruit trees: challenges and new opportunities. Theor Appl Genet 13511(135):3961–3985. https://doi.org/10.1007/S00122-022-04093-0
Khan MA, Duffy B, Gessler C, Patocchi A (2006a) QTL mapping of fire blight resistance in apple. Mol Breed 17:299–306. https://doi.org/10.1007/S11032-006-9000-Y
Khan MA, Duffy B, Gessler C, Patocchi A (2006b) QTL mapping of fire blight resistance in apple. Mol Breed. https://doi.org/10.1007/s11032-006-9000-y
Khan MA, Durel CE, Duffy B et al (2007a) Development of molecular markers linked to the “Fiesta” linkage group 7 major QTL for fire blight resistance and their application for marker-assisted selection. Genome 50:568–577. https://doi.org/10.1139/G07-033
Khan MA, Durel CE, Duffy B et al (2007b) Development of molecular markers linked to the “Fiesta” linkage group 7 major QTL for fire blight resistance and their application for marker-assisted selection. Genome 50:568–577. https://doi.org/10.1139/G07-033
Khan MA, Zhao YF, Korban SS (2013) Identification of genetic loci associated with fire blight resistance in Malus through combined use of QTL and association mapping. Physiol Plant. https://doi.org/10.1111/ppl.12068
Korban SS (1986) Interspecific hybridization in Malus. HortScience 21:41–48. https://doi.org/10.21273/HORTSCI.21.1.41B
Kostick SA, Norelli JL, Evans KM (2019) Novel metrics to classify fire blight resistance of 94 apple cultivars. Plant Pathol. https://doi.org/10.1111/ppa.13012
Kostick SA, Teh SL, Evans KM (2021) Contributions of reduced susceptibility alleles in breeding apple cultivars with durable resistance to fire blight. Plants, 10(409). https://doi.org/10.3390/PLANTS10020409
Le Roux PMF, Khan MA, Broggini GAL et al (2010a) Mapping of quantitative trait loci for fire blight resistance in the apple cultivars “Florina” and “Nova Easygro.”. Genome 53:710–722. https://doi.org/10.1139/G10-047
Le Roux PMF, Khan MA, Broggini GAL et al (2010b) Mapping of quantitative trait loci for fire blight resistance in the apple cultivars “Florina” and “Nova Easygro.”. Genome 53:710–722. https://doi.org/10.1139/G10-047
Lee B-Y, Kim M-S, Choi B-S, Nagano AJ, Au DWT, Wu RSS, Takehana Y, Lee J-S (2019) Construction of high-resolution RAD-seq based linkage map, anchoring reference genome, and QTL mapping of the sex chromosome in the marine medaka Oryzias melastigma. G3 (Bethesda, Md.) 9(11):3537–3545. https://doi.org/10.1534/g3.119.400708
Liebhard R, Koller B, Gianfranceschi L, Gessler C (2003) Creating a saturated reference map for the apple (Malus x domestica Borkh.) genome. Theor Appl Genet 106:1497–1508. https://doi.org/10.1007/s00122-003-1209-0
Loper JE (1991) Evaluation of streptomycin, oxytetracycline, and copper resistance of Erwinia amylovora isolated from pear orchards in Washington state. Plant Dis 75. https://doi.org/10.1094/pd-75-0287
Lorang JM, Sweat TA, Wolpert TJ (2007) Plant disease susceptibility conferred by a “resistance” gene. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A 104:14861–14866. https://doi.org/10.1073/PNAS.0702572104
Luby J, Forsline P, Aldwinckle H et al (2001) Silk road apples collection, evaluation, and utilization of Malus sieversii from Central Asia. HortScience 36:225–231. https://doi.org/10.21273/hortsci.36.2.225
Luby J, Forsline P, Aldwinckle H, Geibel M (1999) Silk road apples-collection, evaluation, and utilization of Malus sieversii from Central Asia. Ashs. https://journals.ashs.org/hortsci/view/journals/hortsci/36/2/article-p225.pdf
Luo F, Evans K, Norelli JL et al (2020) Prospects for achieving durable disease resistance with elite fruit quality in apple breeding. Tree Genet Genomes. https://doi.org/10.1007/s11295-020-1414-x
Mcmanus PS, Stockwell VO, Sundin GW, Jones AL (2002) Antibiotic use in plant agriculture. Annu Rev Phytopathol 40:443–465. https://doi.org/10.1146/annurev.phyto.40.120301.093927
Mendiburu F De, Yaseen M (2020) Agricolae: statistical procedures for agricultural research. R Packag version 14. https://cran.r-project.org/web/packages/agricolae/index.html
Migicovsky Z, Gardner KM, Richards C, Thomas Chao C, Schwaninger HR, Fazio G, Zhong G-Y, Myles S (2021) Genomic consequences of apple improvement. Horticulture Research 8(1):1–13. https://doi.org/10.1038/s41438-020-00441-7
Norelli JL, Jones AL, Aldwinckle HS (2003) Fire blight management in the twenty-first century: using new technologies that enhance host resistance in apple. Plant Dis. https://doi.org/10.1094/PDIS.2003.87.7.756
Norelli JL, Wisniewski M, Droby S (2014) Identification of a QTL for postharvest disease resistance to penicillium expansum in Malus sieversii. Acta Hortic 1053:199–203. https://doi.org/10.17660/ACTAHORTIC.2014.1053.21
Osborne J (2010) Improving your data transformations: applying the Box-Cox improving your data transformations: applying the Box-Cox transformation transformation. Pract Assess Res Eval 15:12. https://doi.org/10.7275/qbpc-gk17
Papp D, Gao L, Thapa R, et al (2020) Field apple scab susceptibility of a diverse Malus germplasm collection identifies potential sources of resistance for apple breeding. CABI Agric Biosci 2020 11 1:1–14. https://doi.org/10.1186/S43170-020-00017-4
Patocchi A, Frei A, Frey JE, Kellerhals M (2009) Towards improvement of marker assisted selection of apple scab resistant cultivars: Venturia inaequalis virulence surveys and standardization of molecular marker alleles associated with resistance genes. Mol Breed 24:337–347. https://doi.org/10.1007/S11032-009-9295-6
Peil A, Bus Vincent M, Geider K, Richter K, Flachowsky H, Hanke M-V (2009) Improvement of fire blight resistance in apple and pear. International Journal of Plant Breeding 3(1):1–27. https://www.openagrar.de/receive/openagrar_mods_00008206
Peil A, Emeriewen OF, Khan A et al (2021) Status of fire blight resistance breeding in Malus. J Plant Pathol 103:3–12. https://doi.org/10.1007/S42161-020-00581-8
Peil A, Flachowsky H, Hanke MV et al (2011) Inoculation of Malus × robusta 5 progeny with a strain breaking resistance to fire blight reveals a minor QTL on LG5. Acta Hortic 896:357–362. https://doi.org/10.17660/ACTAHORTIC.2011.896.49
Peil A, Garcia-Libreros T, Richter K et al (2007) Strong evidence for a fire blight resistance gene of Malus robusta located on linkage group 3. Plant Breed 126:470–475. https://doi.org/10.1111/j.1439-0523.2007.01408.x
Purcell S, Neale B, Todd-Brown K et al (2007a) PLINK: a tool set for whole-genome association and population-based linkage analyses. Am J Hum Genet. https://doi.org/10.1086/519795
Purcell S, Neale B, Todd-Brown K et al (2007b) PLINK: a tool set for whole-genome association and population-based linkage analyses. Am J Hum Genet 81:559–575. https://doi.org/10.1086/519795
Russo NL, Robinson TL, Fazio G, Aldwinckle HS (2007) Field evaluation of 64 apple rootstocks for orchard performance and fire blight resistance. HortScience horts 42(7):1517–1525. https://doi.org/10.21273/HORTSCI.42.7.1517
Sen Ś, Churchill GA (2001) A statistical framework for quantitative trait mapping. Genetics 159(1):371-387. https://doi.org/10.1093/GENETICS/159.1.371
Soufflet-Freslon V, Gianfranceschi L, Patocchi A, Durel CE (2008) Inheritance studies of apple scab resistance and identification of Rvi14, a new major gene that acts together with other broad-spectrum QTL. Genome 51:657–667. https://doi.org/10.1139/G08-046
Sun X, Jiao C, Schwaninger H et al (2020) (2020) Phased diploid genome assemblies and pan-genomes provide insights into the genetic history of apple domestication. Nat Genet 5212(52):1423–1432. https://doi.org/10.1038/s41588-020-00723-9
Untergasser A, Cutcutache I, Koressaar T et al (2012) Primer3—new capabilities and interfaces. Nucleic Acids Res 40:e115–e115. https://doi.org/10.1093/NAR/GKS596
van de Weg E, Di Guardo M, Jänsch M et al (2018a) Epistatic fire blight resistance QTL alleles in the apple cultivar ‘Enterprise’ and selection X-6398 discovered and characterized through pedigree-informed analysis. Mol Breed 38. https://doi.org/10.1007/s11032-017-0755-0
van de Weg E, Di Guardo M, Jänsch M et al (2018b) Epistatic fire blight resistance QTL alleles in the apple cultivar ‘Enterprise’ and selection X-6398 discovered and characterized through pedigree-informed analysis. Mol Breed 38:1–18. https://doi.org/10.1007/S11032-017-0755-0
van der Zwet T, Orolaza-Halbrendt N, Zeller W (2016) CHAPTER 2: spread and current distribution of fire blight. Fire Blight Hist Biol Manag 15–36. https://doi.org/10.1094/9780890544839.003
Van Ooijen JW (2004) MapQTL 5, Software for the Mapping of Quantitative Trait Loci in Experimental Populations. Kyazma BV, Wageningen. https://www.kyazma.nl/index.php/MapQTL/
Volk GM, Peace CP, Henk AD, Howard NP (2022) DNA profiling with the 20K apple SNP array reveals Malus domestica hybridization and admixture in M. sieversii, M. orientalis, and M. sylvestris genebank accessions. Front. Plant Sci 13:3968. https://doi.org/10.3389/fpls.2022.1015658/full
Wallin J, Bogdan M, Szulc PA et al (2021) Ghost QTL and hotspots in experimental crosses: novel approach for modeling polygenic effects. Genetics 217. https://doi.org/10.1093/GENETICS/IYAA041
Wallis A, Yannuzzi IM, Choi MW et al (2021) Investigating the distribution of strains of Erwinia amylovora and Streptomycin resistance in apple orchards in New York using clustered regularly interspaced short palindromic repeat profiles: a 6-year follow-up. Plant Dis 105:3554–3563. https://doi.org/10.1094/PDIS-12-20-2585-RE
Winslow C-EA, Broadhurst J, Buchanan RE et al (1920) The families and genera of the bacteria: final report of the Committee of the Society of American Bacteriologists on Characterization and Classification of Bacterial Types. J Bacteriol 5:191–229. https://doi.org/10.1128/JB.5.3.191-229.1920
Xu S (2003) Theoretical basis of the Beavis effect. Genetics 165:2259–2268. https://doi.org/10.1093/GENETICS/165.4.2259
Yang M, Che S, Zhang Y et al (2019) Universal stress protein in Malus sieversii confers enhanced drought tolerance. J Plant Res 132:825–837. https://doi.org/10.1007/S10265-019-01133-7
Yoder KS (2000) Effect of powdery mildew on apple yield and economic benefits of its management in Virginia. Plant Dis 84:1171–1176. https://doi.org/10.1094/PDIS.2000.84.11.1171
Acknowledgements
This research was funded by the New York State Department of Agriculture & Markets, Apple Research & Development Program (ARDP). We would like to acknowledge the USDA (United States Department of Agriculture) Plant Genetic Resources Unit (PGRU) in Geneva, New York, for providing the plant material. We would like to recognize Dr. Julliany Pereira Silva for helping establish and maintain the mapping populations in the greenhouse and to collect the first year of phenotype data.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Contributions
A.K. conceptualized, designed, and managed the project. R.T. and D.C-S. performed the experiments. R.T. performed all analysis and interpretation as well as drafted the manuscript. R.T., D.C-S., G-Y.Z., and A.K. revised and finalized the manuscript. All authors read and approved the final version.
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Competing interests
The authors declare no competing interests.
Additional information
Communicated by M. Troggio
Publisher’s note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Supplementary Information

Supplementary Figure 1.
A-D) Linkage map plots showing the centiMorgan (cM) distance per chromosome of the four parental linkage maps constructed for populations GMAL4591 (A-B) and GMAL4592 (C-D). E) A marker density plot for the paternal linkage map of GMAL4591 (B) showing regions in blue having lower density and regions in red having a higher density ranging from 0.9cM to 30cM. F) A regression plot showing the correlation of physical position in the Golden Delicious Double Haploid Genome (y-axis) and the cM genetic position of the paternal markers from GMAL4591 (x-axis). (PNG 7.13 mb)

Supplementary Figure 2.
The logarithm of the odds (LOD) plots to display regions of the four parental linkage maps that are significantly (P<0.0001) associated with the percent shoot lesion length (PSLL) across two years of fire blight infection data in two F1 populations (GMAL4591, GMAL4592). The x-axis shows the centimorgan position of the marker on the linkage map and the y-axis shows its LOD value from composite interval mapping (CIM) analysis on 17 linkage groups. The red threshold line represents the LOD cutoff of significance given P<0.0001. In the legend from top to bottom, the red line is the results from the area under the disease progress curve from the 2020 data, the orange is PSLL from 2018, the green is PSLL from 2019, light blue is PSLL (7dai) from 2020, purple is PSLL2 (10dai) from 2020, and pink is PSLL3 (15dai) from 2020. (PNG 1.54 mb)

Supplementary Figure 3.
Biplots of the fire blight percent shoot lesion length (PSLL1-3) and area under the disease progress curve of percent shoot lesion length (AUDPC PSLL) of 2020 plotted against PSLL 2019 for two F1 mapping populations (GMAL4591-top; GMAL4592-bottom). The blue line represents the regression of phenotypic values with the Pearson correlation value and p-value above each plot. For 2020 data, PSLL1, PSLL2, and PSLL3 represent the phenotypic value taken on 7, 10, and 15 dai, respectively. For 2019, PSLL 2019 was taken on 7 dai. (PNG 147 kb)

Supplementary Figure 4.
Q-Q plots of the residual values of fire blight percent shoot lesion length (PSLL1-3) and area under the disease progress curve of percent shoot lesion length (AUDPC PSLL) of 2020 and the PSLL of 2019 for two F1 mapping populations (GMAL4591-top; GMAL4592-bottom). The red line represents the reference line for a normal distribution. For 2020 data, PSLL1, PSLL2, and PSLL3 represent the phenotypic value taken on 7, 10, and 15 dai, respectively. For 2019, PSLL 2019 was taken on 7 dai. The data were transformed using the Box-Cox transformation, using an optimal lambda value of 0.6. (PNG 980 kb)
Supplemental Table 1.
Phenotypic variation for two years of fire blight inoculation data for the F1 apple populations GMAL4591 and GMAL4592. The mean, standard deviation and broad sense heritability (H2) are shown for the leaf length (LL), shoot length (SL), percent shoot lesion length (PSLL), and the area under the disease progress curve of the percent shoot lesion length (AUDPC PSLL). (DOCX 16 kb)
Supplemental Table 2.
Primer sequences and melting temperature (Tm) of the SSR markers linked to Msv_FB7 fire blight resistance QTL on linkage group (LG) 7 developed in this study for marker-assisted selection in apple breeding programs. The top sequence is the forward primer with the M13 tail in bold and underlined while the reverse primer is just below. (DOCX 13 kb)
Supplemental Table 3.
Table of the SSR marker name, genotype name, PI numbers, species, SSR fragment sizes in base pairs (bp) without the M13 tail, information on known fire blight resistance QTL for eight apple genotypes. Genotypes with multiple fragments have different fragment lengths separated by a slash. PI number is the plant introduction (unique identifier) from USDA-GRIN database. (DOCX 17 kb)
Rights and permissions
Springer Nature or its licensor (e.g. a society or other partner) holds exclusive rights to this article under a publishing agreement with the author(s) or other rightsholder(s); author self-archiving of the accepted manuscript version of this article is solely governed by the terms of such publishing agreement and applicable law.
About this article
Cite this article
Tegtmeier, R., Cobb-Smith, D., Zhong, GY. et al. Identification and marker development of a moderate-effect fire blight resistance QTL in M. sieversii, the primary progenitor of domesticated apples. Tree Genetics & Genomes 19, 50 (2023). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11295-023-01626-6
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Published:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11295-023-01626-6