Abstract
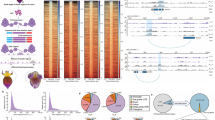
Papaya (Carica papaya L.) is a trioecious plant species, producing three sex forms, male, female, and hermaphrodite. Although the major sex types are genetically determined, the phenotypic sex expression of papaya is influenced by environmental factors. We investigated differential gene expression analysis between the non-functional rudimentary pistils from normal male flowers and developed and functional pistils from the male-to-hermaphrodite sex reversal flowers induced by low temperature aiming to understanding the gene regulatory network that determinates the phenotypic sex expression in papaya. Our differential gene expression analysis revealed 1756 differentially expressed genes between normal male and male-to-hermaphrodite sex reversal flowers. Gene ontology (GO) and Kyoto Encyclopedia of Genes and Genome (KEGG) pathway enrichment analysis showed transcription factors, flower development, histone H3-K9 methylation, and plant hormone signal transduction were among the most significantly enriched GO terms and KEGG pathways. Small RNA analysis was also performed on the pistils from normal male and the male-to-hermaphrodite sex reversal flowers. Our result showed the 24 nt small RNAs were the most abundant in the pistils from both normal and sex reversal flowers, followed by 21 nt small RNAs. We detected expression of 40 plant-conserved miRNAs and 14 papaya-specific miRNAs in the pistils from one or both normal and sex reversal flowers. Sixteen miRNAs exhibited high-expression level and ten of them showed differential expression between the normal male and the male-to-hermaphrodite sex reversal flowers. Our results suggested the male-to-hermaphrodite sex reversal was likely caused by silencing the gynoecium suppression function on the sex determination pathway through epigenetic modification.



Similar content being viewed by others
References
Anders S, Pyl PT, Huber W (2015) HTSeq—a python framework to work with high-throughput sequencing data. Bioinformatics 31:166–169. doi:10.1093/bioinformatics/btu638
Arnaud N, Pautot V (2014) Ring the BELL and tie the KNOX: roles for TALEs in gynoecium development. Plant Evol Dev 5:93. doi:10.3389/fpls.2014.00093
Aryal R, Yang X, Yu Q, et al. (2012) Asymmetric purine-pyrimidine distribution in cellular small RNA population of papaya. BMC Genomics 13:682
Awada M (1958) Relationships of minimum temperature and growth rate with sex expression of papaya plants (Carica papaya L.). Hawaii Agricultural Experiment Station Technical Bulletin 38, University of Hawaii, Honolulu
Awada M (1961) Soil moisture tension in relation of fruit types of papaya plants. Hawaii Farm Sci 10:7–8
Awada M, Ikeda WS (1957) Effects of water and nitrogen application on composition, growth, sugars in fruits, yield, and sex expression of the papaya plants (Carica papaya L.). Hawaii Agricultural Experiment Station Technical Bulletin 33, University of Hawaii, Honolulu.
Benková E, Michniewicz M, Sauer M, et al. (2003) Local, efflux-dependent auxin gradients as a common module for plant organ formation. Cell 115:591–602
Ceccato L, Masiero S, Sinha Roy D, et al. (2013) Maternal control of PIN1 is required for female gametophyte development in Arabidopsis. PLoS One. doi:10.1371/journal.pone.0066148
Cedar H, Bergman Y (2009) Linking DNA methylation and histone modification: patterns and paradigms. Nat Rev Genet 10:295–304. doi:10.1038/nrg2540
Cucinotta M, Colombo L, Roig-Villanova I (2014) Ovule development, a new model for lateral organ formation. Front Plant Sci doi. doi:10.3389/fpls.2014.00117
Curaba J, Singh MB, Bhalla PL (2014) miRNAs in the crosstalk between phytohormone signalling pathways. J Exp Bot 65:1425–1438. doi:10.1093/jxb/eru002
Dai X, Zhao PX (2001) psRNATarget: a plant small RNA target analysis server. Nucleic Acids Res 39:W155–W159
Du Z, Zhou X, Ling Y, et al. (2010) agriGO: a GO analysis toolkit for the agricultural community. Nucleic Acids Res 38:W64–W70. doi:10.1093/nar/gkq310
Gardner PP, Daub J, Tate J, et al. (2011) Rfam: Wikipedia, clans and the “decimal” release. Nucleic Acids Res 39:D141–D145. doi:10.1093/nar/gkq1129
Griffiths-Jones S, Saini HK, van Dongen S, Enright AJ (2008) miRBase: tools for microRNA genomics. Nucleic Acids Res 36:D154–D158. doi:10.1093/nar/gkm952
Hawkins C, Liu Z (2014) A model for an early role of auxin in Arabidopsis gynoecium morphogenesis. Front Plant Sci 5:327. doi:10.3389/fpls.2014.00327
Hay A, Tsiantis M (2010) KNOX genes: versatile regulators of plant development and diversity. Dev Camb Engl 137:3153–3165. doi:10.1242/dev.030049
Hofmeyr JDJ (1938) Genetical studies of Carica papaya L. I. The inheritance and relation of sex and certain plant characteristics. II. Sex reversal and sex forms. So Afr Dept Agri And Sci Bul 187:64
Hu Y, Bao F, Li J (2000) Promotive effect of brassinosteroids on cell division involves a distinct CycD3-induction pathway in Arabidopsis. Plant J Cell Mol Biol 24:693–701
Husbands AY, Benkovics AH, Nogueira FTS, et al. (2015) The ASYMMETRIC LEAVES complex employs multiple modes of regulation to affect adaxial-abaxial patterning and leaf complexity. Plant Cell 27:3321–3335. doi:10.1105/tpc.15.00454
Iorns MJ (1908) Observations on change of sex in Carica papaya. Science 28:125–126. doi:10.1126/science.28.708.125
Jackson JP, Lindroth AM, Cao X, Jacobsen SE (2002) Control of CpNpG DNA methylation by the KRYPTONITE histone H3 methyltransferase. Nature 416:556–560. doi:10.1038/nature731
Jaenisch R, Bird A (2003) Epigenetic regulation of gene expression: how the genome integrates intrinsic and environmental signals. Nat Genet 33:245–254
Janousek B, Siroký J, Vyskot B (1996) Epigenetic control of sexual phenotype in a dioecious plant, Melandrium album. Mol Gen Genet MGG 250:483–490
Jiang Z, Liu X, Peng Z, et al. (2010) AHD2.0: an update version of Arabidopsis hormone database for plant systematic studies. Nucleic Acids Res. doi:10.1093/nar/gkq1066
Juarez MT, Kui JS, Thomas J, et al. (2004) microRNA-mediated repression of rolled leaf1 specifies maize leaf polarity. Nature 428:84–88. doi:10.1038/nature02363
Kumar R, Kushalappa K, Godt D, et al. (2007) The Arabidopsis BEL1-LIKE HOMEODOMAIN proteins SAW1 and SAW2 act redundantly to regulate KNOX expression spatially in leaf margins. Plant Cell 19:2719–2735. doi:10.1105/tpc.106.048769
Kumar V (1952) Studies in Carica papaya Linn. II. Sex-expression in some varieties. Indian J Hort 9:20–28
Kuroki S, Matoba S, Akiyoshi M, et al. (2013) Epigenetic regulation of mouse sex determination by the histone demethylase Jmjd1a. Science 341:1106–1109. doi:10.1126/science.1239864
Lamesch P, Berardini TZ, Li D, et al. (2012) The Arabidopsis information resource (TAIR): improved gene annotation and new tools. Nucleic Acids Res 40:D1202–D1210. doi:10.1093/nar/gkr1090
Lange AH (1961) Factors affecting sex change in the flowers of Carica papaya L. Amer Soc Hort Sci Proc 77:252–264
Langmead B (2010) Aligning short sequencing reads with bowtie. Curr Protoc Bioinforma Ed Board Andreas Baxevanis Al CHAPTER:unit-11.7. doi:10.1002/0471250953.bi1107s32
Liu Q, Yao X, Pi L, et al. (2009a) The ARGONAUTE10 gene modulates shoot apical meristem maintenance and establishment of leaf polarity by repressing miR165/166 in Arabidopsis. Plant J Cell Mol Biol 58:27–40. doi:10.1111/j.1365-313X.2008.03757.x
Liu Q, Zhang Y-C, Wang C-Y, et al. (2009b) Expression analysis of phytohormone-regulated microRNAs in rice, implying their regulation roles in plant hormone signaling. FEBS Lett 583:723–728. doi:10.1016/j.febslet.2009.01.020
Liu Z, Moore PH, Ma H, et al. (2004) A primitive Y chromosome in papaya marks incipient sex chromosome evolution. Nature 427:348–352. doi:10.1038/nature02228
Ming R, Hou S, Feng Y, et al. (2008) The draft genome of the transgenic tropical fruit tree papaya (Carica papaya Linnaeus). Nature 452:991–996. doi:10.1038/nature06856
Ming R, Yu Q, Moore PH (2007) Sex determination in papaya. Semin Cell Dev Biol 18:401–408
Nogueira FTS, Madi S, Chitwood DH, et al. (2007) Two small regulatory RNAs establish opposing fates of a developmental axis. Genes Dev 21:750–755. doi:10.1101/gad.1528607
Nole-Wilson S, Krizek BA (2006) AINTEGUMENTA contributes to organ polarity and regulates growth of lateral organs in combination with YABBY genes. Plant Physiol 141:977–987. doi:10.1104/pp.106.076604
Nole-Wilson S, Rueschhoff EE, Bhatti H, Franks RG (2010) Synergistic disruptions in seuss cyp85A2 double mutants reveal a role for brassinolide synthesis during gynoecium and ovule development. BMC Plant Biol 10:198. doi:10.1186/1471-2229-10-198
Pekker I, Alvarez JP, Eshed Y (2005) Auxin response factors mediate Arabidopsis organ asymmetry via modulation of KANADI activity. Plant Cell 17:2899–2910. doi:10.1105/tpc.105.034876
Rivera C, Saavedra F, Alvarez F, et al. (2015) Methylation of histone H3 lysine 9 occurs during translation. Nucleic Acids Res 43:9097–9106. doi:10.1093/nar/gkv929
Rodriguez RE, Mecchia MA, Debernardi JM, et al. (2010) Control of cell proliferation in Arabidopsis thaliana by microRNA miR396. Dev Camb Engl 137:103–112. doi:10.1242/dev.043067
Rose NR, Klose RJ (2014) Understanding the relationship between DNA methylation and histone lysine methylation. Biochim Biophys Acta 1839:1362–1372. doi:10.1016/j.bbagrm.2014.02.007
Scofield S, Dewitte W, Murray JA (2008) A model for Arabidopsis class-1 KNOX gene function. Plant Signal Behav 3:257–259
Sessions A, Nemhauser JL, McColl A, et al. (1997) ETTIN patterns the Arabidopsis floral meristem and reproductive organs. Dev Camb Engl 124:4481–4491
Shao C, Li Q, Chen S, et al. (2014) Epigenetic modification and inheritance in sexual reversal of fish. Genome Res 24:604–615. doi:10.1101/gr.162172.113
Smaczniak C, Immink RGH, Muiño JM, et al. (2012) Characterization of MADS-domain transcription factor complexes in Arabidopsis flower development. Proc Natl Acad Sci 109:1560–1565. doi:10.1073/pnas.1112871109
Storey WB (1953) Genetics of the papaya. J Hered 44:70–78
Storey WB (1958) Modifications of sex expression in papaya. Hort Adv 2:49–60
Storey WB (1967) Theory of the derivations of the unisexual flowers of caricaceae. Agron Trop 17:273–321
Storey WB (1969) Pistillate papaya flower: a morphological anomaly. Science 163:401–405. doi:10.1126/science.163.3865.401
Supek F, Bošnjak M, Škunca N, Šmuc T (2011) REVIGO summarizes and visualizes long lists of Gene ontology terms. PLoS One 6:e21800. doi:10.1371/journal.pone.0021800
Tachibana M, Nozaki M, Takeda N, Shinkai Y (2007) Functional dynamics of H3K9 methylation during meiotic prophase progression. EMBO J 26:3346–3359. doi:10.1038/sj.emboj.7601767
Trapnell C, Roberts A, Goff L, et al. (2012) Differential gene and transcript expression analysis of RNA-seq experiments with TopHat and cufflinks. Nat Protoc 7:562–578. doi:10.1038/nprot.2012.016
von Goethe JW (1790) Versuch die Metamorphose der Pflanzen zu erklären. C. W. Ettinger, Gotha
Wang J, Na J-K, Yu Q, et al. (2012) Sequencing papaya X and Yh chromosomes reveals molecular basis of incipient sex chromosome evolution. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A 109:13710–13715. doi:10.1073/pnas.1207833109
Wang L, Feng Z, Wang X, et al. (2010) DEGseq: an R package for identifying differentially expressed genes from RNA-seq data. Bioinforma Oxf Engl 26:136–138. doi:10.1093/bioinformatics/btp612
Wang L, Gu X, Xu D, et al. (2011) miR396-targeted AtGRF transcription factors are required for coordination of cell division and differentiation during leaf development in Arabidopsis. J Exp Bot 62:761–773. doi:10.1093/jxb/erq307
Westergaard M (1958) The mechanism of sex determination in dioecious flowering plants. Adv Genet 9:217–281
Wu G, Park MY, Conway SR, et al. (2009) The sequential action of miR156 and miR172 regulates developmental timing in Arabidopsis. Cell 138:750–759. doi:10.1016/j.cell.2009.06.031
Wu J, Mao X, Cai T, et al. (2006) KOBAS server: a web-based platform for automated annotation and pathway identification. Nucleic Acids Res 34:W720–W724. doi:10.1093/nar/gkl167
Wynn AN, Seaman AA, Jones AL, Franks RG (2014) Novel functional roles for PERIANTHIA and SEUSS during floral organ identity specification, floral meristem termination, and gynoecial development. Front Plant Sci 5:130. doi:10.3389/fpls.2014.00130
Yampolsky C (1925) The origin of sex in the phanerogamic flora. Genetica 7:521
Yang X, Li L (2011) miRDeep-P: a computational tool for analyzing the microRNA transcriptome in plants. Bioinforma Oxf Engl 27:2614–2615. doi:10.1093/bioinformatics/btr430
Yu Q, Navajas-Pérez R, Tong E, et al. (2008) Recent origin of dioecious and Gynodioecious Y chromosomes in papaya. Trop Plant Biol 1:49–57. doi:10.1007/s12042-007-9005-7
Zhang H, Jin J, Tang L, et al. (2011) PlantTFDB 2.0: update and improvement of the comprehensive plant transcription factor database. Nucleic Acids Res 39:D1114–D1117. doi:10.1093/nar/gkq1141
Zhang W, Wang X, Yu Q, et al. (2008) DNA methylation and heterochromatinization in the male-specific region of the primitive Y chromosome of papaya. Genome Res 18:1938–1943. doi:10.1101/gr.078808.108
Zhu X, Li X, Chen W, et al. (2012) Evaluation of new reference genes in papaya for accurate transcript normalization under different experimental conditions. PLoS One 7:e44405. doi:10.1371/journal.pone.0044405
Acknowledgments
This work was supported by the grant 2015 N20002-1 from the Department of Science and Technology in Fujian Province and startup fund from Fujian Agriculture and Forestry University.
Data archiving statement
All the sequence data reported here are archived and publicly available at the National Center for Biotechnology Information (NCBI; http://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/). The RNA-Seq sequences can be accessed through NCBI SRA database under SRA ID SRP075300. The small RNA sequences can be accessed through NCBI SRA database under SRA ID SRP075300.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Conflict of interest
The authors declare that they have no conflict of interest.
Additional information
Communicated by C. Chen
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Lin, H., Liao, Z., Zhang, L. et al. Transcriptome analysis of the male-to-hermaphrodite sex reversal induced by low temperature in papaya. Tree Genetics & Genomes 12, 94 (2016). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11295-016-1055-2
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Published:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11295-016-1055-2