Abstract
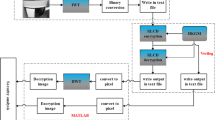
Security is an essential task while focusing on confidential level of patient information during medical data transmission. The image encryption algorithms that considered bit-level permutation can provide better security by changing the position of the pixels concurrently. But these encryption algorithms consume more power and area while implementing it on FPGA for securing the mammographic images based on irreversible logic or conventional gate circuits. Instead, the reversible logic gates can save the power and increase the speed of computation. This work proposed a new bit level image encryption and decryption circuit using reversible logic gates (RL-BLED). The proposed encryption module contains key generation unit, diffusion unit and confusion unit. It used reversible logic (RL) gates for diffusing the binary sequences and permuting the bitplanes in the confusion phase based on the key generated using reversible chaotic sequence generator module. Each unit of the proposed RL-BLED depends on numerous reversible sub-modules including adders, rotators, multipliers, modulo operators, dividers and so on. Here, the quantum cost, garbage outputs, delay and power of each sub-modules are analysed for demonstrating the effectiveness of the RL-BLED structure. The simulation results illustrate that the suggested RL-BLED overtakes the existing models in terms of LUTs, slices, flip flops and frequency.















Similar content being viewed by others
Data Availability
Data sharing not applicable to this article as no datasets were generated or analysed during the current study.
Code Availability
Custom code.
References
Sahni, P., & Mittal, N. (2019). Breast cancer detection using image processing techniques. In M. Kumar & R. K. Pandey (Eds.), Advances in Interdisciplinary Engineering (pp. 813–823). Springer.
Li, H., Chen, D., Nailon, W. H., Davies, M. E., & Laurenson, D. (2019). A deep dual-path network for improved mammogram image processing. In ICASSP 2019–2019 IEEE International Conference on Acoustics, Speech and Signal Processing (ICASSP) (pp. 1224–1228).
Gupta, K. K., Vijay, R., Pahadiya, P., & Saxena, S. (2021). Use of novel thermography features of extraction and different artificial neural network algorithms in breast cancer screening. Wireless Personal Communications. https://doi.org/10.1007/s11277-021-09141-4
Hemavathi, N., Sriranjani, R., Arulmozhi, P., Meenalochani, M., & Deepak, R. U. (2021). Deep learning based early prediction scheme for breast cancer. Wireless Personal Communications, 122, 931.
Song, S. Y., Park, B., Hong, S., Kim, M. J., Lee, E. H., & Jun, J. K. (2019). Comparison of digital and screen-film mammography for breast-cancer screening: A systematic review and Meta-analysis. Journal of Breast Cancer, 22(2), 311–325.
Zuley, M. L., Bandos, A. I., Abrams, G. S., Ganott, M. A., Gizienski, T. A., Hakim, C. M., Kelly, A. E., Nair, B. E., Sumkin, J. H., Waheed, U., & Gur, D. (2019). Contrast enhanced digital mammography (CEDM) helps to safely reduce benign breast biopsies for low to moderately suspicious soft tissue lesions. Academic Radiology, 27, 969.
Rahmatika, A., Handayani, A., & Setiawan, A. W. (2019). Automated segmentation of breast tissue and pectoral muscle in digital mammography. In 2019 International Conference of Artificial Intelligence and Information Technology (ICAIIT) (pp. 397–401).
Mendel, K., Li, H., Sheth, D., & Giger, M. (2019). Transfer learning from convolutional neural networks for computer-aided diagnosis: A comparison of digital breast tomosynthesis and full-field digital mammography. Academic Radiology, 26(6), 735–743.
Chung, H. L., & Parikh, J. R. (2020). Telemammography: Technical advances improve patient access in breast care. Journal of Breast Imaging, 2, 152.
Natesan, R., Wiskin, J., Lee, S., & Malik, B. H. (2019). Quantitative assessment of breast density: Transmission ultrasound is comparable to mammography with tomosynthesis. Cancer Prevention Research, 12(12), 871–876.
Hirose, U., & Kidera, S. (2019). Breast tumor characterization with raw data based machine learning for microwave ultra-wideband mammography. In 2019 International Symposium on Antennas and Propagation (ISAP), IEEE, (pp. 1–3).
Gueron, S., Feghali, W. K., & Gopal, V. (2019). Architecture and instruction set for implementing advanced encryption standard (AES). U.S. Patent 10,432,393.
Gueron, S., Feghali, W. K., Gopal, V., Makaram, R., Dixon, M.G ., Chennupaty, S., & Kounavis, M.E. (2019). Flexible architecture and instruction for advanced encryption standard (AES). U.S. Patent 10,187,201.
Khandare, N., Dalvi, O., Nikam, V., & Pandit, A. (2020). Enhancing privacy and security in medical information with AES and DES. In G. S. Tomar & N. S. Chaudhari (Eds.), International Conference on Intelligent Computing and Smart Communication 2019 (pp. 245–254). Springer.
Roy, S. S., Turan, F., Jarvinen, K., Vercauteren, F., & Verbauwhede, I. (2019). FPGA-based high-performance parallel architecture for homomorphic computing on encrypted data. In 2019 IEEE International Symposium on High Performance Computer Architecture (HPCA) (pp. 387–398).
Banerjee, S., Pal, A. K., Sultana, M., Sengupta, D., & Das, A. (2019). Reversible code converters based on application specific four variable reversible gates. In A. Abraham & P. Dutta (Eds.), Emerging technologies in data mining and information security (pp. 465–477). Springer.
Dasharatha, M., Naik, B. R., Reddy, N. S. S., & Mude, S. (2020) VLSI design and synthesis of reduced power and high speed ALU using reversible gates and vedic multiplier. In Advances in Decision Sciences, Image Processing, Security and Computer Vision, Springer, Cham (pp. 272–280).
Kuchhal, S., & Verma, R. (2015). Security design of DES using reversible logic. International Journal of Computer Science and Network Security (IJCSNS), 15(9), 81.
Sawant, A. G., Nitnaware, V. N., & Deshpande, A. A. (2020). Spartan-6 FPGA Implementation of AES Algorithm. In ICCCE 2019, Springer, Singapore (pp. 205–211).
Sikka, P., Asati, A. R., & Shekhar, C. (2020). Speed optimal FPGA implementation of the encryption algorithms for telecom applications. Microprocessors and Microsystems, 79, 103324.
Manojkumar, T., Karthigaikumar, P., & Ramachandran, V. (2019). An optimized s-box circuit for high speed AES design with enhanced PPRM architecture to secure mammographic images. Journal of Medical Systems, 43(2), 31.
Rohini, H., Pavankumar, A. C., & Shettar, R. B. (2018). A novel approach to optimize design of n-bit AES using reversible logic. In International Conference on Intelligent Data Communication Technologies and Internet of Things, Springer, Cham (pp. 996–1005).
Saravanan, P., & Kalpana, P. (2018). Novel reversible design of advanced encryption standard cryptographic algorithm for wireless sensor networks. Wireless Personal Communications, 100(4), 1427–1458.
Karunamurthi, S., & Natarajan, V. K. (2019). VLSI implementation of reversible logic gates cryptography with LFSR key. Microprocessors and Microsystems, 69, 68–78.
Koziel, B., Azarderakhsh, R., & Kermani, M. M. (2018). A high-performance and scalable hardware architecture for isogeny-based cryptography. IEEE Transactions on Computers, 67(11), 1594–1609.
Mishra, Z., & Acharya, B. (2020). High throughput and low area architectures of secure IoT algorithm for medical image encryption. Journal of Information Security and Applications, 53, 102533.
Hasan, F. S., & Saffo, M. A. (2020). FPGA hardware co-simulation of image encryption using stream cipher based on chaotic maps. Sensing and Imaging, 21(1), 1–22.
Pain, P., Das, K., Sadhu, A., Kanjilal, M. R., & De, D. (2019). Power analysis attack resistable hardware cryptographical circuit design using reversible logic gate in quantum cellular automata. Microsystem Technologies. https://doi.org/10.1007/s00542-019-04581-2
Jaspreet, K., & Harpreet, K. (2014). Synthesis and designing of reversible adder/subtracter circuits’. International Journal of Advanced Research in Electrical, Electronics and Instrumentation Engineering, 3(5), 9325–9332.
Touil, L., & Ouni, B. (2017). Design of hardware RGB to HMMD converter based on reversible logic. IET Image Processing, 11(8), 646–655.
Thapliyal, H., Labrado, C., & Chen, K. (2016). Design procedures and NML cost analysis of reversible barrel shifters optimizing garbage and ancilla lines. The Journal of Supercomputing, 72(3), 1092–1124.
Suckling, J., et al. (1994). The mammographic image analysis society digital mammogram database exerpta medica. International Congress Series, 1069, 375–378.
Masood, F., Driss, M., Boulila, W., Ahmad, J., Ur Rehman, S., Jan, S. U., Qayyum, A., & Buchanan, W. J. (2021). A lightweight chaos-based medical image encryption scheme using random shuffling and XOR operations. Wireless Personal Communications. https://doi.org/10.1007/s11277-021-08584-z
Gupta, M., Gupta, K. K., Khosravi, M. R., Shukla, P. K., Kautish, S., & Shankar, A. (2021). An intelligent session key-based hybrid lightweight image encryption algorithm using logistic-tent map and crossover operator for internet of multimedia things. Wireless Personal Communications, 121(3), 1857–1878.
Xian, Y., Wang, X., Yan, X., Li, Q., & Wang, X. (2020). Image encryption based on chaotic sub-block scrambling and chaotic digit selection diffusion. Optics and Lasers in Engineering, 134, 106202.
Funding
No funding.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Conflict of interest
The author declares that they have no conflict of interest.
Additional information
Publisher's Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Guptha, M.N.S., Eshwarappa, M.N. RL-BLED: A Reversible Logic Design of Bit Level Encryption/Decryption Algorithm for Secure Mammogram Data Transmission. Wireless Pers Commun 125, 939–963 (2022). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11277-022-09584-3
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11277-022-09584-3