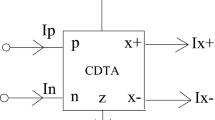
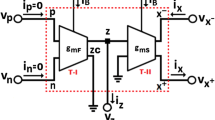
Abstract
This paper introduces novel electronically tunable floating and grounded memristor emulator circuits using voltage differencing gain amplifier and one capacitor. The decremental and incremental memristor emulators have been suggested for both floating as well as grounded type configurations. Decremental to incremental and incremental to decremental configurations of memristor emulators can be easily obtained. The fingerprint of memristor is the pinched hysteresis loops that are maintained for the significant range of frequencies from 5 kHz to 1 MHz. The proposed memristor emulator sustains its range of frequency for both grounded and floating configurations. The simulations have been done in Eldo simulation tool of Mentor Graphics using TSMC 0.18 µm complementary metal-oxide semiconductor (CMOS) technology parameters. The proposed electronically tunable memristor emulators are used to realize analog filters in view of performance verification.

















Similar content being viewed by others
References
Chua, L. (1971). Memristor-the missing circuit element. IEEE Transactions on Circuit Theory, 18(5), 507–519.
Chua, L. O., & Kang, S. M. (1976). Memristive devices and systems. Proceedings of the IEEE, 64(2), 209–223.
Strukov, D. B., Snider, G. S., Stewart, D. R., & Williams, R. S. (2008). The missing memristor found. Nature, 453(7191), 80.
Talukdar, A., Radwan, A. G., & Salama, K. N. (2012). Nonlinear dynamics of memristor based 3rd order oscillatory system. Microelectronics Journal, 43(3), 169–175.
Talukdar, A., Radwan, A. G., & Salama, K. N. (2011). Generalized model for memristor-based Wien family oscillators. Microelectronics Journal, 42(9), 1032–1038.
Talukdar, A., Radwan, A. G., & Salama, K. N. (2011). A memristor-based third-order oscillator: Beyond oscillation. Applied Nanoscience, 1(3), 143–145.
Driscoll, T., Quinn, J., Klein, S., Kim, H. T., Kim, B. J., Pershin, Y. V., di Ventra, M., & Basov, D. N. (2010). Memristive adaptive filters. Applied Physics Letters., 97(9), 093502.
Chew, Z. J., & Li, L. (2012). Printed circuit board based memristor in adaptive lowpass filter. Electronics Letters, 48(25), 1610–1611.
Pershin, Y. V., & Di Ventra, M. (2010). Experimental demonstration of associative memory with memristive neural networks. Neural Networks, 23(7), 881–886.
Pérez-Carrasco, J. A., Zamarreno-Ramos, C., Serrano-Gotarredona, T., Linares-Barranco, B. (2010). On neuromorphic spiking architectures for asynchronous STDP memristive systems. In: Proceedings of 2010 IEEE International Symposium on Circuits and Systems, pp. 1659–1662.
Muthuswamy, B., & Chua, L. O. (2010). Simplest chaotic circuit. International Journal of Bifurcation and Chaos, 20(05), 1567–1580.
Muthuswamy, B. (2010). Implementing memristor based chaotic circuits. International Journal of Bifurcation and Chaos, 20(05), 1335–1350.
Lin, Y., Zhou, P., Chi, M. H., Lv, H., Song, S., Huang, R., Wu, J. G., & Wu, H. M. (2009). Performance improvement of CuOx RRAM for non-volatile applications. ECS Transactions, 18(1), 281.
Yang, J. J., Pickett, M. D., Li, X., Ohlberg, D. A. A., Stewart, D. R., & Williams, R. S. (2008). Memristive switching mechanism for metal/oxide/metal nanodevices. Nature Nanotechnology, 3(7), 429–433.
Pickett, M. D., Strukov, D. B., Borghetti, J. L., Yang, J. J., Snider, G. S., Stewart, D. R., & Williams, R. S. (2009). Switching dynamics in titanium dioxide memristive devices. Journal of Applied Physics, 106(7), 074508.
Robinett, W., Pickett, M., Borghetti, J., Xia, Q., Snider, G. S., Medeiros-Ribeiro, G., & Williams, R. S. (2010). A memristor-based nonvolatile latch circuit. Nanotechnology, 21(23), 235203.
Rák, Á., & Cserey, G. (2010). Macromodeling of the memristor in SPICE. IEEE Transactions on Computer-Aided Design of Integrated Circuits and Systems., 29(4), 632–636.
Biolek, Z., Biolek, D., & Biolkova, V. (2009). SPICE model of memristor with nonlinear dopant drift, Radioengineering 18(2), 210–214.
Biolek, D., Biolek, Z., Biolkova, V. (2009). SPICE modeling of memristive, memcapacitative and meminductive systems. In: 2009 European Conference on Circuit Theory and Design (IEEE), 249–252.
Abdalla, H., & Pickett, M. D. (2011). SPICE modeling of memristors. IEEE International Symposium of Circuits and Systems (ISCAS), 1832–1835.
Mutlu, R., Karakulak, E. (2010). Emulator circuit of Ti02 memristor with linear dopant drift made using analog multiplier. In: IEEE National Conference on Electrical, Electronics and Computer Engineering, pp. 380–384.
Kim, H., Sah, M. P., Yang, C., Cho, S., & Chua, L. O. (2012). Memristor emulator for memristor circuit applications. IEEE Transactions on Circuits and Systems I: Regular Papers, 59(10), 2422–2431.
Sánchez-López, C., Mendoza-Lopez, J., Carrasco-Aguilar, M. A., Morales-Lopez, F. E. (2013). A simple floating memristor emulator circuit based on current conveyors. In: 10th IEEE International Conference on Electrical Engineering, Computing Science and Automatic Control (CCE), pp. 445–448.
Yeşil, A., Babacan, Y., & Kaçar, F. (2014). A new DDCC based memristor emulator circuit and its applications. Microelectronics Journal, 45(3), 282–287.
Yener, S. C., & Kuntman, H. H. (2014). Fully CMOS memristor based chaotic circuit. Radioengineering, 23(4), 1140–1149.
Sánchez-López, C., Carrasco-Aguilar, M. A., & Muñiz-Montero, C. (2015). A 16 Hz–160 kHz memristor emulator circuit. AEU-International Journal of Electronics and Communications, 69(9), 1208–1219.
Shin, S., Zheng, L., Weickhardt, G., Cho, S., & Kang, S. M. (2013). Compact circuit model and hardware emulation for floating memristor devices. IEEE Circuits and Systems Magazine, 13(2), 42–55.
Yu, D. S., Chen, H., Iu, H. H. (2013). A meminductive circuit based on floating memristive emulator. In: 2013 IEEE International Symposium on Circuits and Systems (ISCAS2013), pp. 1692–1695.
Yang, C., Choi, H., Park, S., Sah, M. P., Kim, H., & Chua, L. O. (2014). A memristor emulator as a replacement of a real memristor. Semiconductor Science and Technology, 30(1), 015007.
Chilukuri, M., Jung, S. (2015). A high frequency memristor emulator circuit. In: 2015 IEEE Dallas Circuits and Systems Conference (DCAS), pp. 1–4.
Fitch, A. L., Iu, H. H., Wang, X. Y., Sreeram, V., Qi, W. G. (2012). Realization of an analog model of memristor based on light dependent resistor. In: 2012 IEEE International Symposium on Circuits and Systems, pp. 1139–1142.
Yu, D., Iu, H. H., Fitch, A. L., & Liang, Y. (2014). A floating memristor emulator based relaxation oscillator. IEEE Transactions on Circuits and Systems I: Regular Papers, 61(10), 2888–2896.
Sánchez-López, C., Mendoza-Lopez, J., Carrasco-Aguilar, M. A., & Muñiz-Montero, C. (2014). A floating analog memristor emulator circuit. IEEE Transactions on Circuits and Systems II: Express Briefs, 61(5), 309–313.
Biolek, D., Biolkova, V. I., Kolka, Z., Biolek, Z. (2015). Passive fully floating emulator of memristive device for laboratory experiments. Advances in Electrical and Computer Engineering 112–116.
Alharbi, A. G., Fouda, M. E., Chowdhury, M. H. (2015). Memristor emulator based on practical current controlled model. In: IEEE 58th International Midwest Symposium on Circuits and Systems (MWSCAS), pp. 1–4.
Alharbi, A. G., Khalifa, Z. J., Fouda, M. E., Chowdhury, M. H. (2015). Memristor emulator based on single CCII. In: 27th IEEE International Conference on Microelectronics (ICM), pp.174–177.
Kumngern, M., Moungnoul, P. (2015). A memristor emulator circuit based on operational transconductance amplifiers. In: 12th IEEE International Conference on Electrical Engineering/Electronics, Computer, Telecommunications and Information Technology (ECTICON), pp. 1–5.
Alharbi, A. G., Fouda, M. E., Chowdhury, M. H. (2015). A novel memristor emulator based only on an exponential amplifier and CCII+. In: IEEE International Conference on Electronics, Circuits, and Systems (ICECS), pp. 376–379.
Sözen, H., Çam, U. (2015). New memristor emulator circuit using OTAs and CCIIs. In: 9th International Conference on Electrical and Electronics Engineering (ELECO), pp. 10–14.
Abuelma’atti, M. T., & Khalifa, Z. J. (2015). A continuous-level memristor emulator and its application in a multivibrator circuit. AEU—International Journal of Electronics and Communications., 69(4), 771–775.
Abuelma’atti, M. T., & Khalifa, Z. J. (2016). A new floating memristor emulator and its application in frequency-to-voltage conversion. Analog Integrated Circuits and Signal Processing, 86(1), 141–147.
Kalomiros, J., Stavrinides, S. G., Corinto, F. (2016). A two-transistor non-ideal memristor emulator. In: 5th IEEE International Conference on Modern Circuits and Systems Technologies (MOCAST), pp. 1–4.
Ranjan, R. K., Rani, N., Pal, R., Paul, S. K., & Kanyal, G. (2017). Single CCTA based high frequency floating and grounded type of incremental/decremental memristor emulator and its application. Microelectronics Journal, 60, 119–128.
Ranjan, R. K., Raj, N., Bhuwal, N., & Khateb, F. (2017). Single DVCCTA based high frequency incremental/decremental memristor emulator and its application. AEU-International Journal of Electronics and Communications, 82, 177–190.
Kanyal, G., Kumar, P., Paul, S. K., & Kumar, A. (2018). OTA based high frequency tunable resistorless grounded and floating memristor emulators. AEU-International Journal of Electronics and Communications, 92, 124–145.
Yeşil, A., Babacan, Y., & Kaçar, F. (2018). Design and experimental evolution of memristor with only one VDTA and one capacitor. IEEE Transactions on Computer-Aided Design of Integrated Circuits and Systems., 38(6), 1123–1132.
Yu, D. S., Sun, T. T., Zheng, C. Y., Iu, H. H., & Fernando, T. (2018). A simpler memristor emulator based on varactor diode. Chinese Physics Letters., 35(5), 058401.
Hassanein, A. M., Elsafty, A. H., Said, L. A., Madian, A. H., Radwan, A. G. (2018). Incremental grounded voltage controlled memristor emulator. In: 30th IEEE International Conference on Microelectronics (ICM), pp. 156–159.
Ranjan, R. K., Sharma, P. K., Sagar, R. N., Kumari, B., & Khateb, F. (2019). Memristor emulator circuit using multiple-output OTA and its experimental results. Journal of Circuits, Systems and Computers., 28(10), 1950166.
Vista, J., & Ranjan, A. (2019). A simple floating MOS-memristor for high-frequency applications. IEEE Transactions on Very Large Scale Integration (VLSI) Systems, 27(5), 1186–1195.
Yesil, A., Babacan, Y., & Kacar, F. (2019). Electronically Tunable memristor based on VDCC. AEU International Journal of Electronics and Communications, 107, 282–290.
Yadav, N., Rai, S. K., & Pandey, R. (2020). New grounded and floating memristor emulators using OTA and CDBA. International Journal of Circuit Theory and Applications, 48(7), 1154–1179.
Gupta, S., & Rai, S. K. (2020). New grounded and floating decremental/incremental memristor emulators based on CDTA and its application. Wireless Personal Communications, 113(2), 773–798.
Yadav, N., Rai, S. K., & Pandey, R. (2021). Novel memristor emulators using fully balanced VDBA and grouned capacitor. Iranian Journal of Science and Technology, Transactions of Electrical Engineering, 45, 229–245.
Hezayyin, H. G., Khalil, N. A., Madian, A. H. (2020). Inverse memrsitor emulator active realizations. In: 2nd IEEE Novel Intelligent and Leading Emerging Sciences Conference (NILES), 461–464.
Li, F., Wang, T., Mo, C., & Wu, H. (2021). A unifIed Asymmetric memristive diode-bridge emulator and hardware confirmation. The European Physical Journal Special Topics. https://doi.org/10.1140/epjs/s11734-021-00180-3
Prasad, S. S., Kumar, P., & Ranjan, R. K. (2021). Resistorless memristor emulator using CFTA and its experimental verification. IEEE Access, 9, 64065–64075. https://doi.org/10.1109/ACCESS.2021.3075341
Srivastava, P., Gupta, R. K., Sharma, R. K., & Ranjan, R. K. (2020). MOS-only memristor emulator. Circuits, Systems, and Signal Processing, 39(11), 5848–5861.
Sharma, V. K., Parveen, T., & Ansari, M. S. (2021). Four quadrant analog multiplier based memristor emulator using single active element. AEU-International Journal of Electronics and Communications, 130, 152575. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.aeue.2020.153575
Sharma, V. K., Ansari, M. S., & Parveen, T. (2020). Tunable memristor emulator using off-the-shelf components. Procedia Computer Science, 171, 1064–1073.
Satansup, J., & Tangsrirat, W. (2013). CMOS Realization of voltage differencing gain amplifier (VDGA) and its application to biquad filter. Indian Journal of Engineering and Material Sciences, 20(2013), 457–464.
Funding
Not applicable.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Conflict of interest
Authors declare that they have no conflict of interest.
Data Availability
All data generated or analysed during this study are included in this published article.
Additional information
Publisher's Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Yadav, N., Rai, S.K. & Pandey, R. High Frequency Electronically Tunable Floating Memristor Emulators employing VDGA and Grounded Capacitor. Wireless Pers Commun 121, 3185–3211 (2021). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11277-021-08869-3
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11277-021-08869-3