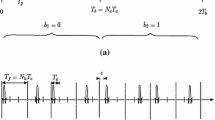
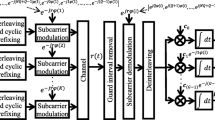
Abstract
Impulse-radio ultra-wideband (IR-UWB) technology has gained popularity in wireless personal area networks (WPANs) because of its promising aspect in providing extremely high data rates at low cost. However, multi-user interference (MUI) adversely affects the IR-UWB communication technique, especially in WPANs concurrent transmission scenarios. In this paper, we solve this problem via proposing a new correlation technique, namely, multi-point impulse correlation (MPIC), based on a new mask equation design. The proposed MPIC technique outperforms the traditional technique in TR receivers in terms of the obtained symbol error rate (SER) value (by 4.5 db) as confirmed by the simulation results. Multiple scenarios were conducted which confirm that the proposed MPIC technique offers better SER performance in comparison with TR. According to the obtained results, MPIC is highly successful in reducing MUI, especially in concurrent schemes and with a large number of users.

















Similar content being viewed by others
References
Dang, Q. H., & van der Veen, A.-J. (2007). A decorrelating multiuser receiver for transmit-reference UWB systems. IEEE Journal on Selected Topics in Signal Processing, 1(3), 431–442.
Guimarães, D. A., & Gomes, G. G. R. (2012). Introduction to ultra wideband impulse radio. Revista Telecomunicacoes, 14(1), 49–61.
Chung, W. C., August, N. J., & Ha, D. S. (2005). Signaling and multiple access techniques for ultra wideband 4G wireless communication systems. IEEE Wireless Communications, 12(2), 46–55.
Reed, J. (2005). An introduction to ultra wideband communication systems. Upper Saddle River, NJ: Prentice Hall PTR.
Huang, T.-J., & Yang, J.-F. (2017). An effective timing synchronization scheme for DHTR UWB receivers. Wireless Personal Communications. doi:10.1007/s11277-017-4009-6.
Lee, W. (2010). Ultra-wideband systems: Review. Naresuan University Engineering Journal, 5(2), 63–77.
Kharrat-Kammoun, F., Le Martret, C., & Ciblat, P. (2009). Performance analysis of IR-UWB in a multi-user environment. IEEE Transactions on Wireless Communications, 8(11), 5552–5563.
Arslan, H., Chen, Z. N., & Di Benedetto, M.-G. (2006). Ultra wideband wireless communication. Hoboken, NJ: Wiley.
Shi, N., & Niemegeers, I. (2009). Multi-hop IR-UWB WPAN architecture and protocols. In IEEE international conference on wireless and mobile computing, networking and communications (pp. 356–362).
Li, J.-S., Kao, H.-C., & Cheng, S.-Y. (2007). Multi-hop networking with space reuse in IEEE 802.15.3 UWB WPANs. In The 2nd international conference on wireless broadband and ultra wideband communications (AusWireless 2007) (pp. 73–73).
Cassioli, D., Win, M., Vatalaro, F., & Molisch, A. (2007). Low complexity rake receivers in ultra-wideband channels. IEEE Transactions on Wireless Communications, 6(4), 1265–1275.
Kim, D. I., Member, S., Jia, T., & Member, S. (2008). M-ary orthogonal coded/balanced ultra-wideband transmitted-reference systems in multipath. IEEE Transactions on Communications, 56(1), 102–111.
Cheng, X., & Guan, Y. L. (2012). Pre/post-rake diversity combining for UWB communications in the presence of pulse overlap. IEEE Transactions on Wireless Communications, 11(2), 481–487.
Tang, J., Xu, Z., & Sadler, B. (2007). Performance analysis of b-bit digital receivers for TR-UWB systems with inter-pulse interference. IEEE Transactions on Wireless Communications, 6(2), 494–505.
Hazra, R., & Tyagi, A. (2013). Cooperative impulse radio ultra-wideband communication using coherent and non-coherent detectors: A review. Wireless Personal Communications, 77(1), 719–748.
Romme, J., & Witrisal, K. (2006). Transmitted-reference UWB systems using weighted autocorrelation receivers. IEEE Transactions on Microwave Theory and Techniques, 54(4), 1754–1761.
Taghipour, J., Vakili, V. T., & Abbasi-Moghadam, D. (2012). Comparison of kurtosis and fourth power detectors with applications to IR-UWB OOK systems. International Journal of Communications, Network and System Sciences, 5(1), 43–49.
D’Amico, A. A., & Taponecco, L. (2006). A differential receiver for UWB systems. IEEE Transactions on Wireless Communications, 5(7), 1601–1605.
Hazra, R., & Tyagi, A. (2014). A survey on various coherent and non-coherent IR-UWB receivers. Wireless Personal Communications, 79(3), 2339–2369.
Jin, Y., Liu, H., Kim, K. J., & Kwak, K. S. (2014). A reconfigurable digital receiver for transmitted reference pulse cluster UWB communications. IEEE Transactions on Vehicular Technology, 63(9), 4734–4740.
Chen, Y., & Beaulieu, N. (2008). Improved receivers for generalized UWB transmitted reference systems. IEEE Transactions on Wireless Communications, 7(2), 500–504.
Milanovic, J., Herceg, M., Vranjes, M., & Job, J. (2015). Method for bandwidth efficiency increasing of M-ary PPM transmitted-reference UWB communication systems. Wireless Personal Communications, 83(2015), 1927–1944.
Witrisal, K., Leus, G., Janssen, G., Pausini, M., Troesch, F., Zasowski, T., et al. (2009). Noncoherent ultra-wideband systems. IEEE Signal Processing Magazine, 26(4), 48–66.
Xu, Z., & Sadler, B. (2006). Multiuser transmitted reference ultra-wideband communication systems. IEEE Journal on Selected Areas in Communications, 24(4), 766–772.
Zhao, S. (2006). Pulsed ultra-wideband: Transmission, detection, and performance. Corvallis: Oregon State University.
Le Boudec, J.-Y., & Merz, R. (2008). Concurrent and parallel transmissions are optimal for low data-rate IR-UWB networks. In 2008 IEEE 19th international symposium on personal, indoor and mobile radio communications (pp. 1–6).
Merz, R., Widmer, J., Le Boudec, J.-Y., & Radunović, B. (2005). A joint PHY/MAC Architecture for low-radiated power TH-UWB wireless ad-hoc networks. Wireless Communications and Mobile Computing, 5(5), 567–580.
Flury, M., & Merz, R. (2007). Managing impulsive interference in impulse. ST Journal of Research Wireless Sensor Networks, 4(1), 118–130.
Jiang, L., Guo, J., & Wang, Y. (2006). A novel approach to interference mitigation with coexisting spectrum users for UWB pulse radio. In International conference on wireless communications, networking and mobile computing (pp. 1–4).
Belghith, S., & Naanaa, A. (2011). Performance enhancement of a time hopping—Pulse position modulation ultra-wide-band system using guided local search. IET Communications, 5(15), 2212–2220.
Young, D. J., & Beaulieu, N. C. (2012). Multiuser interference mitigation in time-hopped ultra-wideband receivers. In IEEE international conference on ultra-wideband (pp. 125–129).
Hung, H.-L. (2015). Performance analysis of multistage interference cancellation in THUWB systems using adaptive differential evolution algorithm with novel mutation and crossover strategies. Wireless Personal Communications, 82(3), 1179–1199.
Hamidoun, K., Elassali, R., Elhillali, Y., Rivenq, A., Elbaamrani, K., & Boukour, F. E. (2015). A new multi-user ultra wide band system based on modified Gegenbauer functions and M-OAM modulation for communication of intelligent transportation systems. Wireless Personal Communications, 82(4), 2115–2134.
Shao, H., & Beaulieu, N. C. (2011). Direct sequence and time-hopping sequence designs for narrowband interference mitigation in impulse radio UWB systems. IEEE Transactions on Communications, 59(7), 1957–1965.
Muqaibel, A. H., & Jadallah, A. N. (2015). SINR evaluation for improved practical coordinated multi-point clustering. Wireless Personal Communications, 83(4), 3091–3102.
Xiong, H. (2017). An efficient narrowband interference suppression approach in ultra-wideband receiver. IEEE Sensors Journal, 17(9), 2741–2748.
Kouassi, K., Clavier, L., Doumbia, I., & Rolland, P.-A. (2013). Optimal PWR codes for TH-PPM UWB multiple-access interference mitigation. IEEE Communications Letters, 17(1), 103–106.
Juanda, F. N. U., Shu, W., & Chang, J. S. (2017). A 10-GS/s 4-bit single-core digital-to-analog converter for cognitive ultrawidebands. IEEE Transactions on Circuits and Systems Part II: Express Briefs, 64(1), 16–20.
Mehbodniya, A., & Aissa, S. (2009). Effects of MB-OFDM system interference on the performance of DS-UWB. IEEE Transactions on Vehicular Technology, 58(8), 4665–4669.
Chen, H., Guo, Z., Yao, R. Y., Shen, X., & Li, Y. (2006). Performance analysis of delayed acknowledgment scheme in UWB-based high-rate WPAN. IEEE Transactions on Vehicular Technology, 55(2), 606–621.
Xu, H., & Yang, L. (2010). Modeling and transceiver design for asymmetric UWB links with heterogeneous nodes. IEEE Transactions on Communications, 58(6), 1834–1842.
Li, M. (2015). Optimal receiver scheme for transmitted-reference ultra-wideband system in coal mine. Journal of Communication, 10(3), 206–212.
Ahmed, Q. Z., Park, K.-H., & Alouini, M.-S. (2015). Ultrawide bandwidth receiver based on a multivariate generalized Gaussian distribution. IEEE Transactions on Wireless Communications, 14(4), 1800–1810.
Di Benedetto, M.-G., & Giancola, G. (2004). Understanding ultra wide band radio fundamentals. Upper Saddle River: Prentice Hall PTR.
Houda, C., Moez, H., & Ridha, B. (2012). Analytical approach for the TH-BPSK ultra-wideband systems performance. International Journal of Computer Theory and Engineering, 4(6), 987–989.
Molisch, A., Cassioli, D., Emami, S., Fort, A., Kannan, B., Karedal, J., et al. (2006). A comprehensive standardized model for ultrawideband propagation channels. IEEE Transactions on Antennas and Propagation, 54(11), 3151–3166.
Giancola, G., & Di Benedetto, M.-G. (2006). A novel approach for estimating multi-user interference in impulse radio UWB networks: The pulse collision model. Signal Processing, 86(9), 2185–2197.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Mohammed, M.S., Singh, M.J. & Abdullah, M. New TR-UWB Receiver Algorithm Design to Mitigate MUI in Concurrent Schemes. Wireless Pers Commun 97, 4431–4450 (2017). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11277-017-4732-z
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11277-017-4732-z