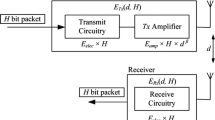
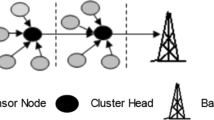
Abstract
Using multiple sink nodes in wireless sensor networks can greatly improve the lifetime and throughput of the network. One of the important issues in multi-sink wireless sensor networks is the congestion problem in sink nodes which reduces the effectiveness of data processing in sink nodes and increases the energy consumption of the sensor nodes. To prevent congestion in the sink nodes, in this paper, a distributed fuzzy logic-based sink selection algorithm is presented for one-hop sensor networks which makes each sensor node able to independently select a sink node based on the congestion situations in all the sink nodes. This scheme can effectively prevent congestion in the sink nodes and provide load balancing among them. Moreover, it reduces the delay of successful data transmissions to the sink nodes and improves the lifetime of wireless sensor networks by reducing the number of packet retransmissions. Simulation results indicate the effectiveness of our proposed solution.




























Similar content being viewed by others
References
Sinha, A., & Lobiyal, D. K. (2013). Performance evaluation of data aggregation for cluster-based wireless sensor network. Human-Centric Computing and Information Sciences, 3, 1–17.
Stanoev, A., Filiposka, S., In, V., & Kocarev, L. (2016). Cooperative method for wireless sensor network localization. Ad Hoc Networks, 40, 61–72.
Masdari, M., Bazarchi, S. M., & Bidaki, M. (2013). Analysis of secure LEACH-based clustering protocols in wireless sensor networks. Journal of Network and Computer Applications, 36(4), 1243–1260.
Masdari, M., & Ahmadzadeh, S. (2016). Comprehensive analysis of the authentication methods in wireless body area networks. Security and Communication Networks, 9(17), 4777–4803.
Masdari, M., & Ahmadzadeh, S. (2017). A survey and taxonomy of the authentication schemes in Telecare Medicine Information Systems. Journal of Network and Computer Applications, 87, 1–19.
Masdari, M., Ahmadzadeh, S., & Bidaki, M. (2017). Key management in wireless body area network: Challenges and issues. Journal of Network and Computer Applications, 91, 36–51.
Madhja, A., Nikoletseas, S., & Raptis, T. P. (2016). Hierarchical, collaborative wireless energy transfer in sensor networks with multiple mobile chargers. Computer Networks, 97, 98–112.
Khan, M. I., Gansterer, W. N., & Haring, G. (2013). Static vs. mobile sink: The influence of basic parameters on energy efficiency in wireless sensor networks. Computer Communications, 36, 965–978.
Rault, T., Bouabdallah, A., & Challal, Y. (2014). Energy efficiency in wireless sensor networks: A top-down survey. Computer Networks, 67, 104–122.
Long, J., Liu, A., Dong, M., & Li, Z. (2015). An energy-efficient and sink-location privacy enhanced scheme for WSNs through ring based routing. Journal of Parallel and Distributed Computing, 81, 47–65.
Madhja, A., Nikoletseas, S., & Raptis, T. P. (2015). Distributed wireless power transfer in sensor networks with multiple mobile chargers. Computer Networks, 80, 89–108.
Cabrera, T., Yuste-Delgado, A., & Macías, D. C. (2011). A fuzzy logic-based and distributed gateway selection for wireless sensor networks. In Proceedings of the Springer international conference on advances in intelligent and soft computing (pp. 243–8).
Bidaki, M., & Masdari, M. (2013). Reputation-based clustering algorithms in mobile ad hoc networks. International Journal of Advanced Science and Technology, 54, 1–12.
Zeng, B., & Dong, Y. (2016). An improved harmony search based energy-efficient routing algorithm for wireless sensor networks. Applied Soft Computing, 41, 135–147.
Banka, H., & Jana, P. K. (2016) PSO-based multiple-sink placement algorithm for protracting the lifetime of wireless sensor networks. In Proceedings of the second international conference on computer and communication technologies (pp. 605–616).
Masdari, M., ValiKardan, S., Shahi, Z., & Azar, S. I. (2016). Towards workflow scheduling in cloud computing: A comprehensive analysis. Journal of Network and Computer Applications, 66, 64–82.
Masdari, M., Nabavi, S. S., & Ahmadi, V. (2016). An overview of virtual machine placement schemes in cloud computing. Journal of Network and Computer Applications, 66, 106–127.
Masdari, M., & Jalali, M. (2016). A survey and taxonomy of DoS attacks in cloud computing. Security and Communication Networks, 9(16), 3724–3751.
Masdari, M., Salehi, F., Jalali, M., & Bidaki, M. (2017). A survey of PSO-based scheduling algorithms in cloud computing. Journal of Network and Systems Management, 25(1), 122–158.
Basagni, S., Carosi, A., Petrioli, C., & Phillips, C. A. (2011). Coordinated and controlled mobility of multiple sinks for maximizing the lifetime of wireless sensor networks. Wireless Networks, 17, 759–778.
Fang, W.-W., Chen, J.-M., Shu, L., Chu, T.-S., & Qian, D.-P. (2010). Congestion avoidance, detection and alleviation in wireless sensor networks. Journal of Zhejiang University SCIENCE C, 11, 63–73.
Dashkova, E., & Gurtov, A. (2012). Survey on congestion control mechanisms for wireless sensor networks. In Internet of things, smart spaces, and next generation networking (pp. 75–85). Berlin: Springer.
Borasia, S., & Raisinghani, V. (2011).”A review of congestion control mechanisms for wireless sensor networks. In Technology systems and management (pp. 201–206). Berlin: Springer.
Castaño, F., Rossi, A., Sevaux, M., & Velasco, N. (2013). On the use of multiple sinks to extend the lifetime in connected wireless sensor networks. Electronic Notes in Discrete Mathematics, 41, 77–84.
Dandekar, D. R., & Deshmukh, P. (2013). Energy balancing multiple sink optimal deployment in multi-hop wireless sensor networks. In 2013 IEEE 3rd international advance computing conference (IACC) (pp. 408–412).
Liu, Q., Mao, Y.-M., Leng, S.-P., Li, L.-J., & Zhuang, Y.-Q. (2011). Optimal deployment of multiple sink nodes in wireless sensor networks. Jisuanji Yingyong/Journal of Computer Applications, 31, 2313–2316.
Das, D., Rehena, Z., Roy, S., & Mukherjee, N. (2013). Multiple-sink placement strategies in wireless sensor networks. In 2013 Fifth international conference on communication systems and networks (COMSNETS) (pp. 1–7).
Monowar, M. M., Rahman, M. O., Pathan, A.-S. K., & Hong, C. S. (2008) Congestion control protocol for wireless sensor networks handling prioritized heterogeneous traffic. In Proceedings of the 5th annual international conference on mobile and ubiquitous systems: computing, networking, and services (p. 17).
Ghaffari, A. (2015). Congestion control mechanisms in wireless sensor networks: A survey. Journal of Network and Computer Applications, 52, 101–115.
Jain, T. K., Saini, D. S., & Bhooshan, S. V. (2015) Lifetime optimization of a multiple sink wireless sensor network through energy balancing. Journal of Sensors, 2015. doi:10.1155/2015/921250.
Isik, S., Donmez, M. Y., & Ersoy, C. (2012). Multi-sink load balanced forwarding with a multi-criteria fuzzy sink selection for video sensor networks. Computer Networks, 56, 615–627.
Ciciriello, P., Mottola, L., & Picco, G. P. (2007) Efficient routing from multiple sources to multiple sinks in wireless sensor networks. In Wireless sensor networks (pp. 34–50). Berlin: Springer.
Cheng, S.-T., & Chang, T.-Y. (2012). An adaptive learning scheme for load balancing with zone partition in multi-sink wireless sensor network. Expert Systems with Applications, 39, 9427–9434.
Sitanayah, L., Brown, K. N., & Sreenan, C. J. (2012). Multiple sink and relay placement in wireless sensor networks. In Proceedings of the 1st workshop artificial intelligence for telecommunications and sensor networks (WAITS’12), 20th European Conference on artificial intelligence (ECAI’12) (pp. 18–23).
Silva, A. P., Burleigh, S., Hirata, C. M., & Obraczka, K. (2015). A survey on congestion control for delay and disruption tolerant networks. Ad Hoc Networks, 25, 480–494.
Xu, J., Liu, W., Lang, F., Zhang, Y., & Wang, C. (2010). Distance measurement model based on RSSI in WSN. Wireless Sensor Network, 2, 606.
Soro, S., & Heinzelman, W. B. (2005). Prolonging the lifetime of wireless sensor networks via unequal clustering. In 2005. Proceedings. 19th IEEE international parallel and distributed processing symposium (p. 8).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Masdari, M., Naghiloo, F. Fuzzy Logic-Based Sink Selection and Load Balancing in Multi-Sink Wireless Sensor Networks. Wireless Pers Commun 97, 2713–2739 (2017). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11277-017-4631-3
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11277-017-4631-3