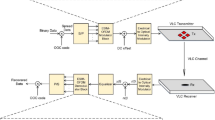
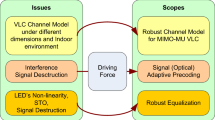
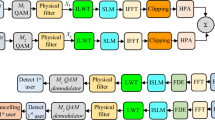
Abstract
Recently, to increase the data capacity of visible light communication (VLC) systems naturally, an ideal combination of orthogonal frequency division multiplexing (OFDM) and multiple-input multiple-output (MIMO-OFDM) technique has proven to be an efficient way. However, to ensure real-valued output for the VLC system, a Hermitian symmetry (HS) is usually levied in the OFDM technique, which reduces the data rate while increasing the computational complexity (CC) of the system. In this paper, a wavelet transform (WT) based non-HS OFDM technique (NHS-OFDM) for the MIMO-VLC system has been presented using non-imaging and imaging receivers to study the performance numerically. The state-of-the-art NHS-OFDM technique was realized by isolating real and imaginary parts of traditional RF-based OFDM signal and then transmitted by a pair of white LED luminaries. By incorporating WT with the OFDM technique, the error performance and data rate of the system are greatly improved, as WT eliminates standard usage of the cyclic prefix. Link-level performance of the recommended MIMO-VLC system was tested, considering BER, CC, and PAPR. Also, closed-form analytical BER expressions were derived and compared with the simulated results in the presence of line-of-sight links. Analytical and simulated results are analogous to each other and confirm that the proposed WT-based NHS-OFDM technique with imaging receiver achieves better BER results, with very low CC. Moreover, the WT-based NHS-OFDM technique also reduces the PAPR without employing any reduction technique.







Similar content being viewed by others
References
Kumar, A., & Gupta, M. (2018). A review on activities of fifth generation mobile communication system. Alexandria Engineering Journal, 57(2), 1125–1135.
Chowdhury, M. Z., Hossan, M. T., Islam, A., & Jang, Y. M. (2018). A comparative survey of optical wireless technologies: Architectures and applications. IEEE Access, 6, 9819–9840.
Shafi, M., Molisch, A. F., Smith, P. J., Haustein, T., Zhu, P., De Silva, P., Tufvesson, F., Benjebbour, A., & Wunder, G. (2017). 5G: A tutorial overview of standards, trials, challenges, deployment, and practice. IEEE Journal on Selected Areas in Communications, 35(6), 1201–1221.
Zhang, D., Zhou, Z., Mumtaz, S., Rodriguez, J., & Sato, T. (2016). One integrated energy efficiency proposal for 5G IoT communications. IEEE Internet of Things Journal, 3(6), 1346–1354.
Ibhaze, A. E., Orukpe, P. E., & Edeko, F. O. (2020). High capacity data rate system: A review of visible light communication technology. Journal of Electronic Science and Technology, 18(3), 100055.
Garber, L. (2011). Turning on the lights for wireless communications. Computer, 44(11), 11–14.
Elgala, H., Mesleh, R., & Haas, H. (2011). Indoor optical wireless communication: potential and state-of-the-art. IEEE Communications Magazine, 49(9), 56–62.
Grobe, L., Paraskevopoulos, A., Hilt, J., Schulz, D., Lassak, F., Hartlieb, F., Kottke, C., Jungnickel, V., & Langer, K. D. (2013). High-speed visible light communication systems. IEEE Communications Magazine, 51(12), 60–66.
Le Minh, H., Brien, D., Faulkner, G., Zeng, L., Lee, K., Jung, D., Oh, Y., & Won, E. T. (2009). 100-Mb/s NRZ visible light communications using a postequalized white LED. IEEE Photonics Technology Letters, 21(15), 1063–1065.
Afgani, M. Z., Haas, H., Elgala, H., & Knipp, D. (2006, March). Visible light communication using OFDM. In \(2^{nd}\) International Conference on Testbeds and Research Infrastructures for the Development of Networks and Communities, 2006. TRIDENTCOM 2006. (pp. 6-pp). IEEE.
Yeh, C. H., Chen, H. Y., Chow, C. W., & Liu, Y. L. (2015). Utilization of multi-band OFDM modulation to increase traffic rate of phosphor-LED wireless VLC. Optics Express, 23(2), 1133–1138.
Wu, L., Zhang, Z., Dang, J., & Liu, H. (2014). Adaptive modulation schemes for visible light communications. Journal of Lightwave Technology, 33(1), 117–125.
Hsu, C. W., Chow, C. W., Lu, I. C., Liu, Y. L., Yeh, C. H., & Liu, Y. (2016). High speed imaging \(3 \times 3\) MIMO phosphor white-light LED based visible light communication system. IEEE Photonics Journal, 8(6), 1–6.
Khalid, A., Asif, H. M., Mumtaz, S., Al Otaibi, S., & Konstantin, K. (2019). Design of MIMO-visible light communication transceiver using maximum rank distance codes. IEEE Access, 7, 89128–89140.
Armstrong, J., & Lowery, A. J. (2006). Power efficient optical OFDM. Electronics letters, 42(6), 370–372.
Moreolo, M. S., Muñoz, R., & Junyent, G. (2010). Novel power efficient optical OFDM based on Hartley transform for intensity-modulated direct-detection systems. Journal of Lightwave Technology, 28(5), 798–805.
Barrami, F., Le Guennec, Y., Novakov, E., Duchamp, J. M., & Busson, P. (2013, October). A novel FFT/IFFT size efficient technique to generate real time optical OFDM signals compatible with IM/DD systems. In 2013 European microwave conference (pp. 1247-1250). IEEE.
Adnan, A., Liu, Y., Chow, C. W., & Yeh, C. H. (2020). Demonstration of non-Hermitian symmetry (NHS) serial-complex-valued orthogonal frequency division multiplexing (SCV-OFDM) for white-light visible light communication (VLC). OSA Continuum, 3(5), 1163–1168.
Khalid, A. (2020). Implementation of wavelet transform based non-Hermitian symmetry OFDM for indoor VLC system using Raspberry Pi. Journal of Optical Communications.
Safari, M., & Uysal, M. (2008). Do we really need OSTBCs for free-space optical communication with direct detection? IEEE Transactions on Wireless Communications, 7(11), 4445–4448.
Deng, P., & Kavehrad, M. (2017). Software defined adaptive MIMO visible light communications after an obstruction. In Optical Fiber Communication Conference, OSA Technical Digest (online) (Optical Society of America, 2017) (pp. Th1E-5). Optical Society of America.
Chen, C., Zhong, W. D., & Wu, D. (2017). Non-Hermitian symmetry orthogonal frequency division multiplexing for multiple-input multiple-output visible light communications. Journal of Optical Communications and Networking, 9(1), 36–44.
Aldababseh, M., & Jamoos, A. (2014). Estimation of FBMC/OQAM fading channels using dual Kalman filters. The Scientific World Journal, 2014.
Jayaprakash, A., & Reddy, G. R. (2015). Discrete ambiguity function based analysis of filter bank multicarrier systems. IETE Technical Review, 32(5), 330–346.
Sarowa, S., Singh, H., Agrawal, S., & Sohi, B. S. (2018). Design of a novel hybrid intercarrier interference mitigation technique through wavelet implication in an OFDM system. Digital Communications and Networks, 4(4), 258–263.
Zeng, L., Brien, D. C., Le Minh, H., Faulkner, G. E., Lee, K., Jung, D., Oh, Y., & Won, E. T. (2009). High data rate multiple input multiple output (MIMO) optical wireless communications using white LED lighting. IEEE Journal on Selected Areas in Communications, 27(9), 1654–1662.
Sushanth, K. S., & Chockalingam, A. (2018, June). Performance of imaging receivers using convex lens in indoor MIMO VLC systems. In 2018 IEEE \(87^{th}\) Vehicular Technology Conference (VTC Spring) (pp. 1-5). IEEE.
Komine, T., & Nakagawa, M. (2004). Fundamental analysis for visible-light communication system using LED lights. IEEE Transactions on Consumer Electronics, 50(1), 100–107.
Cincotti, G., Moreolo, M. S., & Neri, A. (2005). Optical wavelet signals processing and multiplexing. EURASIP Journal on Advances in Signal Processing, 2005(10), 1–10.
Mallat, S. G. (2009). A theory for multiresolution signal decomposition: the wavelet representation. In Fundamental Papers in Wavelet Theory (pp. 494-513). Princeton University Press.
Polikar, R., Topalis, A., Green, D., Kounios, J., & Clark, C. M. (2007). Comparative multiresolution wavelet analysis of ERP spectral bands using an ensemble of classifiers approach for early diagnosis of Alzheimer’s disease. Computers in Biology and Medicine, 37(4), 542–558.
Baig, S., Asif, H. M., Umer, T., Mumtaz, S., Shafiq, M., & Choi, J. G. (2018). High data rate discrete wavelet transform-based PLC-VLC design for 5G communication systems. IEEE Access, 6, 52490–52499.
Dickenson, R. J., & Ghassemlooy, Z. (2004). BER performance of 166 Mbit/s OOK diffuse indoor IR link employing wavelets and neural networks. Electronics Letters, 40(12), 753–755.
Rajbhandari, S., Ghassemlooy, Z., & Angelova, M. (2009). Effective denoising and adaptive equalization of indoor optical wireless channel with artificial light using the discrete wavelet transform and artificial neural network. Journal of Lightwave technology, 27(20), 4493–4500.
Vitthaladevuni, P. K., Alouini, M. S., & Kieffer, J. C. (2005). Exact BER computation for cross QAM constellations. IEEE Transactions on Wireless Communications, 4(6), 3039–3050.
Baig, S., Ali, U., Asif, H. M., Khan, A. A., & Mumtaz, S. (2019). Closed-form BER expression for Fourier and wavelet transform-based pulse-shaped data in downlink NOMA. IEEE Communications Letters, 23(4), 592–595.
Khan, A., & Shin, S. Y. (2018). Wavelet OFDM-based non-orthogonal multiple access downlink transceiver for future radio access. IETE Technical Review, 35(1), 17–27.
Jiang, T., & Wu, Y. (2008). An overview: Peak-to-average power ratio reduction techniques for OFDM signals. IEEE Transactions on Broadcasting, 54(2), 257–268.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Additional information
Publisher's Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Khalid, A. Wavelet transform based non-hermitian symmetry OFDM technique for indoor MIMO-VLC system with an imaging receiver. Wireless Netw 27, 4649–4663 (2021). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11276-021-02762-4
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11276-021-02762-4