Abstract
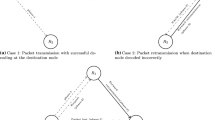
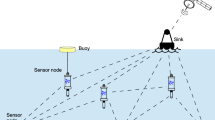
The characteristics of the underwater acoustic communication such as large propagation delay, high bit error rate and half-duplex, bring challenges to traditional automatic repeat request (ARQ) schemes. In this paper, we propose cooperative ARQ protocols based on relay selection in wireless sensor networks. These protocols use cooperative relays that provide an alternative path along a specific source-to-destination route. This alternative path has higher channel quality than that of the direct source–destination path. The main advantage of our methods is that we do not need to be aware of the relays locations. In fact, the relays will be organized by creating a time table at the destination. Furthermore, we evaluate the proposed schemes by comparing them with conventional stop and wait (S&W) ARQ and some other works in terms of throughput efficiency. Analytical and computer simulation results show that the proposed cooperative retransmission protocols can significantly improve the throughput even in a network with a few cooperative relay nodes.











Similar content being viewed by others
References
Akyildiz, I. F., Su, W., Sankarasubramaniam, Y., & Cayirci, E. (2002). A survey on sensor networks. IEEE Communications Magazine, 40(8), 102–114.
Ghoreyshi, S. M., Shahrabi, A., & Boutaleb, T. (2017). Void-handling techniques for routing protocols in underwater sensor networks: Survey and challenges. IEEE Communications Surveys and Tutorials, 19(2), 800–827.
Amjad, M., Sharif, M., Khalil Afzal, M., & Won Kim, S. (2016). TinyOS-new trends, comparative views, and supported sensing applications: A review. IEEE Sensors Journal, 16(9), 2865–2889.
Rashid, B., & Rehmani, M. H. (2016). Applications of wireless sensor networks for urban areas: A survey. Journal of Network and Computer Applications, 60, 192–219.
Amjad, M., Rehmani, M. H., & Mao, S. (2018). Wireless multimedia cognitive radio networks: A comprehensive survey. IEEE Communications Surveys and Tutorials, 20(2), 1056–1103.
Pramod, H. B., & Kumar, R. (2016). Multilayered energy harvesting and aggregation in underwater sensor acoustic networks for performance enhancement. In International conference on emerging technological trends (ICETT) (pp. 1–4). IEEE.
Erdem, H. E., & Cagri Gungor, V. (2017). Lifetime analysis of energy harvesting underwater wireless sensor nodes. In 2017 25th signal processing and communications applications conference (SIU) (pp. 1–4). IEEE.
Ghaznavi, M., & Jamshidi, A. (2015). A reliable spectrum sensing method in the presence of malicious sensors in distributed cognitive radio network. IEEE Sensors Journal, 15(3), 1810–1816.
Ghaznavi, M., & Jamshidi, A. (2013). Efficient method for reducing the average control bits in a distributed cooperative sensing in cognitive radio system. IET Communications, 7(9), 867–874.
Cui, J.-H., Kong, J., Gerla, M., & Zhou, S. (2006). The challenges of building mobile underwater wireless networks for aquatic applications. Ieee Network, 20(3), 12–18.
Akyildiz, I. F., Pompili, D., & Melodia, T. (2005). Underwater acoustic sensor networks: Research challenges. Elseviers Journal of Ad Hoc Networks, 3(3), 257–279.
Heidemann, J., Ye, W., Wills, J., Syed, A., & Li, Y. (2006). Research challenges and applications for underwater sensor networking. In Proceedings of IEEE WCNC (pp. 228–235).
Stojanovic, M. (2005). Optimization of a data link protocol for an underwater acoustic channel. In Europe Oceans 2005 (Vol. 1, pp. 68–73). IEEE.
Tomasi, B., et al. (2015). Cross-layer analysis via Markov models of incremental redundancy hybrid ARQ over underwater acoustic channels. Ad Hoc Networks, 34, 62–74.
Tacca, M., Monti, P., & Fumagalli, A. (2007). Cooperative and reliable ARQ protocols for energy harvesting wireless sensor nodes. IEEE Transactions on Wireless Communications, 6(7), 2519–2529.
Jamshidi, A. (2011). Direct sequence spread spectrum point-to-point communication scheme in underwater acoustic sparse channels. IET Communications, 5(4), 456–466.
Azad, S., Casari, P., Guerra, F., & Zorzi, M. (2011). On ARQ strategies over random access protocols in underwater acoustic networks. In OCEANS 2011 IEEE-Spain (pp. 1–7). IEEE.
Kwatra, P. (2013). ARQ protocol studies in underwater communication networks. In 2013 international conference on signal processing and communication (ICSC) (pp. 121–126). IEEE.
Azad, S., Casari, P., & Zorzi, M. (2013). The underwater selective repeat error control protocol for multiuser acoustic networks: Design and parameter optimization. IEEE Transactions on Wireless Communications, 12(10), 4866–4877.
Chitre, M., & Soh, W.-S. (2015). Reliable point-to-point underwater acoustic data transfer: To juggle or not to juggle? IEEE Journal of Oceanic Engineering, 40(1), 93–103.
Elyas Babiker, A., Nordin, M., & Zakaria, B. (2011). Energy efficiency analysis of error correction techniques in underwater wireless sensor networks. Journal of Engineering Science and Technology, 6, 17–28.
Hara, S., Ogino, A., Okada, M., & Morinaga, N. (1996). Throughput performance of SAW-ARQ protocol with adaptive packet length in mobile packet data transmission. IEEE Transactions on Vehicular Technology, 45, 561–569.
Annamalai, A., & Bhargava, V. (1998). Efficient ARQ error control strategies with adaptive packet length for mobile radio networks. In Proceedings of IEEE international conference on universal personal communications, ICUPC98 (Vol. 2, pp. 1247–1251).
Tan, H. P., Seah, W. K. G., & Doyle, L. (2007). A multi-hop ARQ protocol for underwater acoustic networks. In Proceedings of IEEE Oceans Europe (pp. 1–6).
Lee, J. W., Kim, J. P., Lee, J. H., Jang, Y. S., Dho, K. C., Son, K., & Cho, H. S. (2008). An improved ARQ scheme in underwater acoustic sensor networks. In Proceedings of MTS/IEEE Oceans08.
Lee, J. W., Cheon, J. Y., & Cho, H. S. (2010). A cooperative ARQ scheme in underwater acoustic sensor networks. In Proceedings of IEEE Oceans 2010.
Stojanovic, M. (2007). On the relationship between capacity and distance in an underwater acoustic communication channel. ACM SIGMOBILE Mobile Computing and Communications Review, 11(4), 34–43.
Lee, J. W., Cheon, J. Y., & Cho, H. S. (2011). A cooperative ARQ scheme for multi-hop underwater acoustic sensor networks. In Proceedings of IEEE Oceans 2011.
Mo, H., Mingir, A. C., Alhumyani, H., Albayram, Y., & Cui, J.-H. (2012). UW-HARQ: an underwater hybrid ARQ scheme: design, implementation and initial test. In Proceedings of IEEE OCEANS.
Ghosh, A., Lee, J., Cho, H. (2013). Throughput and energy efficiency of a cooperative hybrid ARQ protocol for underwater acoustic sensor networks. In: SENSORS 2013.
Jianghua, Y., Chen, H., Xie, L., & Hong, J. (2014). Performance analysis of hybrid ARQ schemes in underwater acoustic networks. In Proceedings of IEEE OCEANS (pp. 1–6).
Zhuang, H., Tan, H.-P., Valera, A., & Bai, Z. (2010). Opportunistic ARQ with bidirectional overhearing for reliable multihop underwater networking. In OCEANS 2010 IEEE-Sydney (pp. 1–6). IEEE.
Zhang, Y., Chen, Y., Zhou, S., Xu, X., Shen, X., & Wang, H. (2016). Dynamic node cooperation in an underwater data collection network. IEEE Sensors Journal, 16(11), 4127–4136.
Lin, A., Chen, H., & Xie, L. (2015). Performance analysis of ARQ protocols in multiuser underwater acoustic networks. In OCEANS 2015-MTS/IEEE Washington (pp. 1–6). IEEE.
Zhou, Z., Mo, H., Zhu, Y., Peng, Z., Huang, J., & Cui, J.-H. (2012). Fountain code based adaptive multi-hop reliable data transfer for underwater acoustic networks. In 2012 IEEE international conference on communications (ICC) (pp. 6396–6400). IEEE.
Urick, R. J. (1983). Principles of underwater sound (3rd ed.). New York: McGraw-Hill.
Proakis, J. G. (2006). Digital communications (5th ed.). New York: McGraw-Hill.
Papoulis, A., & Pillai, S. U. (2002). Probability, random variables, and stochastic processes. New York: Tata McGraw-Hill Education.
Petrioli, C., Petroccia, R., Potter, J. R., & Spaccini, D. (2015). The SUNSET framework for simulation, emulation and at-sea testing of underwater wireless sensor networks. Ad Hoc Networks, 34, 224–238.
Petrioli, C., Petroccia, R. (2012). SUNSET: Simulation, emulation and real-life testing of underwater wireless sensor networks. In Proceedings of IEEE UComms (pp. 12–14).
Das, A. P. (2016). Simulation tools for underwater sensor networks: A survey. Network Protocols and Algorithms, 8(4), 41–55.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Jamshidi, A. Efficient cooperative ARQ protocols based on relay selection in underwater acoustic communication sensor networks. Wireless Netw 25, 4815–4827 (2019). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11276-018-1773-5
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11276-018-1773-5