Abstract
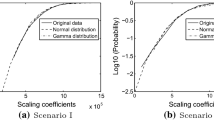
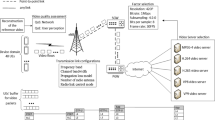
In this work two video-on-demand (VoD) capacity models for H.264 video traces transmitted using 802.11g are proposed, one based on a self-similar traffic distribution and the other one based in the summation of a large number of Pareto distributed random variables. To ascertain the validity of using such modeling techniques a statistical analysis was performed where it was found that H.264 video traces exhibit self-similarity and heavy-tailed properties, as previous video formats that also use variable bit rate encoding. The models were evaluated against trace based simulations using ns-3 and results from hardware testbeds from other works. The model based on Pareto distributions gives a lower bound on a wide range of buffer sizes, while the model based on self-similarity provides a closer approximation to the user load when buffer size is high. The results show that the models can approximate the maximum user load for H.264 transmission on a local area VoD system and that they depend on the access point buffer size and the desired quality of service expressed as packet-loss probability.








Similar content being viewed by others
References
Kim, H., Hou, J. C., Hu, C., & Ge, Y. (2007). Qos provisioning in ieee 802.11-compliant networks: Past, present, and future. Computer Networks, 51(8), 1922–1941.
Reed, D., & Lansford, J. (2014). Wi-fi as a commercial service: New technology and policy implications. Telecommunications Policy, 38(8), 827–837.
Garrett, M. W. & Willinger, W. (1994). Analysis, modeling and generation of self-similar vbr video traffic. In ACM SIGCOMM computer communication review (Vol. 24, pp. 269–280) ACM.
Leland, W. E., Taqqu, M. S., Willinger, W., & Wilson, D. V. (1994). On the self-similar nature of ethernet traffic (extended version). Networking, IEEE/ACM Transactions on, 2(1), 1–15.
Lazaris, A., & Koutsakis, P. (2010). Modeling multiplexed traffic from h. 264/avc videoconference streams. Computer Communications, 33(10), 1235–1242.
Garrett, M. W., Willinger, W. (1994). Analysis, modeling and generation of self-similar VBR video traffic. In ACM SIGCOMM computer communication review (Vol. 24(4), pp. 269–280).
Sahinoglu, Z., & Tekinay, S. (1999). On multimedia networks: Self-similar traffic and network performance. Communications Magazine, IEEE, 37(1), 48–52.
Aguiar, E., Riker, A., Cerqueira, E., Abelm, A., Mu, M., Braun, T., et al. (2014). A real-time video quality estimator for emerging wireless multimedia systems. Wireless Networks, 20(7), 1759–1776.
Gierłowski, K., Kostuch, A., Woźniak, J., & Nowicki, K. (2011). Testbed analysis of video and VoIP transmission performance in IEEE 802.11 b/g/n networks. Telecommunication Systems, 48(3–4), 247–260.
Zaliapin, I., Kagan, Y. Y., & Schoenberg, F. P. (2005). Approximating the distribution of pareto sums. Pure and Applied Geophysics, 162(6–7), 1187–1228.
Pinheiro, B. (2013). NS3.13 + Evalvid module by GERCOM. https://github.com/gercom/evalvid-ns3.
Asmussen, S. (2003). Applied probability and queues. New York: Springer.
Rolski, T., Schmidli, H., Schmidt, V., & Teugels, J. (1999). Stochastic processes for insurance and finance. Wiley series in probability and statistics. Chichester: Wiley.
Leon-Garcia, A. (2008). Probability, statistics, and random processes for electrical engineering. Upper Saddle River: Pearson/Prentice Hall.
Beran, J. (1994). Statistics for long-memory processes. Chapman & Hall/CRC monographs on statistics & applied probability. Abingdon: Taylor & Francis.
Park, K., & Willinger, W. (2000). Self-similar network traffic: An overview. In K. Park & W. Willinger (Eds.), Self-similar network traffic and performance evaluation (pp. 1–38). New York: John Wiley & Sons, Inc.
Duffield, N. G. & O’connell, N. (1995). Large deviations and overflow probabilities for the general single-server queue, with applications. In Mathematical Proceedings of the Cambridge Philosophical Society (Vol. 118, pp. 363–374). Cambridge Univ Press.
Ramirez-Velarde, R. V., & Rodriguez-Dagnino, R. M. (2010). From commodity computers to high-performance environments: Scalability analysis using self-similarity, large deviations and heavy-tails. Concurrency and Computation: Practice and Experience, 22(11), 1494–1515.
Henderson, T. R., Roy, S., Floyd, S., & Riley, G. F. (2006). Ns-3 project goals. In Proceeding from the 2006 workshop on Ns-2: The IP network simulator (Vol. 1(13)).
Seeling, P., & Reisslein, M. (2012). Video transport evaluation with H.264 video traces. IEEE Communications Surveys and Tutorials, in print, 14(4), 1142–1165.
Crovella, M. E., & Lipsky, L. (2000). Simulations with heavy-tailed workloads. Self-similar network traffic and performance evaluation, 3, 89–100.
Klaue, J., Rathke, B., & Wolisz, A. (2003). Evalvid–A framework for video transmission and quality evaluation. Computer performance evaluation. modelling techniques and tools (pp. 255–272). Berlin: Springer.
Saladino, D., Paganelli, A., & Casoni, M. (2013). A tool for multimedia quality assessment in NS3: QoE Monitor. Simulation Modelling Practice and Theory, 32, 30–41.
Abraham, J. & Riley, G. (2012). Simulator agnostic ns-3 applications. In Proceedings of the 5th international ICST conference on simulation tools and techniques, SIMUTOOLS’12 (pp. 391–396).
Kirichenko, L., Radivilova, T., & Deineko, Z. (2011). Comparative analysis for estimating of the hurst exponent for stationary and nonstationary time series. Information Technologies & Knowledge, 5(1), 371–388.
RClegg, R. G. (2006). A practical guide to measuring the Hurst parameter. In 21 st UK performance engineering workshop (Vol. 7(2), pp. 3–14).
Lobo, A., Garca, R., Paeda, X. G., Melendi, D., & Cabrero, S. (2013). Modeling video on demand services taking into account statistical dependences in user behavior. Simulation Modelling Practice and Theory, 31, 96–115.
Taqqu, M. S., Teverovsky, V., & Willinger, W. (1995). Estimators for long-range dependence: An empirical study. Fractals, 3(4), 785–798.
Taqqu, M. S., & Teverovsky, V. (1997). Robustness of whittle-type estimators for time series with long-range dependence. Communications in statistics. Stochastic models, 13(4), 723–757.
Bardet, J.-M., Philippe, A., Oppenheim, G., Taqqu, M., Stoev, S., & Lang, G. (2003). Semi-parametric estimation of the long-range dependence parameter: A survey. In P. Doukhan, G. Oppenheim, & M. S. Taqqu (Eds.), Theory and applications of long-range dependence (pp. 557–577). Basel: Birkhäuser.
Abry, P., & Veitch, D. (1998). Wavelet analysis of long-range-dependent traffic. Information Theory, IEEE Transactions on, 44(1), 2–15.
Font, J. L., Inigo, P., Dominguez, M., Sevillano, J. L., & Amaya, C. (2011). Analysis of source code metrics from ns-2 and ns-3 network simulators. Simulation Modelling Practice and Theory, 19(5), 1330–1346.
Karagiannis, T. Faloutsos, M., Riedi, R. H. (2002). Long-range dependence: now you see it, now you don’t!. In Global telecommunications conference, 2002. GLOBECOM’02. IEEE (Vol. 3, pp. 2165–2169).
Rose, O. (1995). Statistical properties of MPEG video traffic and their impact on traffic modeling in ATM systems. In 20th conference on local computer networks, Proceedings (pp. 397–406).
Xue, F. (2000). Performance analysis of a wavelet-based hurst parameter estimator for self-similar traffic. In: 2000 SCS Symposium on Performance Evaluation of Computer and Telecommunication Systems SPECTS2K.
Reljin, I., Samčović, A., & Reljin, B. (2006). H. 264/AVC video compressed traces: Multifractal and fractal analysis. EURASIP Journal on Applied Signal Processing, 2006, 123.
Stallings, W. (2002). High-speed networks and internets: performance and quality of service. New Delhi: Pearson Education India.
Samoradnitsky, G. & Taqqu, M. S. (1994). Stable non-Gaussian random processes: stochastic models with infinite variance. (Vol. 1).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Barba-Jimenez, C., Ramirez-Velarde, R. & Nolazco-Flores, J.A. Models for wireless H.264 video-on-demand services using self-similarity and heavy-tails. Wireless Netw 23, 2239–2252 (2017). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11276-016-1281-4
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11276-016-1281-4