Abstract
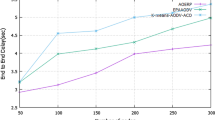
The Ant Colony Optimization (ACO) routing technique is an adaptive and reliable approach to find the paths in routing for Mobile Ad hoc Networks (MANETs). In ACO algorithms, the ant as agents traverses across the network to find the shortest path from the source to its destination. During the traversal, the ants deposits pheromones on its path. The path with high probability of pheromone is chosen as the optimized path to transfer data packets between the source and the destination. The quantity of the pheromone laid down on a path depends on its quality metrics viz. minimum number of hops, minimum energy path cost and packet transfer delay. Due to the high dynamic nature of MANETs, the path with high probability of the pheromone deposition may rapidly become unavailable due to link failures. Therefore, it is a challenging task in MANETs to construct a reliable path that is less likely to be disconnected for a long period of time. In this paper, a novel robust energy efficient ACO routing algorithm named AntHocMMP has been proposed. This algorithm is meant to achieve robustness of paths for reliable communication with adaptive re-transmission delays in MANETs. This proposed algorithm enhances the performance of Max–Min–Path (MMP) approach by using ant as agents to find the optimal path in the network. The selection of the optimal path is based on the residual energy of the nodes in that path. A robust route with minimum energy path cost with a short hop-count is chosen for pheromone deposition. Therefore, to keep the paths connected in a dynamic topology, the proposed AntHocMMP redistributes the pheromone based on the energy path cost and it constructs an alternative path for reliable communication between the source and the destination nodes. In this paper, a study has also been done on the effects of re-transmission delays spent in reliably delivering the packets to the destination nodes. The simulation result shows that AntHocMMP achieves a good packet delivery ratio in a wider communication range than the existing algorithms viz. R-ACO1, LAR, MMP and AntHocNet routing algorithms. The statistical analysis viz. t test and Anova-test have been performed that proves which in turn the proposed AntHocMMP dominates the other existing algorithms in a more significant way.





Similar content being viewed by others
References
Camilo, T., Carreto, C., Silve, J. S., & Boavida, F. An energy-efficient ant-based routing algorithm for wireless sensor networks. Ant Colony Optimization and Swarm Intelligence, LNCS, 4150, 49–59.
Parsapoor, M., & Bilstrup, U. (2013). Ant colony optimization for channel assignment in a clustered mobile ad hoc network. In 4th international conference, ICSI 2013 (pp. 314–322). Springer: Berlin Heidelberg.
Kamali, S., & Opatrny, J. (2007). POSANT: A position based ant colony routing algorithm for mobile ad hoc networks. In Proceedings of the third international conference on wireless and mobile communications (ICWMC’07), pp. 21–28.
Dorigo, M., & Caro, G. D. (1999). The ant colony optimization meta-heuristic, New Ideas in Optimization, pp. 11–32.
Dorigo, M., Birattari, M., & Stutzle, T. (2006). Ant colony optimization: Artificial ants as a computational intelligence technique. IEEE Computational Intelligence Magazine, 1(4), 28–39.
Guines, M., Sorges, U., Bouazizi, I. (2002). ARA—the ant-colony based routing algorithm for MANETs. In ICPP workshops, IEEE computer society, pp. 79–85.
Baskaran, R., Victer Paul, P., & Dhavachelvan, P. (2012). Ant colony optimization for data Cacje technique in MANET. In Advances in intelligent systems and computing, Springer, India, pp. 873–878.
Camara, D., & Loureiro, A. A. F. (2001). GPS/ant-like routing in ad hoc networks. Telecommunication Systems, 18(1–3), 85–100.
Guo, S., Oliver, W. W., & Yang, W. (2007). Energy-aware multicasting in wireless ad hoc networks: A survey and discussion. Computer Communications, 30(9), 2129–2148.
Di Caro, G., Ducatella, F., Gambardella, L. M. (2004). AntHocNet: An ant-based hybrid routing algorithm for mobile ad hoc networks. In Parallel problem solving from nature—PPSN VIII, Vol. 3242, LNCS, pp. 461–470.
Vijayalakshmi, P., Francis, S. J., & Abraham Dinakaran, J. (2014). Max-min-path energy-efficient routing algorithm—A novel approach to enhance network lifetime of MANETs”, ICDCN 2014, Springer LNCS 8314, pp. 512–518.
Krzysztof, W. (2005). Ant algorithm for flow assignment in connection-oriented networks. International Journal of Applied Mathematics and Computer Science, 15(2), 205–220.
Abolhasan, M., Wysocki, T., & Dutkiewicz, E. (2004). A review of routing protocols for mobile ad hoc networks. Ad Hoc Networks, 1, 1–22.
Haas, Z. J., & Pearlman, M. R. (2001). The performance of query control schemes for the zone routing protocol. ACM/IEEE Transactions on Networking, 9(4), 427–438.
Giagkos, Alexandros, & Wilson, Myra S. (2014). BeeIP—A swarm intelligence based routing for wireless ad hoc networks. Information Sciences, 265, 23–35.
Matsuo, H., & Mori, K. (20014). Accelerated ants routing in dynamic networks. In Proceedings of the international conference on software engineering, artificial intelligence, networking and parallel/distributed computing, pp. 333–339.
Dorigo, M., & Stutzle, T. (2004). Ant Colony Optimization. Cambridge: MIT Press.
Blum, C. (2005). Ant colony optimization: Introduction and recent trends. Physics of Life Reviews, 2(4), 353–373.
Perkins, C. E. (2001). Ad hoc networking. Reading: Addison-Wesley.
Toh, C. (2002). Ad hoc mobile wireless networks: Protocols and systems. Englewood Cliffs: Prentice-Hall.
Kadono, D., Izumi, T., Ooshita, F., & Kakugawa, H. (2010). An ant colony optimization routing based on robustness for ad hoc networks with GPSs. Elsevier-Ad Hoc Networks, 8, 63–76.
Correia, F., & Vazao, T. (2010). Simple ant routing algorithm strategies for a (Multipurpose) MANET model. Elsevier-Ad Hoc Networks, 8, 810–823.
Sardar, A. R., Singh, M., Sahoo, R. R., Majumder, K., Sing, J. K., & Sarkar, S. K. (2014). An efficient ant colony based routing algorithm for better quality of services for MANTETs, ICT and critical infrastructure. In Proceeding of the 48th annual convention of CSI—Volume 1, advances in intelligent systems and computing, Vol. 248, Springer International Publishing: Switzerland, pp. 233–240.
Sisodia, R. S., Manoj, B. S., & Murthy, C. R. (2002). A preferred link based routing protocol for wireless ad hoc networks. Journal of Communication and Networks, 4(1), 14–21.
Perkins, C. E., & Bhagwat, P. (1994). Highly dynamic destination-sequenced distance-vector routing (DSDV) for mobile computers. Computer Communications Review, 10, 234–244.
Perkins, C. E., Royer, E. M., & Das, S. R. (1999). Ad hoc on demand distance vector (AODV) routing. In IEEE workshop on mobile computing systems and applications, pp. 90–100.
Dorigo, M., & Gambardella, L. M. (1997). Ant colony system: A cooperative learning approach to the traveling salesman problem. IEEE Transactions on Evolutionary Computation, 1(1), 53–66.
Pandy, N. P. (2005). Artificial intelligence and intelligent systems (pp. 532–574). Oxford: Oxford University Press.
Acknowledgments
The author wishes to thank the Karunya Univesity for providing financial support and lab facilities to carry out the research work. The authors also wish to thank the editor, the reviewers and all the supporting higher officials for their continuous support and encouragement in the successful completion of the research work.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Vijayalakshmi, P., Francis, S.A.J. & Abraham Dinakaran, J. A robust energy efficient ant colony optimization routing algorithm for multi-hop ad hoc networks in MANETs. Wireless Netw 22, 2081–2100 (2016). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11276-015-1082-1
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11276-015-1082-1