Abstract
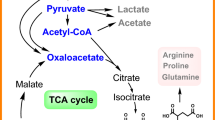
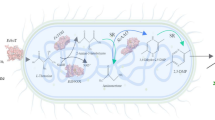
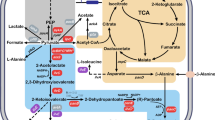
Phenyllactic acid (PLA), a natural antimicrobial substance, has many potential applications in the food, animal feed, pharmaceutical and cosmetic industries. However, its production is limited by the complex reaction steps involved in its chemical synthesis. Through advances in metabolic engineering and synthetic biology strategies, enzymatic or whole-cell catalysis was developed as an alternative method for PLA production. Herein, we review recent developments in metabolic engineering and synthetic biology strategies that promote the microbial production of high-value PLA. Specially, the advantages and disadvantages of the using of the three kinds of substrates, which includes phenylpyruvate, phenylalanine and glucose as starting materials by natural or engineered microbes is summarized. Notably, the bio-conversion of PLA often requires the consumption of expensive coenzyme NADH. To overcome the issues of NADH regeneration, efficiently internal cofactor regeneration systems constructed by co-expressing different enzyme combinations composed of lactate dehydrogenase with others for enhancing the PLA production, as well as their possible improvements, are discussed. In particular, the construction of fusion proteins with different linkers can achieve higher PLA yield and more efficient cofactor regeneration than that of multi-enzyme co-expression. Overall, this review provides a comprehensive overview of PLA biosynthesis pathways and strategies for increasing PLA yield through biotechnology, providing future directions for the large-scale commercial production of PLA and the expansion of downstream applications.


Similar content being viewed by others
References
Aalbers FS, Fraaije MW (2019) Enzyme fusions in Biocatalysis: coupling reactions by pairing enzymes. ChemBioChem 20(1):20–28. https://doi.org/10.1002/cbic.201800394
Abdul-Rahim O, Wu Q, Price TK, Pistone G, Diebel K, Bugni TS, Wolfe AJ (2021) Phenyl-lactic acid is an active ingredient in bactericidal supernatants of Lactobacillus crispatus. J Bacteriol 203(19). https://doi.org/10.1128/jb.00360-21
Anami Y, Yamazaki CM, Xiong W, Gui X, Zhang N, An Z, Tsuchikama K (2018) Glutamic acid-valine-citrulline linkers ensure stability and efficacy of antibody-drug conjugates in mice. Nat Commun 9(1):2512. https://doi.org/10.1038/s41467-018-04982-3
Benedict K, Chiller TM, Mody RK (2016) Invasive fungal infections acquired from contaminated Food or Nutritional supplements: a review of the literature. Foodborne Pathog Dis 13(7):343–349. https://doi.org/10.1089/fpd.2015.2108
Castellano P, Perez Ibarreche M, Blanco Massani M, Fontana C, Vignolo GM (2017) Strategies for Pathogen Biocontrol using lactic acid Bacteria and their metabolites: a Focus on Meat Ecosystems and Industrial environments. Microorganisms 5(3). https://doi.org/10.3390/microorganisms5030038
Chatterjee M, D’Morris S, Paul V, Warrier S, Vasudevan AK, Vanuopadath M, Nair SS, Paul-Prasanth B, Mohan CG, Biswas R (2017) Mechanistic understanding of phenyllactic acid mediated inhibition of quorum sensing and biofilm development in Pseudomonas aeruginosa. Appl Microbiol Biotechnol 101(22):8223–8236. https://doi.org/10.1007/s00253-017-8546-4
Choi KY, Jung EO, Jung DH, Pandey BP, Lee N, Yun H, Park HY, Kim BG (2012) Novel iron-sulfur containing NADPH-Reductase from Nocardia farcinica IFM10152 and fusion construction with CYP51 lanosterol demethylase. Biotechnol Bioeng 109(3):630–636. https://doi.org/10.1002/bit.24359
Costa JR, Tonon RV, Cabral L, Gottschalk L, Pastrana L, Pintado ME (2020) Valorization of Agricultural Lignocellulosic Plant Byproducts through enzymatic and enzyme-assisted extraction of high-value-added Compounds: a review. ACS Sustain Chem Eng 8(35):13112–13125. https://doi.org/10.1021/acssuschemeng.0c02087
De Melo Pereira GV, De Carvalho Neto DP, De O, Junqueira AC, Karp SG, Letti LAJ, Magalhaes Junior AI, Soccol CR (2020) A review of selection criteria for starter Culture Development in the Food Fermentation Industry. Food Reviews International 36(2):135–167. https://doi.org/10.1080/87559129.2019.1630636
Debonne E, Vermeulen A, Bouboutiefski N, Ruyssen T, Van Bockstaele F, Eeckhout M, Devlieghere F (2020) Modelling and validation of the antifungal activity of DL-3-phenyllactic acid and acetic acid on bread spoilage moulds. Food Microbiol 88:103407. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.fm.2019.103407
Fan L, Wang Y, Tuyishime P, Gao N, Li Q, Zheng P, Sun J, Ma Y (2018) Engineering Artificial Fusion Proteins for enhanced methanol Bioconversion. ChemBioChem 19(23):2465–2471. https://doi.org/10.1002/cbic.201800424
Guan J, Guan Y-X, Yun J, Yao S-J (2018a) Chromatographic separation of phenyllactic acid from crude broth using cryogels with dual functional groups. J Chromatogr A 1554:92–100. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.chroma.2018.04.043
Guan J, Guan YX, Yun J, Yao SJ (2018b) Chromatographic separation of phenyllactic acid from crude broth using cryogels with dual functional groups. J Chromatogr A 1554:92–100. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.chroma.2018.04.043
Guan J, Han C, Guan Y, Zhang S, Yun J, Yao S (2019) Optimizational production of phenyl lactic acid by a Lactobacillus buchneri strain via uniform design with overlay sampling methodology. Chin J Chem Eng 27(2):418–425. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.cjche.2018.04.005
He RJ, Finan B, Mayer JP, DiMarchi RD (2019) Peptide conjugates with small molecules designed to Enhance Efficacy and Safety. Molecules 24(10). https://doi.org/10.3390/molecules24101855
Heil M, Podebrad F, Beck T, Mosandl A, Sewell AC, Bohles H (1998) Enantioselective multidimensional gas chromatography mass spectrometry in the analysis of urinary organic acids. J Chromatogr B 714(2):119–126. https://doi.org/10.1016/s0378-4347(98)00233-3
Hendrickson JA, Hu C, Aitken SL, Beyda N (2019) Antifungal Resistance: a concerning Trend for the Present and Future. Curr Infect Dis Rep 21(12). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11908-019-0702-9
Hou Y, Gao B, Cui J, Tan Z, Qiao C, Jia S (2019) Combination of multi-enzyme expression fine-tuning and co-substrates addition improves phenyllactic acid production with an Escherichia coli whole-cell biocatalyst. Bioresour Technol 287:121423. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.biortech.2019.121423
Hrncirova L, Hudcovic T, Sukova E, Machova V, Trckova E, Krejsek J, Hrncir T (2019) Human gut microbes are susceptible to antimicrobial food additives in vitro. Folia Microbiol 64(4):497–508. https://doi.org/10.1007/s12223-018-00674-z
Huccetogullari D, Luo ZW, Lee SY (2019) Metabolic engineering of microorganisms for production of aromatic compounds. Microbial Cell Factories 18. https://doi.org/10.1186/s12934-019-1090-4
Kadyan S, Rashmi HM, Pradhan D, Kumari A, Chaudhari A, Deshwal GK (2021) Effect of lactic acid bacteria and yeast fermentation on antimicrobial, antioxidative and metabolomic profile of naturally carbonated probiotic whey drink. LWT 142:111059. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.lwt.2021.111059
Kawaguchi H, Teramura H, Uematsu K, Hara KY, Hasunuma T, Hirano K, Sazuka T, Kitano H, Tsuge Y, Kahar P, Niimi-Nakamura S, Oinuma KI, Takaya N, Kasuga S, Ogino C, Kondo A (2015) Phenyllactic acid production by simultaneous saccharification and fermentation of pretreated sorghum bagasse. Bioresour Technol 182:169–178. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.biortech.2015.01.097
Lavermicocca P, Valerio F, Visconti A (2003) Antifungal activity of phenyllactic acid against molds isolated from bakery products. Appl Environ Microbiol 69(1):634–640. https://doi.org/10.1128/aem.69.1.634-640.2003
Lee W, Park YT, Lim S, Yeom SH, Jeon C, Lee HS, Yeon YJ (2021) Efficient production of Phenyllactic Acid by whole-cell Biocatalysis with Cofactor Regeneration System. Biotechnol Bioprocess Eng 26(3):402–407. https://doi.org/10.1007/s12257-020-0270-8
Li L, Shin SY, Lee KW, Han NS (2014) Production of natural antimicrobial compound D-phenyllactic acid using Leuconostoc mesenteroides ATCC 8293 whole cells involving highly active D-lactate dehydrogenase. Lett Appl Microbiol 59(4):404–411. https://doi.org/10.1111/lam.12293
Li M, Meng X, Sun Z, Zhu C, Ji H (2019) Effects of NADH availability on 3-Phenyllactic acid production by Lactobacillus plantarum expressing formate dehydrogenase. Curr Microbiol 76(6):706–712. https://doi.org/10.1007/s00284-019-01681-0
Li X, Ning Y, Liu D, Yan A, Wang Z, Wang S, Miao M, Zhu H, Jia Y (2015) Metabolic mechanism of phenyllactic acid naturally occurring in chinese pickles. Food Chem 186:265–270. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.foodchem.2015.01.145
Lind H, Sjogren J, Gohil S, Kenne L, Schnurer J, Broberg A (2007) Antifungal compounds from cultures of dairy propionibacteria type strains. FEMS Microbiol Lett 271(2):310–315. https://doi.org/10.1111/j.1574-6968.2007.00730.x
Liu F, Sun Z, Wang F, Liu Y, Zhu Y, Du L, Wang D, Xu W (2020) Inhibition of biofilm formation and exopolysaccharide synthesis of Enterococcus faecalis by phenyllactic acid. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.fm.2019.103344. Food Microbiology 86
Liu W, Wang P (2007) Cofactor regeneration for sustainable enzymatic biosynthesis. Biotechnol Adv 25(4):369–384. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.biotechadv.2007.03.002
Liu Y, Wang D, Sun Z, Liu F, Du L, Wang D (2021) Preparation and characterization of gelatin/chitosan/3-phenylacetic acid food-packaging nanofiber antibacterial films by electrospinning. Int J Biol Macromol 169:161–170. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ijbiomac.2020.12.046
Lu H, Bai Y, Fan T-p, Zhao Y, Zheng X, Cai Y (2018) Identification of a L-Lactate dehydrogenase with 3,4-dihydroxyphenylpyruvic reduction activity for L-Danshensu production. Process Biochem 72:119–123. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.procbio.2018.06.011
Luo X, Zhang Y, Yin F, Hu G, Jia Q, Yao C, Fu Y (2020a) Enzymological characterization of a novel d-lactate dehydrogenase from Lactobacillus rossiae and its application in d-phenyllactic acid synthesis. 3 Biotech 10(3):101. https://doi.org/10.1007/s13205-020-2098-5
Luo X, Zhang Y, Yin L, Zheng W, Fu Y (2020b) Efficient synthesis of D-phenyllactic acid by a whole-cell biocatalyst co-expressing glucose dehydrogenase and a novel D-lactate dehydrogenase from Lactobacillus rossiae. 3 Biotech 10(1). https://doi.org/10.1007/s13205-019-2003-2
Luo X, Zhang Y, Yin L, Zheng W, Fu Y (2020c) Efficient synthesis of d-phenyllactic acid by a whole-cell biocatalyst co-expressing glucose dehydrogenase and a novel d-lactate dehydrogenase from Lactobacillus rossiae. 3 Biotech 10(1):14. https://doi.org/10.1007/s13205-019-2003-2
Martins FCOL, Sentanin MA, De Souza D (2019) Analytical methods in food additives determination: compounds with functional applications. Food Chem 272:732–750. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.foodchem.2018.08.060
Meruvu H (2022) Redefining methods for augmenting lactic acid bacteria robustness and phenyllactic acid biocatalysis: integration valorizes simplicity. Crit Rev Food Sci Nutr. https://doi.org/10.1080/10408398.2022.2141681
Mokoena MP (2017) Lactic acid Bacteria and their bacteriocins: classification, biosynthesis and applications against Uropathogens. A Mini-Review Molecules 22(8). https://doi.org/10.3390/molecules22081255
Mu W, Liu F, Jia J, Chen C, Zhang T, Jiang B (2009) 3-Phenyllactic acid production by substrate feeding and pH-control in fed-batch fermentation of Lactobacillus sp SK007. Bioresour Technol 100(21):5226–5229. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.biortech.2009.05.024
Mu W, Yu S, Zhu L, Jiang B, Zhang T (2012) Production of 3-phenyllactic acid and 4-hydroxyphenyllactic acid by Pediococcus acidilactici DSM 20284 fermentation. Eur Food Res Technol 235(3):581–585. https://doi.org/10.1007/s00217-012-1768-x
Ning Y, Yan A, Yang K, Wang Z, Li X, Jia Y (2017) Antibacterial activity of phenyllactic acid against Listeria monocytogenes and Escherichia coli by dual mechanisms. Food Chem 228:533–540. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.foodchem.2017.01.112
Patgiri A, Skinner OS, Miyazaki Y, Schleifer G, Marutani E, Shah H, Sharma R, Goodman RP, To TL, Robert Bao X, Ichinose F, Zapol WM, Mootha VK (2020) An engineered enzyme that targets circulating lactate to alleviate intracellular NADH:NAD(+) imbalance. Nat Biotechnol 38(3):309–313. https://doi.org/10.1038/s41587-019-0377-7
Priyadarshini A, Rajauria G, O’Donnell CP, Tiwari BK (2019) Emerging food processing technologies and factors impacting their industrial adoption. Critical. Reviews in Food Science and Nutrition 59(19):3082–3101. https://doi.org/10.1080/10408398.2018.1483890
Qin Z, Wang D, Luo R, Li T, Xiong X, Chen P (2021) Using unnatural protein fusions to engineer a Coenzyme Self-Sufficiency System for D-Phenyllactic Acid Biosynthesis in Escherichia coli. Front Bioeng Biotechnol 9(1327). https://doi.org/10.3389/fbioe.2021.795885
Rajanikar RV, Nataraj BH, Naithani H, Ali SA, Panjagari NR, Behare PV (2021) Phenyllactic acid: a green compound for food biopreservation. Food Control 128:108184. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.foodcont.2021.108184
Reshamwala SMS, Pagar SK, Velhal VS, Maranholakar VM, Talangkar VG, Lali AM (2014) Construction of an efficient Escherichia coli whole-cell biocatalyst for D-mannitol production. J Biosci Bioeng 118(6):628–631. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jbiosc.2014.05.004
Romero JL, Grande Burgos MJ, Perez-Pulido R, Galvez A, Lucas R (2017) Resistance to Antibiotics, Biocides, Preservatives and Metals in Bacteria isolated from Seafoods: co-selection of strains resistant or tolerant to different classes of Compounds. Front Microbiol 8. https://doi.org/10.3389/fmicb.2017.01650
Ryan LAM, Dal Bello F, Czerny M, Koehler P, Arendt EK (2009) Quantification of Phenyllactic Acid in Wheat Sourdough using high Resolution Gas Chromatography-Mass Spectrometry. J Agric Food Chem 57(3):1060–1064. https://doi.org/10.1021/jf802578e
Schmidt M, Lynch KM, Zannini E, Arendt EK (2018) Fundamental study on the improvement of the antifungal activity of Lactobacillus reuteri R29 through increased production of phenyllactic acid and reuterin. Food Control 88:139–148. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.foodcont.2017.11.041
Shishodia SK, Tiwari S, Shankar J (2019) Resistance mechanism and proteins in aspergillus species against antifungal agents. Mycology 10(3):151–165. https://doi.org/10.1080/21501203.2019.1574927
Siedler S, Balti R, Neves AR (2019) Bioprotective mechanisms of lactic acid bacteria against fungal spoilage of food. Current. Opin Biotechnol 56:138–146. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.copbio.2018.11.015
Soon JM, Brazier AKM, Wallace CA (2020) Determining common contributory factors in food safety incidents – A review of global outbreaks and recalls 2008–2018. Trends. Food Sci Technol 97:76–87. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.tifs.2019.12.030
Sorrentino E, Tremonte P, Succi M, Iorizzo M, Pannella G, Lombardi SJ, Sturchio M, Coppola R (2018a) Detection of Antilisterial Activity of 3-Phenyllactic acid using Listeria innocua as a model. Front Microbiol 9. https://doi.org/10.3389/fmicb.2018.01373
Sorrentino E, Tremonte P, Succi M, Iorizzo M, Pannella G, Lombardi SJ, Sturchio M, Coppola R (2018b) Detection of Antilisterial Activity of 3-Phenyllactic acid using Listeria innocua as a model. Front Microbiol 9:1373. https://doi.org/10.3389/fmicb.2018.01373
Sun H-L, Chuai J, Wei H, Zhang X, Yu H (2019) Multi-functional organic gelator derived from phenyllactic acid for phenol removal and oil recovery. J Hazard Mater 366:46–53. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jhazmat.2018.11.095
Sun X, Yin L, Zhu H, Zhu J, Hu J, Luo X, Huang H, Fu Y (2022) Enhanced Antimicrobial Cellulose/Chitosan/ZnO biodegradable. Compos Membrane Membr 12(2). https://doi.org/10.3390/membranes12020239
Tong S, Wang X, Shen M, Lv L, Lu M, Bu Z, Yan J (2017) Enantioseparation of 3-phenyllactic acid by chiral ligand exchange countercurrent chromatography. J Sep Sci 40(8):1834–1842. https://doi.org/10.1002/jssc.201601384
Tuberoso CIG, Bifulco E, Caboni P, Sarais G, Cottiglia F, Floris I (2011) Lumichrome and phenyllactic acid as chemical markers of Thistle (Galactites tomentosa Moench. Honey J Agricultural Food Chem 59(1):364–369. https://doi.org/10.1021/jf1039074
Valerio F, Lavermicocca P, Pascale M, Visconti A (2004) Production of phenyllactic acid by lactic acid bacteria: an approach to the selection of strains contributing to food quality and preservation. FEMS Microbiol Lett 233(2):289–295. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.femsle.2004.02.020
Van Thi Thuy H, Fleet GH, Zhao J (2018) Unravelling the contribution of lactic acid bacteria and acetic acid bacteria to cocoa fermentation using inoculated organisms. Int J Food Microbiol 279:43–56. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ijfoodmicro.2018.04.040
Wang X, Hou Y, Liu L, Li J, Du G, Chen J, Wang M (2018a) A new approach for efficient synthesis of phenyllactic acid from L-phenylalanine: pathway design and cofactor engineering. J Food Biochem 42(5). https://doi.org/10.1111/jfbc.12584
Wang X, Hou Y, Liu L, Li J, Du G, Chen J, Wang M (2018b) A new approach for efficient synthesis of phenyllactic acid from L-phenylalanine: pathway design and cofactor engineering. J Food Biochem 42(5):e12584. https://doi.org/10.1111/jfbc.12584
Wang XT, Hou Y, Liu L, Li JH, Du GC, Chen J, Wang M (2018c) A new approach for efficient synthesis of phenyllactic acid from L-phenylalanine: pathway design and cofactor engineering. J Food Biochem 42(5). https://doi.org/10.1111/jfbc.12584
Wang Y, Luo X, Sun X, Hu J, Guo Q, Shen B, Fu Y (2022) Lactate dehydrogenase encapsulated in a metal-organic framework: a novel stable and reusable biocatalyst for the synthesis of D-phenyllactic acid. Colloids Surf B 216:112604. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.colsurfb.2022.112604
Wang YJ, Ren HQ, Zhao HM (2018d) Expanding the boundary of biocatalysis: design and optimization of in vitro tandem catalytic reactions for biochemical production. Crit Rev Biochem Mol Biol 53(2):115–129. https://doi.org/10.1080/10409238.2018.1431201
Wu H, Guang C, Zhang W, Mu W (2021a) Recent development of phenyllactic acid: physicochemical properties, biotechnological production strategies and applications. Critical Reviews in Biotechnology. https://doi.org/10.1080/07388551.2021.2010645
Wu W, Deng G, Liu C, Gong X, Ma G, Yuan Q, Yang E, Li X, Luo Y (2020a) Optimization and multiomic basis of Phenyllactic Acid overproduction by Lactobacillus plantarum. J Agric Food Chem 68(6):1741–1749. https://doi.org/10.1021/acs.jafc.9b07136
Wu W, Deng G, Liu C, Gong X, Ma G, Yuan Q, Yang E, Li X, Luo Y (2020b) Optimization and multiomic basis of Phenyllactic Acid overproduction by Lactobacillus plantarum. J Agric Food Chem 68(6):1741–1749. https://doi.org/10.1021/acs.jafc.9b07136
Wu X, Zhang C, Xing XH, Yun Z, Zhao L, Wu Q (2021b) Construction and characterization of novel bifunctional fusion proteins composed of alcohol dehydrogenase and NADH oxidase with efficient oxidized cofactor regeneration. https://doi.org/10.1002/bab.2225. Biotechnol Appl Biochem
Xu GC, Zhang LL, Ni Y (2016) Enzymatic preparation of D-phenyllactic acid at high space-time yield with a novel phenylpyruvate reductase identified from Lactobacillus sp. CGMCC 9967. J Biotechnol 222:29–37. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jbiotec.2015.12.011
Xu J-J, Sun J-Z, Si K-L, Guo C-F (2021) 3-Phenyllactic acid production by Lactobacillus crustorum strains isolated from naturally fermented vegetables. Lwt 149:111780. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.lwt.2021.111780
Xu J, Xu X, Wang Q, Fan X (2015) Chiral separation of phenyllactic acid by helical structure from spring dextrin. J Incl Phenom Macrocyclic Chem 82(3–4):515–521. https://doi.org/10.1007/s10847-015-0487-x
Xu J, Zhao W, Ning Y, Bashari M, Chen Y, Jin Z, Yang N, Xu X (2012) Enantiomer separation of phenyllactic acid by HPLC with Hp-β-cyclodextrin as chiral mobile phase additive. J Incl Phenom Macrocyclic Chem 76(3–4):461–465. https://doi.org/10.1007/s10847-012-0228-3
Xu JJ, Fu LJ, Si KL, Yue TL, Guo CF (2020) 3-phenyllactic acid production by free-whole-cells of Lactobacillus crustorum in batch and continuous fermentation systems. J Appl Microbiol 129(2):335–344. https://doi.org/10.1111/jam.14599
Yang F, Sadam H, Zhang Y, Xia J, Yang X, Long J, Li S, Shao L (2020) A de novo sacrificial-MOF strategy to construct enhanced-flux nanofiltration membranes for efficient dye removal. Chem Eng Sci 225. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ces.2020.115845
Yu K, Liu CC, Kim BG, Lee DY (2015a) Synthetic fusion protein design and applications. Biotechnol Adv 33(1):155–164. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.biotechadv.2014.11.005
Yu S, Zhou C, Zhang T, Jiang B, Mu W (2015b) Short communication: 3-phenyllactic acid production in milk by Pediococcus pentosaceus SK25 during laboratory fermentation process. J Dairy Sci 98(2):813–817. https://doi.org/10.3168/jds.2014-8645
Yu S, Zhou C, Zhang T, Jiang B, Mu W (2015c) Short communication: 3-Phenyllactic acid production in milk by Pediococcus pentosaceus SK25 during laboratory fermentation process. J Dairy Sci 98(2):813–817. https://doi.org/10.3168/jds.2014-8645
Zhang D-l, Li W-l, Zhang J-b, Tang W-r, Chen X-f, Cao K-w, Chu Q-c, Ye J-n (2010) Determination of unconjugated aromatic acids in urine by capillary electrophoresis with dual electrochemical detection - potential application in fast diagnosis of phenylketonuria. Electrophoresis 31(17):2989–2996. https://doi.org/10.1002/elps.201000191
Zhang D, Zhang T, Lei Y, Lin W, Chen X, Wu M (2022a) Enantioselective Biosynthesis of L-Phenyllactic Acid From Phenylpyruvic Acid In Vitro by L-Lactate Dehydrogenase Coupling With Glucose Dehydrogenase. Frontiers in Bioengineering and Biotechnology 10. https://doi.org/10.3389/fbioe.2022.846489
Zhang J, Li X (2018) Novel strategy for phenyllactic acid biosynthesis from phenylalanine by whole cell recombinant Escherichia coli coexpressing l<-phenylalanine oxidase and l-lactate dehydrogenase. Biotechnol Lett 40(1):165–171. https://doi.org/10.1007/s10529-017-2456-5
Zhang J, Zhang C, Lei P, Xin X, Liu D, Yi H (2022b) Isolation, purification, identification, and discovery of the antibacterial mechanism of LD-phenyllactic acid produced by lactiplantibacillus plantarum CXG9 isolated from a traditional chinese fermented vegetable. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.foodcont.2021.108490. Food Control 132
Zhang X, Zhang S, Shi Y, Shen F, Wang H (2014a) A new high phenyl lactic acid-yielding Lactobacillus plantarum IMAU10124 and a comparative analysis of lactate dehydrogenase gene. FEMS Microbiol Lett 356(1):89–96. https://doi.org/10.1111/1574-6968.12483
Zhang XX, Abd Elazim AM, Ruiz G, Yu RC (2014b) Fracture behaviour of steel fibre-reinforced concrete at a wide range of loading rates. Int J Impact Eng 71:89–96. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ijimpeng.2014.04.009
Zhao W, Ding H, Lv C, Hu S, Huang J, Zheng X, Yao S, Mei L (2018a) Two-step biocatalytic reaction using recombinant Escherichia coli cells for efficient production of phenyllactic acid from 1-phenylalanine. Process Biochem 64:31–37. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.procbio.2017.09.019
Zhao W, Ding H, Lv C, Hu S, Huang J, Zheng X, Yao S, Mei L (2018b) Two-step biocatalytic reaction using recombinant Escherichia coli cells for efficient production of phenyllactic acid from l-phenylalanine. Process Biochem 64:31–37. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.procbio.2017.09.019
Zheng R, Zhao T, Hung Y-C, Adhikari K (2019) Evaluation of Bactericidal Effects of Phenyllactic Acid on Escherichia coli O157:H7 and Salmonella Typhimurium on Beef Meat. J Food Prot 82(12):2016–2022. https://doi.org/10.4315/0362-028x.Jfp-19-217
Zheng Z, Ma C, Gao C, Li F, Qin J, Zhang H, Wang K, Xu P (2011) Efficient Conversion of Phenylpyruvic Acid to Phenyllactic Acid by using whole cells of Bacillus coagulans SDM. PLoS ONE 6(4). https://doi.org/10.1371/journal.pone.0019030
Zheng Z, Xia M, Fang X, Jiang T, Ouyang J (2018a) Enhanced biosynthesis of chiral phenyllactic acid from L-phenylalanine through a new whole-cell biocatalyst. Bioprocess Biosyst Eng 41(8):1205–1212. https://doi.org/10.1007/s00449-018-1949-5
Zheng Z, Xia M, Fang X, Jiang T, Ouyang J (2018b) Enhanced biosynthesis of chiral phenyllactic acid from L-phenylalanine through a new whole-cell biocatalyst. Bioprocess Biosyst Eng 41(8):1205–1212. https://doi.org/10.1007/s00449-018-1949-5
Zheng Z, Zhao M, Zang Y, Zhou Y, Ouyang J (2015) Production of optically pure L-phenyllactic acid by using engineered Escherichia coli coexpressing L-lactate dehydrogenase and formate dehydrogenase. J Biotechnol 207:47–51. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jbiotec.2015.05.015
Zhou Q, Gu R, Li P, Lu Y, Chen L, Gu Q (2020a) Anti-Salmonella mode of action of natural L-phenyl lactic acid purified from Lactobacillus plantarum ZJ316. Appl Microbiol Biotechnol 104(12):5283–5292. https://doi.org/10.1007/s00253-020-10503-4
Zhou Q, Gu R, Li P, Lu Y, Chen L, Gu Q (2020b) Anti-Salmonella mode of action of natural l-phenyl lactic acid purified from Lactobacillus plantarum ZJ316. Applied. Microbiol Biotechnol 104(12):5283–5292. https://doi.org/10.1007/s00253-020-10503-4
Zhou Q, Gu R, Xue B, Li P, Gu Q (2021) Phenyl lactic acid alleviates Samonella Typhimurium-induced colitis via regulating microbiota composition, SCFA production and inflammatory responses. Food Funct 12(12):5591–5606. https://doi.org/10.1039/d1fo00166c
Zhou X, Zhou J, Xin F, Ma J, Zhang W, Wu H, Jiang M, Dong W (2018) Heterologous expression of a novel dlactate dehydrogenase from Lactobacillus sp. ZX1 and its application for dphenyllactic acid production. Int J Biol Macromol 119:1171–1178. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ijbiomac.2018.08.036
Zhu Y, Hu F, Zhu Y, Wang L, Qi B (2015) Enhancement of phenyllactic acid biosynthesis by recognition site replacement of D-lactate dehydrogenase from Lactobacillus pentosus. Biotechnol Lett 37(6):1233–1241. https://doi.org/10.1007/s10529-015-1778-4
Zhu Y, Jiang Z, Chen J, Xu J, Wang L, Qi B (2017a) Fusion of D-Lactate dehydrogenase and formate dehydrogenase for increasing production of (R)-3-Phenyllactic acid in recombinant Escherichia coli BL21 (DE3). J Biobased Mater Bioenergy 11:372–378. https://doi.org/10.1166/jbmb.2017.1680
Zhu Y, Wang Y, Xu J, Chen J, Wang L, Qi B (2017b) Enantioselective biosynthesis of l-Phenyllactic acid by whole cells of recombinant Escherichia coli. Molecules 22(11). https://doi.org/10.3390/molecules22111966
Acknowledgements
This research was financially supported by the National Key Research and Development Program of China (2022YFC2105700, 2021YFC2103300, 2021YFE0190800), the National Natural Science Foundation of China (21978027), Scientific Research Foundation of State Key Lab of Coal Mine Disaster Dynamics and Control (2011DA105287-ZR202002), the Fundamental Research Funds for the Central Universities (2022CDJHLW006, 2020CDCGJ020, 2020CDCGHG068), Science and Technology Project of Traditional Chinese Medicine of Chongqing Health Committee (2020ZY023976), Chongqing Outstanding Youth Fund (cstc2021jcyj-jqX0013), and Youth Project of Science and Technology Research Program of Chongqing Education Commission of China (KJQN201900112).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Contributions
Tinglan Li: Investigation, Writing – original draft, Data curation. Zhao Qin: Visualization, Software, Methodology, Formal analysis. Dan Wang: Supervision, Resources, Funding acquisition, Writing – review & editing. Xue Xia: Software, Methodology, Data curation. Xiaojie Zhou: Supervision, Data curation. Ge Hu: Supervision, Resources, Visualization, Conceptualization.
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Competing interests
The authors declare no competing interests.
Additional information
Publisher’s Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Tinglan Li and Zhao Qin contributed equally to this work.
Rights and permissions
Springer Nature or its licensor (e.g. a society or other partner) holds exclusive rights to this article under a publishing agreement with the author(s) or other rightsholder(s); author self-archiving of the accepted manuscript version of this article is solely governed by the terms of such publishing agreement and applicable law.
About this article
Cite this article
Li, T., Qin, Z., Wang, D. et al. Coenzyme self-sufficiency system-recent advances in microbial production of high-value chemical phenyllactic acid. World J Microbiol Biotechnol 39, 36 (2023). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11274-022-03480-5
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11274-022-03480-5