Abstract
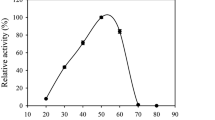
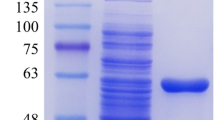
Feruloyl esterase (FAE; EC 3.1.1.73) cleaves the ester bond between ferulic acid (FA) and sugar, to assist the release of FAs and degradation of plant cell walls. In this study, two FAEs (Fae13961 and Fae16537) from the anaerobic fungus Pecoramyces sp. F1 were heterologously expressed in Pichia pastoris (P. pastoris). Compared with Fae16537, Fae13961 had higher catalytic efficiency. The optimum temperature and pH of both the FAEs were 45 ℃ and 7.0, respectively. They showed good stability—Fae16537 retained up to 80% activity after incubation at 37 ℃ for 24 h. The FAEs activity was enhanced by Ca2+ and reduced by Zn2+, Mn2+, Fe2+ and Fe3+. Additionally, the effect of FAEs on the hydrolytic efficiency of xylanase and cellulase was also determined. The FAE Fae13961 had synergistic effect with xylanase and it promoted the degradation of xylan substrates by xylanase, but it did not affect the degradation of cellulose substrates by cellulase. When Fae13961 was added in a mixture of xylanase and cellulase to degrade complex agricultural biomass, it significantly enhanced the mixture's ability to disintegrate complex substrates. These FAEs could serve as superior auxiliary enzymes for other lignocellulosic enzymes in the process of degradation of agricultural residues for industrial applications.







Similar content being viewed by others
Data availability
The datasets generated during and/or analysed during the current study are available from the corresponding author on reasonable request.
Abbreviations
- SEM:
-
Standard error of mean
- FAE:
-
Feruloyl esterase
- FA:
-
Ferulic acid
- MFA:
-
Methyl ferulate
- CAZymes:
-
Carbohydrate active enzymes
- LB:
-
Luria–Bertani broth
- BMGY:
-
Buffered glycerol-complex medium
- BMMY:
-
Buffered methanol-complex medium
- MD:
-
Minimal dextrose solid medium
- CMC-Na:
-
Sodium carboxymethyl cellulose
References
Agrawal D, Tsang A, Chadha BS (2021) Economizing the lignocellulosic hydrolysis process using heterologously expressed auxiliary enzymes feruloyl esterase D (CE1) and β-xylosidase (GH43) derived from thermophilic fungi Scytalidium thermophilum. Bioresour Technol 339:125603. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.biortech.2021.125603
Álvarez C, González A, Ballesteros I, Negro MJ (2021) Production of xylooligosaccharides, bioethanol, and lignin from structural components of barley straw pretreated with a steam explosion. Bioresour Technol 342:125953. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.biortech.2021.125953
Benoit I, Asther M, Sulzenbacher G, Record E, Marmuse L, Parsiegla G, Gimbert I, Asther M, Bignon C (2006) Respective importance of protein folding and glycosylation in the thermal stability of recombinant feruloyl esterase A. FEBS Lett 580(25):5815–5821. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.febslet.2006.09.039
Bento-Silva A, Vaz Pattodo Rosário Bronze MCM (2018) Relevance, structure and analysis of ferulic acid in maize cell walls. Food Chem 246:360–378. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.foodchem.2017.11.012
Bonzom C, Hüttner S, Mirgorodskaya E, Chong SL, Uthoff S, Steinbüchel A, Verhaert RMD, Olsson L (2019) Glycosylation influences activity, stability and immobilization of the feruloyl esterase 1a from Myceliophthora thermophila. AMB Express 9(1):126. https://doi.org/10.1186/s13568-019-0852-z
Bradford MM (1976) A rapid and sensitive method for the quantitation of microgram quantities of protein utilizing the principle of protein-dye binding. Anal Biochem 72:248–254. https://doi.org/10.1006/abio.1976.9999
Debeire P, Khoune P, Jeltsch JM, Phalip V (2012) Product patterns of a feruloyl esterase from Aspergillus nidulans on large feruloyl-arabino-xylo-oligosaccharides from wheat bran. Bioresour Technol 119:425–428. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.biortech.2012.01.185
Dimarogona M, Topakas E, Christakopoulos P, Chrysina ED (2020) The crystal structure of a Fusarium oxysporum feruloyl esterase that belongs to the tannase family. FEBS Lett 594(11):1738–1749. https://doi.org/10.1002/1873-3468.13776
Đorđević T, Milošević M, Antov M (2021) Advance diversity of enzymatically modified arabinoxylan from wheat chaff. Food Chem 339:128093. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.foodchem.2020.128093
Fillingham IJ, Kroon PA, Williamson G, Gilbert HJ, Hazlewood GP (1999) A modular cinnamoyl ester hydrolase from the anaerobic fungus Piromyces equi acts synergistically with xylanase and is part of a multiprotein cellulose-binding cellulase-hemicellulase complex. Biochem J 343(Pt 1):215–24
Fu Z, Zhu Y, Teng C, Fan G, Li X (2021) Biochemical characterization of a novel feruloyl esterase from Burkholderia pyrrocinia B1213 and its application for hydrolyzing wheat bran. 3 Biotech 12(1):24. https://doi.org/10.1007/s13205-021-03066-2
Gopalan N, Rodríguez-Duran LV, Saucedo-Castaneda G, Nampoothiri KM (2015) Review on technological and scientific aspects of feruloyl esterases: a versatile enzyme for biorefining of biomass. Bioresour Technol 193:534–544. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.biortech.2015.06.117
Gromiha MM, Selvaraj S (2004) Inter-residue interactions in protein folding and stability. Prog Biophys Mol Biol 86(2):235–277. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.pbiomolbio.2003.09.003
Gruninger RJ, Puniya AK, Callaghan TM, Edwards JE, Youssef N, Dagar SS, Fliegerova K, Griffith GW, Forster R, Tsang A (2014) Anaerobic fungi (phylum Neocallimastigomycota): advances in understanding their taxonomy, life cycle, ecology, role and biotechnological potential. FEMS Microbiol Ecol 90(1):1–17. https://doi.org/10.1111/1574-6941.12383
Gruninger RJ, Cote C, McAllister TA, Abbott DW (2016) Contributions of a unique β-clamp to substrate recognition illuminates the molecular basis of exolysis in ferulic acid esterases. Biochem J 473(7):839–849. https://doi.org/10.1042/bj20151153
Hassan S, Hugouvieux-Cotte-Pattat N (2011) Identification of two feruloyl esterases in Dickeya dadantii 3937 and induction of the major feruloyl esterase and of pectate lyases by ferulic acid. J Bacteriol 193(4):963–970. https://doi.org/10.1128/JB.01239-10
Hou Y, Pan Y, Yan M, He H, Yang Q, Zhong Y (2017) Influence of randomly inserted feruloyl esterase A on β-glucosidase activity in Trichoderma reesei. Appl Biochem Biotechnol 183(1):254–264. https://doi.org/10.1007/s12010-017-2442-3
Jin L, Zhang X, Shi H, Wang W, Qiao Z, Yang W, Du W (2020) Identification of a novel N-Acyl homoserine lactone synthase, AhyI, in aeromonas hydrophila and structural basis for its substrate specificity. J Agric Food Chem 68(8):2516–2527. https://doi.org/10.1021/acs.jafc.9b07833
Kelle S, Nieter A, Krings U, Zelena K, Berger RG (2016) Heterologous production of a feruloyl esterase from Pleurotus sapidus synthesizing feruloyl-saccharide esters. Biotechnol Appl Biochem 63(6):852. https://doi.org/10.1002/bab.1430
Larkin MA, Blackshields G, Brown NP, Chenna R, McGettigan PA, McWilliam H, Valentin F, Wallace IM, Wilm A, Lopez R, Thompson JD, Gibson TJ, Higgins DG (2007) Clustal W and Clustal X version 2.0. Bioinformatics 23(21):2947–8. https://doi.org/10.1093/bioinformatics/btm404
Laskowski RA, Rullmannn JA, MacArthur MW, Kaptein R, Thornton JM (1996) AQUA and PROCHECK-NMR: programs for checking the quality of protein structures solved by NMR. J Biomol NMR 8(4):477–486. https://doi.org/10.1007/bf00228148
Li F, Ding Z, Ke W, Xu D, Zhang P, Bai J, Mudassar S, Muhammad I, Guo X (2019) Ferulic acid esterase-producing lactic acid bacteria and cellulase pretreatments of corn stalk silage at two different temperatures: ensiling characteristics, carbohydrates composition and enzymatic saccharification. Bioresour Technol 282:211–221. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.biortech.2019.03.022
Li Y, Meng Z, Xu Y, Shi Q, Ma Y, Aung M, Cheng Y, Zhu W (2021) Interactions between anaerobic fungi and methanogens in the rumen and their biotechnological potential in biogas production from lignocellulosic materials. Microorganisms 9(1):190. https://doi.org/10.3390/microorganisms9010190
Liu S, Soomro L, Wei X, Yuan X, Gu T, Li Z, Wang Y, Bao Y, Wang F, Wen B, Xin F (2021a) Directed evolution of feruloyl esterase from Lactobacillus acidophilus and its application for ferulic acid production. Bioresour Technol 332:124967. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.biortech.2021.124967
Liu Y, Wang J, Bao C, Dong B, Cao Y (2021b) Characterization of a novel GH10 xylanase with a carbohydrate binding module from Aspergillus sulphureus and its synergistic hydrolysis activity with cellulase. Int J Biol Macromol 182:701–711. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ijbiomac.2021.04.065
Ljungdahl LG (2008) The cellulase/hemicellulase system of the anaerobic fungus Orpinomyces PC-2 and aspects of its applied use. Ann N Y Acad Sci 1125(1):308–321. https://doi.org/10.1196/annals.1419.030
Mafa MS, Malgas S, Pletschke BI (2021) Feruloyl esterase (FAE-1) sourced from a termite hindgut and GH10 xylanases synergy improves degradation of arabinoxylan. AMB Express 11(1):21. https://doi.org/10.1186/s13568-021-01180-1
Mäkelä MR, Dilokpimol A, Koskela SM, Kuuskeri J, de Vries RP, Hildén K (2018) Characterization of a feruloyl esterase from Aspergillus terreus facilitates the division of fungal enzymes from Carbohydrate Esterase family 1 of the carbohydrate-active enzymes (CAZy) database. Microb Biotechnol 11(5):869–880. https://doi.org/10.1111/1751-7915.13273
Mathew S, Abraham TE (2004) Ferulic acid: an antioxidant found naturally in plant cell walls and feruloyl esterases involved in its release and their applications. Crit Rev Biotechnol 24(2–3):59–83. https://doi.org/10.1080/07388550490491467
Mendoza F, Lluch JM, Masgrau L (2017) Computational insights into active site shaping for substrate specificity and reaction regioselectivity in the EXTL2 retaining glycosyltransferase. Org Biomol Chem 15(43):9095–9107. https://doi.org/10.1039/c7ob01937h
Moraïs S, Barak Y, Caspi J, Hadar Y, Lamed R, Shoham Y, Wilson DB, Bayer EA (2010) Cellulase-xylanase synergy in designer cellulosomes for enhanced degradation of a complex cellulosic substrate. mBio 1(5):e00285-10. https://doi.org/10.1128/mBio.00285-10
Moukouli M, Topakas E, Christakopoulos P (2008) Cloning, characterization and functional expression of an alkalitolerant type C feruloyl esterase from Fusarium oxysporum. Appl Microbiol Biotechnol 79(2):245–254. https://doi.org/10.1007/s00253-008-1432-3
Murashima K, Kosugi A, Doi RH (2003) Synergistic effects of cellulosomal xylanase and cellulases from Clostridium cellulovorans on plant cell wall degradation. J Bacteriol 185(5):1518–24. https://doi.org/10.1128/jb.185.5.1518-1524.2003
Qi M, Wang P, Selinger LB, Yanke LJ, Forster RJ, McAllister TA (2011) Isolation and characterization of a ferulic acid esterase (Fae1A) from the rumen fungus Anaeromyces mucronatus. J Appl Microbiol 110(5):1341–1350. https://doi.org/10.1111/j.1365-2672.2011.04990.x
Rahmani N, Kahar P, Lisdiyanti P, Hermiati E, Lee J, Yopi PB, Ogino C, Kondo A (2018) Xylanase and feruloyl esterase from actinomycetes cultures could enhance sugarcane bagasse hydrolysis in the production of fermentable sugars. Biosci Biotechnol Biochem 23:1–12. https://doi.org/10.1080/09168451.2018.1438169
Ralph J, Bunzel M, Marita JM, Hatfield RD, Lu F, Kim H, Schatz PF, Grabber JH, Steinhart H (2004) Peroxidase-dependent cross-linking reactions of p-hydroxycinnamates in plant cell walls. Phytochem Rev 3(1):79–96. https://doi.org/10.1023/B:PHYT.0000047811.13837.fb
Reijngoud J, Arentshorst M, Ruijmbeek C, Reid I, Alazi ED, Punt PJ, Tsang A, Ram AFJ (2021) Loss of function of the carbon catabolite repressor CreA leads to low but inducer-independent expression from the feruloyl esterase B promoter in Aspergillus niger. Biotechnol Lett 43(7):1323–1336. https://doi.org/10.1007/s10529-021-03104-2
Rigoldi F, Spero L, Dalle Vedove A, Redaelli A, Parisini E, Gautieri A (2016) Molecular dynamics simulations provide insights into the substrate specificity of FAOX family members. Mol Biosyst 12(8):2622–2633. https://doi.org/10.1039/c6mb00405a
Robert X, Gouet P (2014) Deciphering key features in protein structures with the new ENDscript server. Nucleic Acids Res 42:W320–W324. https://doi.org/10.1093/nar/gku316
Salmaso V, Moro S (2018) Bridging molecular docking to molecular dynamics in exploring ligand-protein recognition process: an overview. Front Pharmacol 9:923. https://doi.org/10.3389/fphar.2018.00923
Scheller HV, Ulvskov P (2010) Hemicelluloses. Annu Rev Plant Biol 61(1):263–289. https://doi.org/10.1146/annurev-arplant-042809-112315
Schmitz E, Leontakianakou S, Norlander S, Nordberg Karlsson E, Adlercreutz P (2022) Lignocellulose degradation for the bioeconomy: the potential of enzyme synergies between xylanases, ferulic acid esterase and laccase for the production of arabinoxylo-oligosaccharides. Bioresour Technol 343:126114. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.biortech.2021.126114
Seppälä S, Wilken SE, Knop D, Solomon KV, O’Malley MA (2017) The importance of sourcing enzymes from non-conventional fungi for metabolic engineering and biomass breakdown. Metab Eng 44:45–59. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ymben.2017.09.008
Su R, Ni K, Wang T, Yang X, Zhang J, Liu Y, Shi W, Yan L, Jie C, Zhong J (2019) Effects of ferulic acid esterase-producing Lactobacillus fermentum and cellulase additives on the fermentation quality and microbial community of alfalfa silage. PeerJ 7:e7712. https://doi.org/10.7717/peerj.7712
Topakas E, Vafiadi C, Christakopoulos P (2007) Microbial production, characterization and applications of feruloyl esterases. Process Biochem 42(4):497–509. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.procbio.2007.01.007
Trott O, Olson AJ (2010) AutoDock Vina: improving the speed and accuracy of docking with a new scoring function, efficient optimization, and multithreading. J Comput Chem 31(2):455–461. https://doi.org/10.1002/jcc.21334
Watanabe M, Yoshida E, Fukada H, Inoue H, Tokura M, Ishikawa K (2015) Characterization of a feruloyl esterase B from Talaromyces cellulolyticus. Biosci Biotechnol Biochem 79(11):1845–1851. https://doi.org/10.1080/09168451.2015.1058700
Waterhouse A, Bertoni M, Bienert S, Studer G, Tauriello G, Gumienny R, Heer FT, de Beer TAP, Rempfer C, Bordoli L, Lepore R, Schwede T (2018) SWISS-MODEL: homology modelling of protein structures and complexes. Nucleic Acids Res 46(W1):W296-w303. https://doi.org/10.1093/nar/gky427
Wefers D, Cavalcante JJV, Schendel RR, Deveryshetty J, Wang K, Wawrzak Z, Mackie RI, Koropatkin NM, Cann I (2017) Biochemical and structural analyses of two cryptic esterases in Bacteroides intestinalis and their synergistic activities with cognate xylanases. J Mol Biol 429(16):2509–2527. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jmb.2017.06.017
Wei X, Wang YL, Wen BT, Liu SJ, Wang L, Sun L, Gu TY, Li Z, Bao Y, Fan SL, Zhou H, Wang F, Xin F (2021) The α-helical cap domain of a novel esterase from gut Alistipes shahii shaping the substrate-binding pocket. J Agric Food Chem 69(21):6064–6072. https://doi.org/10.1021/acs.jafc.1c00940
Wilkins MR, Gasteiger E, Bairoch A, Sanchez JC, Williams KL, Appel RD, Hochstrasser DF (1999) Protein identification and analysis tools in the ExPASy server. Methods Mol Biol 112:531–552. https://doi.org/10.1385/1-59259-584-7:531
Wong DWS, Chan VJ, Batt SB, Sarath G, Liao H (2011) Engineering Saccharomyces cerevisiae to produce feruloyl esterase for the release of ferulic acid from switchgrass. J Ind Microbiol Biotechnol 38(12):1961–1967. https://doi.org/10.1007/s10295-011-0985-9
Wong D, Chan V, Liao H (2020) Hydrolysis of ferulic acids in corn fiber by a metagenomic feruloyl esterase. BioResources 16:825–834. https://doi.org/10.15376/biores.16.1.825-834
Wu JP, Li M, Zhou Y, Yang LR, Xu G (2015) Introducing a salt bridge into the lipase of Stenotrophomonas maltophilia results in a very large increase in thermal stability. Biotechnol Lett 37(2):403–407. https://doi.org/10.1007/s10529-014-1683-2
Wu H, Li H, Xue Y, Luo G, Gan L, Liu J, Mao L, Long M (2017) High efficiency co-production of ferulic acid and xylooligosaccharides from wheat bran by recombinant xylanase and feruloyl esterase. Biochem Eng J 120:41–48. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.bej.2017.01.001
Yang W, Sun L, Dong P, Chen Y, Zhang H, Huang X, Wu L, Chen L, Jing D, Wu Y (2022) Structure-guided rational design of the Geobacillus thermoglucosidasius feruloyl esterase GthFAE to improve its thermostability. Biochem Biophys Res Commun 600:117–122. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.bbrc.2022.02.074
Yin X, Hu D, Li JF, He Y, Zhu TD, Wu MC (2015a) Contribution of disulfide bridges to the thermostability of a type A feruloyl esterase from Aspergillus usamii. PLoS ONE 10(5):e0126864. https://doi.org/10.1371/journal.pone.0126864
Yin X, Li JF, Wang CJ, Hu D, Wu Q, Gu Y, Wu MC (2015b) Improvement in the thermostability of a type A feruloyl esterase, AuFaeA, from Aspergillus usamii by iterative saturation mutagenesis. Appl Microbiol Biotechnol 99(23):10047–10056. https://doi.org/10.1007/s00253-015-6889-2
You C, Huang Q, Xue H, Xu Y, Lu H (2010) Potential hydrophobic interaction between two cysteines in interior hydrophobic region improves thermostability of a family 11 xylanase from Neocallimastix patriciarum. Biotechnol Bioeng 105(5):861–870. https://doi.org/10.1002/bit.22623
Zhang SB, Wu ZL (2011) Identification of amino acid residues responsible for increased thermostability of feruloyl esterase A from Aspergillus niger using the PoPMuSiC algorithm. Bioresour Technol 102(2):2093–2096. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.biortech.2010.08.019
Zhang SB, Pei XQ, Wu ZL (2012) Multiple amino acid substitutions significantly improve the thermostability of feruloyl esterase A from Aspergillus niger. Bioresour Technol 117:140–147. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.biortech.2012.04.042
Zhang H, Wen B, Liu Y, Du G, Wei X, Imam K, Zhou H, Fan S, Wang F, Wang Y, Xin F (2021) A reverse catalytic triad Asp containing loop shaping a wide substrate binding pocket of a feruloyl esterase from Lactobacillus plantarum. Int J Biol Macromol 184:92–100. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ijbiomac.2021.06.033
Acknowledgements
Thanks for Dr. Yuqi Li and Ms. Yuping Ma for their generous donation of cellulase and xylanase.
Funding
This study was supported by the Natural Science Foundation of China (Grant nos. 31772627 and 32061143034).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Contributions
The research was conceived and designed by JM, YM, YC, WZ. The experiments were conducted by JM and YM. New analytical tools were contributed by YL. Experimental data was analyzed by ZS and XS. The manuscript was prepared by JM. The revision of the manuscript was contributed by YL and VP. All authors read and approved the final manuscript.
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Competing interests
The authors have no relevant financial or non-financial interests to disclose.
Ethical approval
The study did not require ethics approval.
Consent to participate
Not applicable.
Consent to publish
Not applicable.
Additional information
Publisher's Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Supplementary Information
Below is the link to the electronic supplementary material.
Rights and permissions
Springer Nature or its licensor (e.g. a society or other partner) holds exclusive rights to this article under a publishing agreement with the author(s) or other rightsholder(s); author self-archiving of the accepted manuscript version of this article is solely governed by the terms of such publishing agreement and applicable law.
About this article
Cite this article
Ma, J., Ma, Y., Li, Y. et al. Characterization of feruloyl esterases from Pecoramyces sp. F1 and the synergistic effect in biomass degradation. World J Microbiol Biotechnol 39, 17 (2023). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11274-022-03466-3
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11274-022-03466-3