Abstract
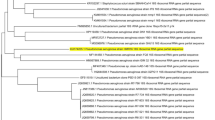
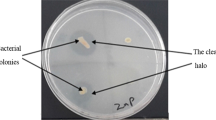
Bacterial systems have evolved a number of mechanisms, both active and passive, to manage toxic concentrations of heavy metals in their environment. The present study is aimed at describing the zinc resistance mechanism in a rhizospheric isolate, Pseudomonas fluorescens strain Psd. The strain was able to sustain an external Zn2+ concentration of up to 5 mM in the medium. The strategy for metal management by the strain was found to be extracellular biosorption with a possible role of exopolysaccharides in metal accumulation. The attainment of equilibrium in biosorption reaction was found to be dependent on initial Zn2+ concentration, with the reaction reaching equilibrium faster (50 min) at high initial Zn2+ concentration. Biosorption kinetics of the process was adjusted to pseudo-first order rate equation. With the help of Langmuir and Freundlich adsorption isotherms, it was established that Zn2+ biosorption by the bacterium is a thermodynamically favourable process.










Similar content being viewed by others
References
Babu BV, Ramakrishna V (2003) Modeling of adsorption isotherm constants using regression analysis and neural network. In: Proceedings of the 2nd International conference on water quality management, February 13–15, New Delhi
Barceloux DG (1999) Zinc. J Toxicol Clin Toxicol 37:279–292
Bautista-Hernández DA, Ramírez-Burgos LI, Duran-Páramo E, Fernández-Linares L (2012) Zinc and lead biosorption by Delftia tsuruhatensis: a bacterial strain resistant to metals isolated from mine tailings. J Water Resour Prot 4:207–216
Belimov AA, Kunakova AM, Safronova VI, Stepanok VV, Yudkin LY, Alekseev YV, Kozhemyakov AP (2004) Employment of rhizobacteria for the inoculation of barley plants cultivated in soil contaminated with lead and cadmium. Microbiology 73:99–106
Bhagat R, Srivastava S (1994) Effect of Zn on morphology and ultrastructure of Pseudomonas stutzeri. J Gen Appl Microbiol 40:265–270
Binupriya AR, Sathishkumar M, Kavitha D, Swaminathan K, Yun SE, Mun SP (2007) Experimental and isothermal studies on sorption of Congo red by modified mycelial biomass of wood-rotting fungus. Clean 35:143–150
Bitton G, Freihofer V (1978) Influence of extracellular polysaccharides on the toxicity of copper and cadmium toward Klebsiella aerogenes. Microb Ecol 4:119–125
Cha JS, Cooksey DA (1991) Copper resistance in Pseudomonas syringae mediated by periplasmic and outer membrane proteins. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 88:8915–8919
Chen C, Wang JL (2007) Characteristics of Zn2+ biosorption by Saccharomyces cerevisiae. Biomed Environ Sci 20:478–482
Chen XC, Wang YP, Lin Q, Shi JY, Wu WX, Chen YX (2005) Biosorption of copper (II) and zinc (II) from aqueous solution by Pseudomonas putida CZ1. Colloids Surf B 46:101–107
Chen D, Qian PY, Wang WX (2008) Biokinetics of cadmium and zinc in a marine bacterium: influences of metal interaction and pre-exposure. Environ Toxicol Chem 27(8):179–186
Chen X, Hu S, Shen C, Dou C, Shi J, Chen Y (2009) Interaction of Pseudomonas putida CZ1 with clays and ability of the composite to immobilize copper and zinc from solution. Bioresour Technol 100:330–337
Choudhury R, Srivastava S (2001a) Zinc resistance mechanisms in bacteria. Curr Sci 81:768–775
Choudhury R, Srivastava S (2001b) Mechanism of zinc resistance in Pseudomonas putida strain S4. World J Microbiol Biotechnol 17:149–153
Errasquin EL, Vazquez C (2003) Tolerance and uptake of heavy metals by Trichoderma atroviride isolated from sludge. Chemosphere 50:137–143
Filipovic-Covacevic Z, Sipos L, Briski F (2000) Biosorption of chromium, copper, nickel and zinc ions onto fungal pellets of Aspergillus niger 405 from aqueous solutions. Food Technol Biotechnol 38(3):211–216
Gilotra U, Srivastava S (1997) Plasmid-bound copper sequestration in Pseudomonas pickettii strain US321. Curr Microbiol 34:378–381
Gowri PM, Srivastava S (1996) Reduced uptake based zinc resistance in Azospirillum brasilense sp7. Curr Sci 71:139–142
Guiné V, Spadini L, Sarret G, Muris M, Delolme C, Gaudet JP, Martins JM (2006) Zinc sorption to three gram-negative bacteria: combined titration, modeling, and EXAFS study. Environ Sci Technol 40(6):1806–1813
Ho YS, McKay G (1998) A comparison of chemisorption kinetic models applied to pollutant removal on various sorbents. Process Saf Environ Prot 76(4):332–340
Ho YS, McKay G (1999) The sorption of lead(II) ions on peat. Water Res 33:578–584
Horikoshi T, Nakijima A, Sakaguchi T (1981) Studies on accumulation of heavy metal elements in biological systems. Eur J Appl Microbiol Biotechnol 12:90–96
Jayaraman J (1981) Biomolecules I. In: Jayaraman J (ed) Laboratory manual in biochemistry. Wiley Eastern, New Delhi, pp 49–60
Khan MS, Zaidi A, Wani PA, Oves M (2009) Role of plant growth promoting rhizobacteria in remediation of metal contaminated soils. Environ Chem Lett 7:1–19
Kochar M, Upadhyay A, Srivastava S (2011) Indole-3-acetic acid biosynthesis in the biocontrol strain Pseudomonas fluorescens Psd and plant growth regulation by hormone overexpression. Res Microbiol 162(4):426–435
Kumar KV (2006) Linear and non-linear regression analysis for the sorption kinetics of methylene blue onto activated carbon. J Hazard Mater B137:1538–1544
Lagergren S (1898) About the theory of so-called adsorption of soluble substances. K Sven Vetenskapsakad Handl 24(4):1–39
Ledin M (2000) Accumulation of metals by microorganisms—processes and importance for soil systems. Earth Sci Rev 51:1–31
Liu H-L, Chen B-Y, Lan Y-W, Cheng YC (2004) Biosorption of Zn(II) and Cu(II) by the indigenous Thiobacillus thiooxidans. Chem Eng J 97:195–201
Lu D, Boyd B, Lingwood CA (1997) Identification of the key protein for zinc uptake in Hemophilus influenzae. J Biol Chem 272(46):29033–29038
Mameri N, Boudries N, Addour L, Belhocine D, Lounici H, Grib H, Pauss A (1999) Batch zinc biosorption by a bacterial nonliving Streptomyces rimosus biomass. Water Res 33:1347–1354
Oh SE, Hassan SHA, Joo JH (2009) Biosorption of heavy metals by lyophilized cells of Pseudomonas stutzeri. World J Microbiol Biotechnol 25:1771–1778
Pardo R, Herguedas M, Barrado E, Vega M (2003) Biosorption of cadmium, copper, lead and zinc by inactive biomass of Pseudomonas putida. Anal Bioanal Chem 376:26–32
Preetha B, Viruthagiri T (2005) Biosorption of zinc (II) by Rhizopus arrhizus: equilibrium and kinetic modelling. Afr J Biotechnol 4(6):506–508
Rho JY, Kim JH (2002) Heavy metal biosorption and its significance to metal tolerance of Streptomycetes. J Microbiol 40(1):51–54
Saxena D, Joshi N, Srivastava S (2002) Mechanism of copper resistance in a copper mine isolate Pseudomonas putida strain S4. Curr Microbiol 45:410–414
Tan T, Cheng P (2003) Biosorption of metal ions with Penicillium chrysogenum. Appl Biochem Biotechnol 104:119–128
Taniguchi J, Hemmi H, Tanahashi K, Amano N, Nakayama T, Nishino T (2000) Zinc biosorption by a zinc-resistant bacterium, Brevibacterium sp. Strain HZM-1. Appl Microbiol Biotechnol 54:581–588
Upadhyay A, Srivastava S (2008) Characterization of a new isolate of Pseudomonas fluorescens strain Psd as a potential biocontrol agent. Lett Appl Microbiol 47:98–105
Upadhyay A, Srivastava S (2010) Evaluation of multiple plant growth promoting traits of an isolate of Pseudomonas fluorescens strain Psd. Indian J Exp Biol 48(6):601–609
Upadhyay A, Srivastava S (2011) Phenazine-1-carboxylic acid is a more important contributor to biocontrol Fusarium oxysporum than pyrrolnitrin in Pseudomonas fluorescens strain Psd. Microbiol Res 166(4):323–335
Vijayaraghavan K, Yun YS (2008) Bacterial biosorbents and biosorption. Biotechnol Adv 26:266–291
Whiting SN, deSouza MP, Terry N (2001) Rhizosphere bacteria mobilize Zn for hyperaccumulation by Thlaspi caerulescens. Environ Sci Technol 15:3144–3150
Zhou W, Wang J, Shen B, Hou W, Zhang Y (2009) Biosorption of copper (II) and cadmium(II) by a novel exopolysaccharide secreted from deep-sea mesophilic bacterium. Colloids Surf B Biointerfaces 72(2):295–302
Zhuang X, Chen J, Shim H, Bai Z (2007) New advances in plant growth-promoting rhizobacteria for bioremediation. Environ Int 33(3):406–441
Acknowledgments
The financial assistance provided by Department of Biotechnology, Govt. of India is gratefully acknowledged. Authors also acknowledge the support provided to Department of Genetics under UGC-SAP and DST-FIST programs of Govt. of India.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Upadhyay, A., Srivastava, S. Mechanism of zinc resistance in a plant growth promoting Pseudomonas fluorescens strain. World J Microbiol Biotechnol 30, 2273–2282 (2014). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11274-014-1648-6
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11274-014-1648-6