Abstract
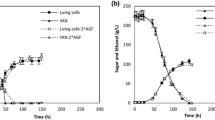
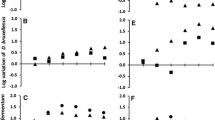
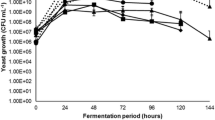
Traditional tequila fermentation is a complex microbial process performed by different indigenous yeast species. Usually, they are classified in two families: Saccharomyces and Non-Saccharomyces species. Using mixed starter cultures of several yeasts genera and species is nowadays considered to be beneficial to enhance the sensorial characteristics of the final products (taste, odor). However, microbial interactions occurring in such fermentations need to be better understood to improve the process. In this work, we focussed on a Saccharomyces cerevisiae/Kluyveromyces marxianus yeast couple. Indirect interactions due to excreted metabolites, thanks to the use of a specific membrane bioreactor, and direct interaction due to cell-to-cell contact have been explored. Comparison of pure and mixed cultures was done in each case. Mixed cultures in direct contact showed that both yeast were affected but Saccharomyces rapidly dominated the cultures whereas Kluyveromyces almost disappeared. In mixed cultures with indirect contact the growth of Kluyveromyces was decreased compared to its pure culture but its concentration could be maintained whereas the growth of Saccharomyces was enhanced. The loss of viability of Kluyveromyces could not be attributed only to ethanol. The sugar consumption and ethanol production in both cases were similar. Thus the interaction phenomena between the two yeasts are different in direct and indirect contact, Kluyveromyces being always much more affected than Saccharomyces.






Similar content being viewed by others
References
Abranches J, Morais PB, Rosa CA, Mendonça-Hagler LC, Hagler AN (1997) The incidence of killer activity and extracellular proteases in tropical yeast communities. Can J Microbiol 43:328–336
Albasi C, Tartaridis P, Taillandier P, Strehaiano P (2002) A new tool for the quantification of microbial interactions in liquid medium: application to wine lactic acid bacteria. Sc Aliments 22:189–198
Amaya-Delgado L, Herrera-Lopez EJ, Arrizon J, Arellano-Plaza M, Gschaedler A (2013) Performance evaluation of Pichia kluyveri, Kluyveromyces marxianus and Saccharomyces cerevisiae in industrial tequila fermentation. World J Microbiol Biotechnol 29:875–881
Ciani M, Beco L, Comitini F (2006) Fermentation behavior and metabolic interactions of multistarter wine yeast fermentations. Intern J Food Microbiol 108:239–245
Ciani M, Comitini F, Mannazzu I, Domizio P (2010) Controlled mixed culture fermentation: a new perspective on the use of non-Saccharomyces yeasts in wine making. FEMS Yeast Res 10:123–133
Fiore C, Arrizon J, Gschaedler A, Flores J, Romano P (2005) Comparison between yeasts from grape and agave musts for traits of technological interest. World J Microbiol Biotechnol 21:1141–1147
Fleet GH, Lafon-Lafourcade S, Ribereau-Gayon P (1984) Evolution of yeasts and lactic acid bacteria during fermentation and storage of Bordeaux wines. Appl Environ Microbiol 48:1034–1038
Graciano-Fonseca G, Heinzle E, Wittmann C, Gombert AK (2008) The yeast Kluyveromyces marxianus and its biotechnological potential. Appl Microbiol Biotechnol 79:339–354
Lachance MA (1995) Yeast communities in a natural tequila fermentation. Antonie Van Leeuwenhoek 68:151–160. doi:10.1007/BF00873100
Lane MM, Morrissey JP (2010) Review: Kluyveromyces marxianus: a yeast emerging from its sister’s shadow. Fungal Biol Rev 24:17–26
Lappe-Oliveras P, Moreno-Terrazas R, Arrizoón-Gavinño J, Herrera-Suárez T, García-Mendoza A, Gschaedler-Mathis A (2008) Yeasts associated with the production of Mexican alcoholic non distilled and distilled Agave beverages. FEMS Yeast Res 8:1037–1052
López-Alvarez A, Díaz-Pérez A, Sosa-Aguirre C, Macías-Rodríguez L, Campos-García J (2012) Ethanol yield and volatile compound content in fermentation of agave must by Kluyveromyces marxianus UMPe-1 comparing with Saccharomyces cerevisiae baker’s yeast used in tequila production. J Biosci Bioeng 113:614–618
Nissen P, Arneborg N (2003) Characterization of early deaths of non-Saccharomyces yeasts in mixed cultures with Saccharomyces cerevisiae. Arch Microbiol 180:257–263
Pérez-Nevado F, Albergaria H, Hogg T, Giri F (2006) Cellular death of two non-Saccharomyces wine-related yeasts during mixed fermentations with Saccharomyces cerevisiae. Intern J Food Microbiol 108:336–345
Romano P, Fiore C, Paraggio M, Caruso M, Capece A (2003) Function of yeast species and strains in wine flavor. Intern J Food Microbiol 86:169–180
Salgado-Manjarrez E, Albasi C, Riba JP (2000) A two-reservoir, hollow-fiber bioreactor for the study of mixed-population dynamics: design aspects and validation of the approach. Biotechnol Bioeng 69:401–408
Scharpf LG, Seitz EW, Morris JA, Farbood MI (1986) Generation of flavor and odor compounds through fermentation processes. In: Parliament TH, Croteau R (eds) Biogeneration of aroma, vol 317. American Chemical Society, Washington, DC, pp 323–346
Sosa OA, Manca de Nadra MC, Farías ME (2008) Behavior of Kloeckera apiculata flocculent strain in co-culture with Saccharomyces cerevisiae. Food Technol Biotechnol 46:413–418
Acknowledgments
Authors acknowledge the National Council of Science and Technology (CONACYT) in Mexico for financial support (Scholarship No. 175927), to the CIATEJ, Mexico for providing the strains to the National Polytechnic Institute of Toulouse, France for the materials and technological support.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Lopez, C.L.F., Beaufort, S., Brandam, C. et al. Interactions between Kluyveromyces marxianus and Saccharomyces cerevisiae in tequila must type medium fermentation. World J Microbiol Biotechnol 30, 2223–2229 (2014). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11274-014-1643-y
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11274-014-1643-y