Abstract
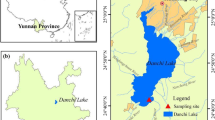
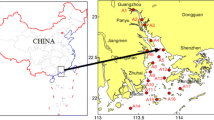
Sixteen polycyclic aromatic hydrocarbons (PAHs) in 37 surface sediments and a sediment core from the Dongzhai National Nature Reserve in Hainan island of China were analysed. The total concentration of the 16 PAHs ranged from 15.7 to 464.0 ng g−1 (mean value of 76.7 ng g−1) in the surface sediments, and 8.6–115.9 ng g−1 (average 39.3 ng g−1) in the sediment core. Combustions of petroleum, biomass, coal, and grass were the major pyrogenic sources in surface sediments, and some areas had petrogenic sources (mainly petroleum spills). Results of the ecological risk assessment show little negative effect of most of the PAHs in the study area. The depositional flux of PAHs generally increased from the deeper layers toward the upper layers of the sediments. The flux rate rapidly increased after the 1980s, in contrast to that of some developed countries.






Similar content being viewed by others
References
Abdel-Shafy HI, Mansour MSM (2016) A review on polycyclic aromatic hydrocarbons: source, environmental impact, effect on human health and remediation. Egypt J Pet 25(1):107–123
Andersson M, Klug M, Eggen OA, Ottesen RT (2014) Polycyclic aromatic hydrocarbons (PAHs) in sediments from lake Lille Lungegårdsvannet in Bergen, western Norway; appraising pollution sources from the urban history. Sci Total Environ 470–471(7):1160–1172
Budzinski H, Jones I, Bellocq J, Pierrad C, Garrigues P (1997) Evaluation of sediment contamination by polycyclic aromatic hydrocarbons in the Gironde estuary. Mar Chem 58(1–2):85–97
Cao LL, Wang P, Tian HT, Xie J, He YS (2013) Distribution and ecological evaluation of heavy metals in multi-mediums of Dongzhai Harbor. Mar Sci Bull 32(4):403–407
Cavalcante RM, Sousa FW, Nasciment RF, Silveira ER, Freire GS (2009) The impact of urbanization on tropical mangroves (Fortaleza, Brazil): evidence from PAH distribution in sediments. J Environ Manage 91(2):328–335
Dobbins RA, Fletcher RA, Benner JBA, Hoeft S (2006) Polycyclic aromatic hydrocarbons in flames, in diesel fuels, and in diesel emissions. Combust Flame 144(4):773–781
Fang MD, Hsieh PC, Ko FC, Baker JE, Lee CL (2007) Sources and distribution of polycyclic aromatic hydrocarbons in the sediments of Kaoping River and Submarine Canyon system, Taiwan. Mar Pollut Bull. 54(8):1179–1189
Guo ZG, Lin T, Zhang G, Yang ZS, Fang M (2006) High-resolution depositional records of polycyclic aromatic hydrocarbons in the central continental shelf mud of the East China Sea. Environ Sci Technol 40(17):5304–5311
Guo ZG, Lin T, Zhang G, Zheng M, Zhang ZY, Hao YC, Fang M (2007) The sedimentary fluxes of polycyclic aromatic hydrocarbons in the Yangtze River Estuary coastal sea for the past century. Sci Total Environ 386(1):33–41
Guo JY, Wu FC, Luo XJ, Liang Z, Liao HQ, Zhang RY, Li W, Zhao XL, Chen SJ, Mai BX (2010) Anthropogenic input of polycyclic aromatic hydrocarbons into five lakes in Western China. Environ Pollut 158(6):2175–2180
Guo JY, Wu FC, Zhang L, Liao HQ, Zhang RY, Lim W, Zhao XL, Chen SJ, Mai BX (2011) Screening Level of PAHs in Sediment Core from Lake Hongfeng, Southwest China. Arch Environ Contam Toxicol 60(4):590–596
Harrison RM, Smith DJT, Luhana L (1996) Source apportionment of atmospheric polycyclic aromatic hydrocarbons collected from an urban location in Birmingham, UK. Environ Sci Technol 30(3):825–832
Hedges JI, Stren JH (1984) Carbon and nitrogen determinations of carbonate-containing solids. Limnol Oceanogr 29:657–663
Ji YN, Zhao ZZ, Wu D, Fu XN (2016) Distribution and bioavailability of seven heavy metals in mangrove wetland sediments in Dongzhai Harbor, Hainan Island, China. Chin J Appl Ecol Chin J Appl Ecol 27(2):593–600
Kannan K, Johnson-Restrepo B, Yohn SS, Giesy JP, Long DT (2005) Spatial and temporal distribution of polycyclic aromatic hydrocarbons in sediments from Michigan inland lakes. Environ Sci Technol 39(13):4700–4706
Ke L, Wong TWY, Wong YS, Tam NFY (2002) Fate of polycyclic aromatic hydrocarbon (PAH) contamination in a mangrove swamp in Hong Kong following an oil spill. Mar Pollut Bull 45(1–12):339–347
Khalili NR, Scheff PA, Holsen TM (1995) PAH source fingerprints for coke ovens, diesel and gasoline engines, highway tunnels, and wood combustion emission. Atmos Environ 29(4):533–542
Kim GB, Maruya KA, Lee RF, Lee JH, Koh CH, Tanabe S (1999) Distribution and sources of polycyclic aromatic hydrocarbons in sediments from Kyeonggi Bay, Korea. Mar Pollut Bull 38(1):7–15
Kuo LJ, Lee CL, Louchouarn P, Huh CA, Liu JT, Chen JC, Lee KJ (2014) A centennial record of anthropogenic impacts and extreme weather events in southwestern Taiwan: evidence from sedimentary molecular markers in coastal margin. Mar Pollut Bull 86(49):244–253
Larsen RK, Baker JE (2003) Source apportionment of polycyclic aromatic hydrocarbons in the urban atmosphere: a comparison of three methods. Environ Sci Technol 37(9):1873–1881
Li FL, Zeng XK, Yang JD, Zhou K, Zan QJ, Lei AN, Tam NFY (2014a) Contamination of polycyclic aromatic hydrocarbons (PAHs) in surface sediments and plants of mangrove swamps in Shenzhen, China. Mar Pollut Bull 85(2):590–596
Li PY, Xue R, Wang YH, Zhang RJ, Zhang G (2014b) Influence of anthropogenic activities on PAHs in sediments in a significant gulf of low-latitude developing regions, the Beibu Gulf, South China Sea: distribution, sources, inventory and probability risk. Mar Pollut Bull 90(1–2):218–226
Li F, Zeng XK, Yang JD, Zhou K, Zan QJ, Lei AP, Tam NFY (2014c) Contamination of polycyclic aromatic hydrocarbons (PAHs) in surface sediments and plants of mangrove swamps in Shenzhen, China. Mar Pollut Bull 85(2):590–596
Li CH, Wong YS, Wang HY, Nora Tam NF (2015) Anaerobic biodegradation of PAHs in mangrove sediment with amendment of NaHCO3. J Environ Sci 30(4):148–156
Lima ALC, Eglinton TI, Reddy CM (2003) High-resolution record of pyrogenic polycyclic aromatic hydrocarbon deposition during the 20th century. Environ Sci Technol 37(1):53–61
Lin T, Qin YW, Zheng BH, Li YY, Zhang L, Guo ZG (2012) Sedimentary record of polycyclic aromatic hydrocarbons in a reservoir in Northeast China. Environ Pollut 163(4):256–260
Liu HF, Qi SH, Su QK, Fu YR, Wang J, Mu Q (2007) Compositive characteristics of organochlorine pesticides in surface sediments of Dongzhai Harbor, Hainan Island. China Environ Sci 27(1):97–101
Liu Y, Yu N, Li Z, Wei YP, Ma LM, Zhao JF (2012) Sedimentary record of PAHs in the Liangtan River and its relation to socioeconomic development of Chongqing, Southwest China. Chemosphere 89(7):893–899
Long ER, MacDonald DD, Smith SL, Calder FD (1995) Incidence of adverse biological effects within ranges of chemical concentrations in marine and estuarine sediments. Environ Manage 19(1):81–97
Lovelock CE, Cahoon DR, Friess DA, Guntenspergen GR, Krauss KW, Ree FR, Rogers K, Saunder ML, Sidik F, Swales A (2015) The vulnerability of Indo-Pacific mangrove forests to sea-level rise. Nature 526(7574):559–563
Magi E, Bianco R, Ianni C, Carro M (2002) Distribution of polycyclic aromatic hydrocarbons in the sediments of the Adriatic Sea. Environ Pollut 119(1):91–98
Mai BX, Qi SH, Zeng EY, Yang QS, Zhang G, Fu JM, Sheng GY, Peng PG, Wang ZS (2003) Distribution of polycyclic aromatic hydrocarbons in the coastal region off Macao, China: assessment of input sources and transport pathways using compositional analysis. Environ Sci Technol 37(21):4855–4863
Marr LC, Kirchstetter TW, Harley RA, Miguel AH, Hering SV, Hammond SK (1999) Characterization of polycyclic aromatic hydrocarbons in motor vehicle fuels and exhaust emissions. Environ Sci Technol 33(18):3091–3099
Nicola FD, Maisto G, Prati MV, Alfani A (2005) Temporal variations in PAH concentrations in Quercus ilex L (holm oak) leaves in an urban area. Chemosphere 61(3):432–440
Ramdine G, Fichet D, Louis M, Lemoine S (2012) Polycyclic aromatic hydrocarbons (PAHs) in surface sediment and oysters (Crassostrearhizophorae) from mangrove of Guadeloupe: levels, bioavailability, and effects. Ecotoxicol Environ Saf 79(4):80–89
Raza M, Zakaria MP, Hashim NR, Yim UH, Kannan N, Ha SY (2013) Composition and source identification of polycyclic aromatic hydrocarbons in mangrove sediments of Peninsular Malaysia: indication of anthropogenic input. Environ Earth Sci 70(6):2425–2436
Soclo HH, Garrigues PH, Ewald M (2000) Origin of polycyclic aromatic hydrocarbons (PAHs) in coastal marine sediments: case studies in Cotonou (Benin) and Aquitaine (France) areas. Mar Pollut Bull 40(5):387–396
Soliman YS, Al Ansari EMS, Wade TL (2014) Concentration, composition and sources of PAHs in the coastal sediments of the exclusive economic zone (EEZ) of Qatar, Arabian Gulf. Mar Pollut Bull 85(2):542–548
Venturini N, Tommasi LR (2004) Polycyclic aromatic hydrocarbons and changes in the trophic structure of polychaete assemblages in sediments of Todos os Santos Bay, Northeastern, Brazil. Mar Pollut Bull 48(1–2):97–107
Wang Q, Li RR (2016) Journey to burning half of global coal: trajectory and drivers of China’s coal use. Renew Sustain Energy Rev 58:341–346
Wang Z, Chen JW, Qiao XL, Yang P, Tian FL, Huang LP (2007) Distribution and sources of polycyclic aromatic hydrocarbons from urban to rural soils: a case study in Dalian, China. Chemosphere 68(5):965–971
Webb EL, Friess DA, Krauss KW (2013) A global standard for monitoring coastal wetland vulnerability to accelerated sea-level rise. Nat Clim Change 3(5):458–465
Wei MX, He BM (2009) Primary discussion on change trend of culture ecological environment and continuous development strategy in Qinzhou Bay. Mar Environ Sci 6:764–767
Wu QH, Leung JYS, Tam NFY, Chen SJ, Mai BX, Zhou XZ, Xia LH, Geng XH (2014) Biological risk and pollution history of polycyclic aromatic hydrocarbons (PAHs) in Nansha mangrove, South China. Mar Pollut Bull 85(1):92–98
Xu SS, Liu WX, Tao S (2006) Emission of polycyclic aromatic hydrocarbons in China. Environ Sci Technol 40(3):702–708
Xu J, Guo JY, Liu GR, Shi GL, Guo CS, Zhang Y, Feng YC (2014) Historical trends of concentrations, source contributions and toxicities for PAHs in dated sediment cores from five lakes in western China. Sci Total Environ 470–471(2):519–526
Yang HH, Lee WJ, Chen SJ, Lai SO (1998) PAH emission from various industrial stacks. J Hazard Mater 60(2):159–174
Yang RQ, Xie T, Li A, Yang HD, Turner S, Wu GJ, Jing CY (2016) Sedimentary records of polycyclic aromatic hydrocarbons (PAHs) in remote lakes across the Tibetan Plateau. Environ Pollut 214:1–7
Yuan DX, Yang DN, Chen M, Xu PX, Qian YR, Wang JL (2001) Concentrations and distribution of polycyclic aromatic hydrocarbons and organo-chlorides in surface sediment of Xiamen Western Harbour and Minjiang Estuary. Acta Sci Circumst 21(1):107–112
Yunker MB, Macdonald RW, Vingarzan R, Mitchell RH, Goyette D, Sylvestre S (2002) PAHs in the Fraser River basin: a critical appraisal of PAH ratios as indicators of PAH source and composition. Org Geochem 33(4):489–515
Zhang J, Cai LZ, Yuan DX, Chen M (2004) Distribution and sources of polynuclear aromatic hydrocarbons in Mangrove surface sediments of Deep Bay, China. Mar Pollut Bull. 49(5–6):479–486
Zhang D, Liu J, Jiang X, Cao K, Yin P, Zhang X (2016) Distribution, sources and ecological risk assessment of PAHs in surface sediments from the Luan River Estuary, China. Mar Pollut Bull 102(1):223–229
Zou YF, Li Y, Zhao ZZ, Ji YN, Wu D (2015) Vertical distribution and pollution assessment of heavy metals in mangrove sediments of Dongzhai Harbor, Hainan. Agric Sci Technol 16(9):1994–1998
Funding
This study was supported by the Open Research Fund Program of Guangxi Key Lab of Mangrove Conservation and Utilization (Grant No. GKLMC-201503), the Basic Fund of Ministry of Science and Technology (Grant No. 2013FY112200), the Marine Geology Survey Project (Grant No. GZH201100203), and the National Natural Science Foundation of China (Grant No. 41306064).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Zhang, D., Yan, D., Jiang, X. et al. Influence of anthropogenic activities on polycyclic aromatic hydrocarbons in sediments from mangrove wetland at Dongzhai Harbor, China: distribution, sources, probability risk, and temporal trend. Wetlands Ecol Manage 26, 613–625 (2018). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11273-018-9595-x
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11273-018-9595-x