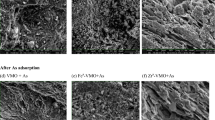
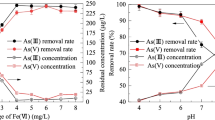
Abstract
This study addresses the environmental concern of organic-arsenic pollution resulting from the discharge of dimethyl arsenic acid (DMA) through non-point sources into surface and groundwater, posing severe health risks. While efforts have primarily focused on eliminating inorganic arsenic, the toxicity of organic arsenic, particularly DMA, has been over-disregarded and necessitates a thorough examination. In response, this research focuses on developing effective adsorbents for the removal of organic arsenic, with a specific emphasis on DMA. Using the co-precipitation method, ferric manganese binary oxide (FMBO) was synthesized and compared with manganese dioxide (MnO2) and ferric oxide (FeOOH). The produced adsorbents were evaluated using a range of characterization methods, such as X-ray powder diffraction (XRD), specific surface area (SBET), zeta (ζ)-potential, scanning electron microscopy (SEM) with energy dispersive X-ray (EDX), and Fourier transform infrared spectroscopy (FTIR). The impact of pH, adsorption kinetics, and adsorption isotherms were investigated in batch studies to ascertain efficacy. The Elovich model, which suggests heterosphere diffusion reactions, best explained the adsorption data, according to the results followed by the pseudo-second-order model. pH had a major impact on DMA adsorption; at pH 4.0, FMBO showed a maximum adsorption capacity of 665.28 μg/g, which was higher than that of FeOOH (581.32 μg/g) and MnO2 (510.56 μg/g). Fitting descriptions of DMA adsorption onto FMBO, FeOOH, and MnO2 were provided by the Langmuir and Sips models. Systematic characterization by FTIR and SEM–EDX highlighted FMBO’s predominant role in DMA adsorption at lower pH. Regeneration experiments demonstrated a slight decrease in DMA adsorption from 99.04 to 94.90% after five consecutive cycles, affirming FMBO’s substantial capability to remove DMA from aqueous solutions. This study underscores the potential of FMBO as an efficient adsorbent for combating organic-arsenic pollution.









Similar content being viewed by others
Data Availability
The datasets used and/or analyzed during the current study are available from the corresponding author on reasonable request.
References
Abebe, B., Taddesse, A. M., Kebede, T., Teju, E., & Diaz, I. (2017). Fe-Al-Mn ternary oxide nanosorbent: Synthesis, characterization and phosphate sorption property. Journal of Environmental Chemical Engineering, 5, 1330–1340.
Ahangari, A., Raygan, S., & Ataie, A. (2019). Capabilities of nickel zinc ferrite and its nanocomposite with CNT for adsorption of arsenic (V) ions from wastewater. Journal of Environmental Chemical Engineering, 7, 103493.
Ali, I. (2012). New generation adsorbents for water treatment. Chemical Reviews, 112, 5073–5091.
Aliahmadipoor, P., Ghazanfari, D., Gohari, R. J., & Akhgar, M. R. (2020). Preparation of PVDF/FMBO composite electrospun nanofiber for effective arsenate removal from water. RSC Advances, 10, 24653–24662.
Baig, S. A., Sheng, T., Sun, C., Xue, X., Tan, L., & Xu, X. (2014). Arsenic removal from aqueous solutions using Fe3O4-HBC composite: Effect of calcination on adsorbents performance. PLoS ONE, 9, e100704.
Borges, G. A., Ferreira, G. M. D., Siqueira, K. P. F., Dias, A., Navarro, K. O. N., Silva, S., Rodrigues, G. D., & Mageste, A. B. (2020). Adsorption of organic and inorganic arsenic from aqueous solutions using MgAl-LDH with incorporated nitroprusside. Journal of Colloid and Interface Science, 575, 194–205.
Chen, L., Xin, H., Fang, Y., Zhang, C., Zhang, F., Cao, X., Zhang, C., & Li, X. (2014). Application of metal oxide heterostructures in arsenic removal from contaminated water. Journal of Nanomaterials, 2014, 1–10.
Cheng, Z., Van Geen, A., Louis, R., Nikolaidis, N., & Bailey, R. (2005). Removal of methylated arsenic in groundwater with iron filings. Environmental Science & Technology, 39, 7662–7666.
Cohen, S. M., Arnold, L. L., Eldan, M., Lewis, A. S., & Beck, B. D. (2006). Methylated arsenicals: The implications of metabolism and carcinogenicity studies in rodents to human risk assessment. Critical Reviews in Toxicology, 36, 99–133.
Dou, X., Zhang, Y., Zhao, B., Wu, X., Wu, Z., & Yang, M. (2011). Arsenate adsorption on an Fe–Ce bimetal oxide adsorbent: EXAFS study and surface complexation modeling. Colloids and Surfaces a: Physicochemical and Engineering Aspects, 379, 109–115.
Ergül, B., Bektaş, N., & Salim Öncel, M. (2014). The use of manganese oxide minerals for the removal arsenic and selenium anions from aqueous solutions. Energy and Environmental Engineering, 2, 103–112.
Eslami, H., Ehrampoush, M. H., Esmaeili, A., Ebrahimi, A. A., Ghaneian, M. T., Falahzadeh, H., & Salmani, M. H. (2019). Synthesis of mesoporous Fe-Mn bimetal oxide nanocomposite by aeration co-precipitation method: Physicochemical, structural, and optical properties. Materials Chemistry and Physics, 224, 65–72.
Faisal, A. A. H., Al-Wakel, S. F. A., Assi, H. A., Naji, L. A., & Naushad, M. (2020). Waterworks sludge-filter sand permeable reactive barrier for removal of toxic lead ions from contaminated groundwater. Journal of Water Process Engineering, 33, 101112.
Fang, Z., Zhang, K., Zhang, X., & Pan, B. (2022). Enhanced water decontamination from methylated arsenic by utilizing ultra-small hydrated zirconium oxides encapsulated inside gel-type anion exchanger. Chemical Engineering Journal, 430, 132641.
Fransiscus, Y., Widi, R. K., Aprilasti, G. O. & Yuharma, M. D.: 2018, ‘Adsorpstion of phosphate in aqueous solutions using manganese dioxide’, International Journal on Advanced Science, Engineeering and Information Technology 8.
Gong, Z., Lu, X., Cullen, W. R., & Le Chris, X. (2001). Unstable trivalent arsenic metabolites, monomethylarsonous acid and dimethylarsinous acid. Journal of Analytical Atomic Spectrometry, 16, 1409–1413.
Hao, L., Liu, M., Wang, N., & Li, G. (2018). A critical review on arsenic removal from water using iron-based adsorbents. RSC Advances, 8, 39545–39560.
Hong, H.-J., Farooq, W., Yang, J.-S., & Yang, J.-W. (2010). Preparation and evaluation of Fe-Al binary oxide for arsenic removal: Comparative study with single metal oxides. Separation Science and Technology, 45, 1975–1981.
Hu, C., Chen, Q., Liu, H., & Qu, J. (2015). Coagulation of methylated arsenic from drinking water: Influence of methyl substitution. Journal of Hazardous Materials, 293, 97–104.
Jiang, L., Xiao, S., & Chen, J. (2015). Removal behavior and mechanism of Co(II) on the surface of Fe–Mn binary oxide adsorbent. Colloids and Surfaces a: Physicochemical and Engineering Aspects, 479, 1–10.
Joshi, T. P.: 2019, ‘Efficiency and mechanisms of iron and manganese based adsorbents for the removal of aromatic organoarsenic compounds’.
Joshi, T. P., Koju, R., Cheng, H., Qi, Z., Liu, R., Bai, Y., Hu, C., Peng, J. & Joshi, D. R.: 2023, ‘High efficient removal of 4-aminophenylarsonic acid from aqueous solution via enhanced FeOOH using Mn (VII)’, Environmental Science and Pollution Research, 1–10.
Joshi, T. P., Zhang, G., Cheng, H., Liu, R., Liu, H., & Qu, J. (2017a). Transformation of para arsanilic acid by manganese oxide: Adsorption, oxidation, and influencing factors. Water Research, 116, 126–134.
Joshi, T. P., Zhang, G., Jefferson, W. A., Perfilev, A. V., Liu, R., Liu, H., & Qu, J. (2017b). Adsorption of aromatic organoarsenic compounds by ferric and manganese binary oxide and description of the associated mechanism. Chemical Engineering Journal, 309, 577–587.
Joshi, T. P., Zhang, G., Koju, R., Qi, Z., Liu, R., Liu, H., & Qu, J. (2017c). The removal efficiency and insight into the mechanism of para arsanilic acid adsorption on Fe-Mn framework. Science of the Total Environment, 601–602, 713–722.
Kecili, R. & Hussain, C. M.: 2018, ‘Mechanism of adsorption on nanomaterials’, 89–115.
Kenyon, E. M., & Hughes, M. F. (2001). A concise review of the toxicity and carcinogenicity of dimethylarsinic acid. Toxicology, 160, 227–236.
Koju, R., Dhakal, A., Gwachha, S., Joshi, D. R., Joshi, T. P., & Shrestha, S. M. (2020). Adsorption of inorganic As(III) from aqueous solutions by iron-manganese oxide. Scientific World, 13, 46–50.
Lafferty, B. J., Ginder-Vogel, M., & Sparks, D. L. (2010). ‘Arsenite oxidation by a poorly crystalline manganese-oxide 1. Stirred-Flow Experiments’, Environmental Science & Technology, 44, 8460–8466.
Lafferty, B. J., & Loeppert, R. (2005). Methyl arsenic adsorption and desorption behavior on iron oxides. Environmental Science & Technology, 39, 2120–2127.
Lan, H., Li, J., Sun, M., An, X., Hu, C., Liu, R., Liu, H., & Qu, J. (2016). Efficient conversion of dimethylarsinate into arsenic and its simultaneous adsorption removal over FeCx/N-doped carbon fiber composite in an electro-Fenton process. Water Research, 100, 57–64.
Li, Y., Hu, X., Ren B., & Yang, W. (2016). Preparation of iron-copper binary oxide and its effective removal on antimony(V) from water. Desalination and Water Treatment, 57(55), 26461–26471.
Lim, S. F., Zheng, Y. M., & Chen, J. P. (2009). Organic arsenic adsorption onto a magnetic sorbent. Langmuir, 25, 4973–4978.
Liu, R., Xu, W., He, Z., Lan, H., Liu, H., Qu, J., & Prasai, T. (2015). Adsorption of antimony(V) onto Mn(II)-enriched surfaces of manganese-oxide and FeMn binary oxide. Chemosphere, 138, 616–624.
Lu, J., Liu, H., Zhao, X., Jefferson, W., Cheng, F., & Qu, J. (2014). Phosphate removal from water using freshly formed Fe–Mn binary oxide: Adsorption behaviors and mechanisms. Colloids and Surfaces a: Physicochemical and Engineering Aspects, 455, 11–18.
Maji, S., Ghosh, A., Gupta, K., Ghosh, A., Ghorai, U., Santra, A., Sasikumar, P., & Ghosh, U. C. (2018). Efficiency evaluation of arsenic(III) adsorption of novel graphene oxide@iron-aluminium oxide composite for the contaminated water purification. Separation and Purification Technology, 197, 388–400.
Marafante, E., Vahter, M., Norin, H., Envall, J., Sandström, M., Christakopoulos, A., & Ryhage, R. (1987). Biotransformation of dimethylarsinic acid in mouse, hamster and man. Journal of Applied Toxicology, 7, 111–117.
McCann, C. M., Peacock, C. L., Hudson-Edwards, K. A., Shrimpton, T., Gray, N. D., & Johnson, K. L. (2018). In situ arsenic oxidation and sorption by a Fe-Mn binary oxide waste in soil. Journal of Hazardous Materials, 342, 724–731.
Mohammad, S. J., Abd Rasin, F., & Alsammarraie, A. M. A. (2019). Characterizations of Fe/Mn binary oxide by nitrogen adsorption. IOP Conference Series: Materials Science and Engineering, 557, 012062.
Naushad, M. (2014). Surfactant assisted nano-composite cation exchanger: Development, characterization and applications for the removal of toxic Pb2+ from aqueous medium. Chemical Engineering Journal, 235, 100–108.
Ning, R. Y. (2002). Arsenic removal by reverse osmosis. Desalination, 143, 237–241.
Nordstrom, D. K. (2002). Public health Worldwide Occurrences of Arsenic in Ground Water. Science, 296, 2143–2145.
Olson, K. R., & Cihacek, L. (2022). Agent blue spraying in the Mekong Delta during the Vietnam war: Fate of the arsenic based herbicide weapon used to destroy rice crop and mangrove forests. Open Journal of Soil Science, 12, 253–294.
Organization, W. H.: 2017, ‘Guidelines for drinking-water quality: First addendum to the fourth edition’.
Park, J.-H., Kim, S.-J., Nam, I.-H., Ryu, J., Jung, G.-Y., & Han, Y.-S. (2022). Microbial mediated reaction of dimethylarsinic acid in wetland water and sediments. Water Research, 222, 118873.
Pignatello, J. J., Oliveros, E., & MacKay, A. (2006). Advanced oxidation processes for organic contaminant destruction based on the fenton reaction and related chemistry. Critical Reviews in Environmental Science and Technology, 36, 1–84.
Qi, Z., Joshi, T. P., Liu, R., Li, Y., Liu, H., & Qu, J. (2018). Adsorption combined with superconducting high gradient magnetic separation technique used for removal of arsenic and antimony. Journal of Hazardous Materials, 343, 36–48.
Ren, Z., Zhang, G., & Chen, J. P. (2011). Adsorptive removal of arsenic from water by an iron-zirconium binary oxide adsorbent. Journal of Colloid and Interface Science, 358, 230–237.
Shaji, E., Santosh, M., Sarath, K. V., Prakash, P., Deepchand, V., & Divya, B. V. (2021). Arsenic contamination of groundwater: A global synopsis with focus on the Indian Peninsula. Geoscience Frontiers, 12, 101079.
Shakoor, M. B., Niazi, N. K., Bibi, I., Shahid, M., Saqib, Z. A., Nawaz, M. F., Shaheen, S. M., Wang, H., Tsang, D. C. W., Bundschuh, J., Ok, Y. S., & Rinklebe, J. (2019). Exploring the arsenic removal potential of various biosorbents from water. Environment International, 123, 567–579.
Siddiqui, S. I., & Chaudhry, S. A. (2017). Iron oxide and its modified forms as an adsorbent for arsenic removal: A comprehensive recent advancement. Process Safety and Environmental Protection, 111, 592–626.
Sing, K. S. (1985). Reporting physisorption data for gas/solid systems with special reference to the determination of surface area and porosity (Recommendations 1984). Pure and Applied Chemistry, 57, 603–619.
Sinha, D., & Prasad, P. (2020). Health effects inflicted by chronic low-level arsenic contamination in groundwater: A global public health challenge. Journal of Applied Toxicology : JAT, 40, 87–131.
Smedley, P. L., & Kinniburgh, D. G. (2002). A review of the source, behaviour and distribution of arsenic in natural waters. Applied Geochemistry, 17, 517–568.
Sujana, M. G., & Anand, S. (2013). Ferric hydroxide: Preparation, characterisation and fluoride removal studies from water. Desalination and Water Treatment, 52, 6453–6463.
Suzuki, S., Gi, M., Fujioka, M., Kakehashi, A., & Wanibuchi, H. (2023). Dimethylarsinic acid induces bladder carcinogenesis via the amphiregulin pathway. Toxicology Letters, 384, 128–135.
Tabassum, R. A., Shahid, M., Niazi, N. K., Dumat, C., Zhang, Y., Imran, M., Bakhat, H. F., Hussain, I., & Khalid, S. (2019). Arsenic removal from aqueous solutions and groundwater using agricultural biowastes-derived biosorbents and biochar: A column-scale investigation. International Journal of Phytoremediation, 21, 509–518.
Thommes, M., Kaneko, K., Neimark, A. V., Olivier, J. P., Rodriguez-Reinoso, F., Rouquerol, J., & Sing, K. S. W. (2015). Physisorption of gases, with special reference to the evaluation of surface area and pore size distribution (IUPAC Technical Report). Pure and Applied Chemistry, 87, 1051–1069.
Tofik, A. S., Taddesse, A. M., Tesfahun, K. T., & Girma, G. G. (2016). Fe–Al binary oxide nanosorbent: Synthesis, characterization and phosphate sorption property. Journal of Environmental Chemical Engineering, 4, 2458–2468.
Tzabar, N., & ter Brake, H. J. M. (2016). Adsorption isotherms and Sips models of nitrogen, methane, ethane, and propane on commercial activated carbons and polyvinylidene chloride. Adsorption, 22, 901–914.
Vakili, M., Deng, S., Shen, L., Shan, D., Liu, D., & Yu, G. (2017). Regeneration of chitosan-based adsorbents for eliminating dyes from aqueous solutions. Separation & Purification Reviews, 48, 1–13.
Wan, J., Simon, S., Deluchat, V., Dictor, M. C., & Dagot, C. (2013). ‘Adsorption of As(III), As(V) and dimethylarsinic acid onto synthesized lepidocrocite’, Journal of environmental science and health. Part a, Toxic/hazardous Substances & Environmental Engineering, 48, 1272–1279.
Wei, M., Wanibuchi, H., Yamamoto, S., Li, W., & Fukushima, S. (1999). Urinary bladder carcinogenicity of dimethylarsinic acid in male F344 rats. Carcinogenesis, 20, 1873–1876.
Wei, Y. T., Zheng, Y. M., & Chen, J. P. (2011). Uptake of methylated arsenic by a polymeric adsorbent: Process performance and adsorption chemistry. Water Research, 45, 2290–2296.
Wu, W., Jiang, C. Z., & Roy, V. A. (2016). Designed synthesis and surface engineering strategies of magnetic iron oxide nanoparticles for biomedical applications. Nanoscale, 8, 19421–19474.
Xie, X., Lu, C., Xu, R., Yang, X., Yan, L., & Su, C. (2022). Arsenic removal by manganese-doped mesoporous iron oxides from groundwater: Performance and mechanism. Science of the Total Environment, 806, 150615.
Xu, F., Chen, H., Dai, Y., Wu, S., & Tang, X. (2019). Arsenic adsorption and removal by a new starch stabilized ferromanganese binary oxide in water. Journal of Environmental Management, 245, 160–167.
Xu, T., Cai, Y., & O’Shea, K. E. (2007). Adsorption and photocatalyzed oxidation of methylated arsenic species in TiO2 suspensions. Environmental Science and Technology, 41, 5471–5477.
Xu, W., Lan, H., Wang, H., Liu, H., & Qu, J. (2014). Comparing the adsorption behaviors of Cd, Cu and Pb from water onto Fe-Mn binary oxide, MnO2 and FeOOH. Frontiers of Environmental Science & Engineering, 9, 385–393.
Xu, W., Wang, H., Liu, R., Zhao, X., & Qu, J. (2011). The mechanism of antimony(III) removal and its reactions on the surfaces of Fe-Mn binary oxide. Journal of Colloid and Interface Science, 363, 320–326.
Yang, C., Ju, T., Wang, X., Ji, Y., Yang, C., Lv, H., Wang, Y., Dong, W., Dang, F., Shi, X., Wang, W., & Fan, Y. (2020). The preparation of a novel iron/manganese binary oxide for the efficient removal of hexavalent chromium [Cr(vi)] from aqueous solutions. RSC Advances, 10, 10612–10623.
Yang, K., Zhou, J., Lou, Z., Zhou, X., Liu, Y., Li, Y., Baig, S. A., & Xu, X. (2018). Removal of Sb (V) from aqueous solutions using Fe-Mn binary oxides: The influence of iron oxides forms and the role of manganese oxides. Chemical Engineering Journal, 354, 577–588.
Zeng, H., Qiao, T., Zhao, Y., Yu, Y., Zhang, J., & Li, D. (2019). Characterization and arsenic adsorption behaviors of water treatment residuals from waterworks for iron and manganese removal. International Journal of Environmental Research and Public Health, 16, 4912.
Zhang, G., Liu, F., Liu, H., Qu, J., & Liu, R. (2014). Respective role of Fe and Mn oxide contents for arsenic sorption in iron and manganese binary oxide: An X-ray absorption spectroscopy investigation. Environmental Science and Technology, 48, 10316–10322.
Zhang, G., Liu, H., Liu, R., & Qu, J. (2009). Removal of phosphate from water by a Fe-Mn binary oxide adsorbent. Journal of Colloid and Interface Science, 335, 168–174.
Zhang, G., Qu, J., Liu, H., Liu, R., & Wu, R. (2007). Preparation and evaluation of a novel Fe-Mn binary oxide adsorbent for effective arsenite removal. Water Research, 41, 1921–1928.
Zhang, M., Dai, M., Xia, L. & Song, S.: 2017, ‘Comparison of arsenic adsorption on goethite and amorphous ferric oxyhydroxide in water’, Water, Air, & Soil Pollution 228.
Zheng, Q., Hou, J., Hartley, W., Ren, L., Wang, M., Tu, S., & Tan, W. (2020). As(III) adsorption on Fe-Mn binary oxides: Are Fe and Mn oxides synergistic or antagonistic for arsenic removal? Chemical Engineering Journal, 389, 124470.
Zhou, J., Zhou, X., Yang, K., Cao, Z., Wang, Z., Zhou, C., Baig, S. A., & Xu, X. (2020). Adsorption behavior and mechanism of arsenic on mesoporous silica modified by iron-manganese binary oxide (FeMnOx/SBA-15) from aqueous systems. Journal of Hazardous Materials, 384, 121229.
Zou, S.-W., Koh, K. Y., Chen, Z., Wang, Y.-Y., Chen, J. P., & Zheng, Y.-M. (2022). Adsorption of organic and inorganic arsenic from aqueous solution: Optimization, characterization and performance of Fe–Mn–Zr ternary magnetic sorbent. Chemosphere, 288, 132634.
Acknowledgements
This research work was carried out with the aid of a grant from UNESCO and the International Development Research Centre (IDRC), Ottawa, Canada. The views expressed herein do not necessarily represent those of UNESCO, IDRC, or its Board of Governors. We are grateful to the Key Laboratory of Drinking Water Science and Technology at the Research Center for Eco-Environmental Sciences of the Chinese Academy of Sciences, Beijing 100085, China, for helping the characterization of the adsorbents with partial financial support by the National Natural Science Foundation of China (Grant-Number: 51908541) and the Alliance of International Science Organizations (ANSO-CR-KP-2020-05). We are grateful to the Nepal Academy of Science and Technology (NAST) for providing all the laboratory facilities.
Funding
UNESCO and the International Development Research Center (IDRC), Ottawa, Canada, Grant Number: 4500406708, Author Tista Prasai Joshi has received funds.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Contributions
Naina Byanjankar: methodology, conceptualization, and writing—original draft preparation; Tista Prasai Joshi: conceptualization, methodology, writing—reviewing and editing, and supervision; Agni Dhakal: methodology; Dev Raj Joshi: writing—reviewing and editing; Rashmi Koju: methodology, reviewing, and editing; Zenglu Qi: methodology and software; Chengzhi Hu: validation; Ruiping Liu: supervision. All authors read and approved the final manuscript.
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Ethics Approval and Consent to Participate
Not applicable.
Consent for Publication
Not applicable.
Competing Interests
The authors declare no competing interests.
Additional information
Publisher's Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Rights and permissions
Springer Nature or its licensor (e.g. a society or other partner) holds exclusive rights to this article under a publishing agreement with the author(s) or other rightsholder(s); author self-archiving of the accepted manuscript version of this article is solely governed by the terms of such publishing agreement and applicable law.
About this article
Cite this article
Byanjankar, N., Joshi, T.P., Dhakal, A. et al. Removal of Dimethyl Arsenic Acid from Aqueous Solution by Ferric Manganese Binary Oxide. Water Air Soil Pollut 235, 196 (2024). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11270-024-07008-5
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11270-024-07008-5