Abstract
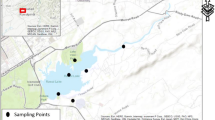
The prevalence of microplastic contamination has become a major problem worldwide, with the potential to harm aquatic ecosystems and human well-being. This study investigated the occurrence of microplastics (MPs) in sediment samples obtained from Dal Lake, situated in the northwest Himalayas, India. Thirty-two sediment samples collected from different sites inside the lake were thoroughly analyzed using a stereomicroscope. The research showed that the average concentration of microplastics (MPs) in the sediment was 416 ± 38 MP/kg (mean ± standard error, n = 32) based on the weight of the dry sediment. The most frequently seen colours of MPs were blue, white, black, red, and orange. The majority of the total consists of fiber-shaped particles, accounting for 86.5%, while fragments make up 11%, and films make up 2.5%. Raman spectroscopy revealed the high occurrence of Polyamides, namely Nylon, comprising 62.5% of the sample. Small amounts of Polyethylene, Polyvinylchloride, and Polypropylene were also detected. The findings of this research suggest that tourism, fishing activities, and untreated wastewater are major contributors to the presence of microplastics (MPs) in the lake. In addition, local community habits, such as the use of packaging materials, automobiles, and cosmetics, also contribute to microplastic pollution. Sediment quality was assessed using hazard indicators such as the Polymer Hazard Index (PHI), Pollution Load Index (PLI), and Potential Ecological Risk Index (PERI). The occurrence of high levels of PHI (> 1000) in some regions is attributed to the presence of high-risk polymers such as polyamide (PA) and polyvinyl chloride (PVC). The sediments were classified as medium-risk according to the PERI values, whereas the PLI values revealed a relatively low contamination level (< 10), falling into Hazard Category I. The results of this research provide a crucial understanding of the categories, dispersion, and sources of microplastics (MPs) in Dal Lake. This understanding serves as the basis for focused efforts to protect the lake's biological balance and ensure the well-being of humans, both now and in the future.
Graphical abstract







Similar content being viewed by others
Data Availability
All data generated or analysed during this study are included in this published article.
References
Akhter, R., Masoodi, F.A., Wani, T.A., Raja, J., & Rather, S.A. (2020). Ethnic Fermented Foods and Beverages of Jammu and Kashmir. In: J. Tamang (Ed.), Ethnic Fermented Foods and Beverages of India: Science History and Culture. Singapore: Springer. https://doi.org/10.1007/978-981-15-1486-9_10
Alfonso, M. B., Arias, A. H., Ronda, A. C., & Piccolo, M. C. (2021). Continental microplastics: Presence, features, and environmental transport pathways. Science of the Total Environment, 799, 149447. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.scitotenv.2021.149447
Amelia, T. S. M., Khalik, W. M. A. W. M., Ong, M. C., Shao, Y. T., Pan, H.-J., & Bhubalan, K. (2021). Marine microplastics as vectors of major ocean pollutants and its hazards to the marine ecosystem and humans. Progress in Earth and Planetary Science, 8(1), 12. https://doi.org/10.1186/s40645-020-00405-4
Anema, J. R., Brolo, A. G., Felten, A., & Bittencourt, C. (2010). Surface-enhanced Raman scattering from polystyrene on gold clusters. Journal of Raman Spectroscopy, 41(7), 745–751. https://doi.org/10.1002/jrs.2504
Bharath K, M., S, S., Natesan, U., Ayyamperumal, R., Kalam S, N., S, A., K, S., & C, A. (2021). Microplastics as an emerging threat to the freshwater ecosystems of Veeranam lake in south India: A multidimensional approach. Chemosphere, 264(2), 128502. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.chemosphere.2020.128502
Bhat, U. N., & Khan, A. B. (2019). A retrospective environmental assessment of the natural heritage of Dal lake for prospective implication scenarios. Ecology and Sustainable Development, 2(1), 10. https://doi.org/10.22606/esd.2019.21001
Blettler, M. C. M., Ulla, M. A., Rabuffetti, A. P., & Garello, N. (2017). Plastic pollution in freshwater ecosystems: Macro-, meso-, and microplastic debris in a floodplain lake. Environmental Monitoring and Assessment, 189(11), 581. https://doi.org/10.1007/s10661-017-6305-8
Boucher, J., & Friot, D. (2017). Primary microplastics in the oceans: A global evaluation of sources. Gland, Switzerland. https://doi.org/10.2305/IUCN.CH.2017.01.en
Brander, S. M., Renick, V. C., Foley, M. M., Steele, C., Woo, M., Lusher, A., Carr, S., Helm, P., Box, C., Cherniak, S., Andrews, R. C., & Rochman, C. M. (2020). Sampling and quality assurance and quality control: A guide for scientists investigating the occurrence of microplastics across matrices. Applied Spectroscopy, 74(9), 1099–1125. https://doi.org/10.1177/0003702820945713
Cabernard, L., Roscher, L., Lorenz, C., Gerdts, G., & Primpke, S. (2018). Comparison of Raman and Fourier transform infrared spectroscopy for the quantification of microplastics in the aquatic environment. Environmental Science and Technology, 52(22), 13279–13288. https://doi.org/10.1021/acs.est.8b03438
Carney Almroth, B. M., Åström, L., Roslund, S., Petersson, H., Johansson, M., & Persson, N. K. (2018). Quantifying shedding of synthetic fibers from textiles; a source of microplastics released into the environment. Environmental Science and Pollution Research International, 25(2), 1191–1199. https://doi.org/10.1007/s11356-017-0528-7
Caron, A. G. M., Thomas, C. R., Berry, K. L. E., Motti, C. A., Ariel, E., & Brodie, J. E. (2018). Ingestion of microplastic debris by green sea turtles (Chelonia mydas) in the Great Barrier Reef: Validation of a sequential extraction protocol. Marine Pollution Bulletin, 127, 743–751. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.marpolbul.2017.12.062
Chakraborty, I., Banik, S., Biswas, R., Yamamoto, T., Noothalapati, H., & Mazumder, N. (2022). Raman spectroscopy for microplastic detection in water sources: A systematic review. International Journal of Environmental Science and Technology. https://doi.org/10.1007/s13762-022-04505-0
Chernykh, D. V., Biryukov, R. Y., Kuryatnikova, N. A., & Malygina, N. S. (2022). Microplastics in the snow cover of urban landscapes: A case study of Barnaul. Geography and Natural Resources, 43(Suppl. 1), S44–S49. https://doi.org/10.1134/S1875372822050080
Cole, M., Lindeque, P., Halsband, C., & Galloway, T. S. (2011). Microplastics as contaminants in the marine environment: A review. Marine Pollution Bulletin, 62(12), 2588–2597. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.marpolbul.2011.09.025
D’Avignon, G., Gregory-Eaves, I., & Ricciardi, A. (2022). Microplastics in lakes and rivers: An issue of emerging significance to limnology. Environmental Reviews, 30(2), 228–244. https://doi.org/10.1139/er-2021-0048
De Frond, H., Thornton Hampton, L., Kotar, S., Gesulga, K., Matuch, C., Lao, W., Weisberg, S. B., Wong, C. S., & Rochman, C. M. (2022). Monitoring microplastics in drinking water: An interlaboratory study to inform effective methods for quantifying and characterizing microplastics. Chemosphere, 298, 134282. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.chemosphere.2022.134282
Dris, R., Gasperi, J., Rocher, V., Saad, M., Renault, N., & Tassin, B. (2015). Microplastic contamination in an urban area: A case study in Greater Paris. Environmental Chemistry, 12(5), 592–599. https://doi.org/10.1071/EN14167
Duis, K., & Coors, A. (2016). Microplastics in the aquatic and terrestrial environment: Sources (with a specific focus on personal care products), fate and effects. Environmental Sciences Europe, 28(1), 2. https://doi.org/10.1186/s12302-015-0069-y
Dusaucy, J., Gateuille, D., Perrette, Y., & Naffrechoux, E. (2021). Microplastic pollution of worldwide lakes. Environmental Pollution, 284, 117075. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.envpol.2021.117075
Egessa, R., Nankabirwa, A., Ocaya, H., & Pabire, W. G. (2020). Microplastic pollution in surface water of Lake Victoria. Science of the Total Environment, 741, 140201. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.scitotenv.2020.140201
Eriksen, M., Lebreton, L. C. M., Carson, H. S., Thiel, M., Moore, C. J., Borerro, J. C., Galgani, F., Ryan, P. G., & Reisser, J. (2014). Plastic pollution in the World’s oceans: More than 5 trillion plastic pieces weighing over 250,000 tons afloat at sea. PLoS ONE, 9(12), e111913. https://doi.org/10.1371/journal.pone.0111913
Esterhuizen, M., & Kim, Y. J. (2022). Effects of polypropylene, polyvinyl chloride, polyethylene terephthalate, polyurethane, high-density polyethylene, and polystyrene microplastic on Nelumbo nucifera (Lotus) in water and sediment. Environmental Science and Pollution Research, 29, 17580–17590. https://doi.org/10.1007/s11356-021-17033-0
Free, C. M., Jensen, O. P., Mason, S. A., Eriksen, M., Williamson, N. J., & Boldgiv, B. (2014). High-levels of microplastic pollution in a large, remote, mountain lake. Marine Pollution Bulletin, 85(1), 156–163. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.marpolbul.2014.06.001
Galafassi, S., Nizzetto, L., & Volta, P. (2019). Plastic sources: A survey across scientific and grey literature for their inventory and relative contribution to microplastics pollution in natural environments, with an emphasis on surface water. Science of the Total Environment, 693, 133499. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.scitotenv.2019.07.305
Golwala, H., Zhang, X., Iskander, S. M., & Smith, A. L. (2021). Solid waste: An overlooked source of microplastics to the environment. Science of the Total Environment, 769, 144581. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.scitotenv.2020.144581
Hartmann, N. B., Hüffer, T., Thompson, R. C., Hassellöv, M., Verschoor, A., Daugaard, A. E., Rist, S., Karlsson, T., Brennholt, N., Cole, M., Herrling, M. P., Hess, M. C., Ivleva, N. P., Lusher, A. L., & Wagner, M. (2019). Are we speaking the same language? Recommendations for a definition and categorization framework for plastic debris. Environmental Science and Technology, 53(3), 1039–1047. https://doi.org/10.1021/acs.est.8b05297
Hüffer, T., Metzelder, F., Sigmund, G., Slawek, S., Schmidt, T. C., & Hofmann, T. (2019). Polyethylene microplastics influence the transport of organic contaminants in soil. Science of the Total Environment, 657, 242–247. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.scitotenv.2018.12.047
Jain, S. K., Agarwal, P. K., & Singh, V. P. (2007). Hydrology and water resources of India. Springer.
Jansen, M. A. K., Barnes, P. W., Bornman, J. F., Rose, K. C., Madronich, S., White, C. C., Zepp, R. G., & Andrady, A. L. (2023). The Montreal Protocol and the fate of environmental plastic debris. Photochemical & Photobiological Sciences, 22(5), 1203–1211. https://doi.org/10.1007/s43630-023-00372-x
Karthik, R., Robin, R. S., Purvaja, R., Ganguly, D., Anandavelu, I., Raghuraman, R., Hariharan, G., Ramakrishna, A., & Ramesh, R. (2018). Microplastics along the beaches of southeast coast of India. Science of the Total Environment, 645, 1388–1399. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.scitotenv.2018.07.242
Kasavan, S., Yusoff, S., Rahmat Fakri, M. F. R., & Siron, R. (2021). Plastic pollution in water ecosystems: A bibliometric analysis from 2000 to 2020. Journal of Cleaner Production, 313, 127946. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jclepro.2021.127946
Kershaw, P. J., Turra, A., Galgani, F., & GESAMP. (2019). Guidelines for the monitoring and assessment of plastic litter and microplastics in the ocean [Report]. GESAMP Joint Group of Experts on the Scientific Aspects of Marine Environmental Protection. https://doi.org/10.25607/OBP-435
Koelmans, A. A., Redondo-Hasselerharm, P. E., Mohamed Nor, N. H., & Gouin, T. (2023). On the probability of ecological risks from microplastics in the Laurentian Great lakes. Environmental Pollution, 325, 121445. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.envpol.2023.121445
Kumar, R., Verma, A., Shome, A., Sinha, R., Sinha, S., Jha, P. K., Kumar, R., Kumar, P., Shubham, D., Das, S., Sharma, P., & Vara Prasad, P. V. (2021). Impacts of plastic pollution on ecosystem services, sustainable development goals, and need to focus on circular economy and policy interventions. Sustainability, 13(17), article 17. https://doi.org/10.3390/su13179963
Kumar, R., Parvaze, S., Huda, M. B., & Allaie, S. P. (2022). The changing water quality of lakes—A case study of Dal Lake, Kashmir Valley. Environmental Monitoring and Assessment, 194(3), 228. https://doi.org/10.1007/s10661-022-09869-x
Lee, S. Y., An, J., Kim, J., & Kwon, J. H. (2022). Enhanced settling of microplastics after biofilm development: A laboratory column study mimicking wastewater clarifiers. Environmental Pollution, 311, 119909. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.envpol.2022.119909
Lithner, D., Larsson, A., & Dave, G. (2011). Environmental and health hazard ranking and assessment of plastic polymers based on chemical composition. Science of the Total Environment, 409(18), 3309–3324. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.scitotenv.2011.04.038
Maes et al, 2020 Maes, T., van Diemen de Jel, J., Vethaak, A. D., Desender, M., Bendall, V. A., van Velzen, M., & Leslie, H. A. (2020). You are what you eat, microplastics in porbeagle sharks from the North East Atlantic: Method development and analysis in spiral valve content and tissue. Frontiers in Marine Science, 7, 273. https://doi.org/10.3389/fmars.2020.00273
Masura, J., Baker, J., Foster, G., & Arthur, C. (2015). Laboratory Methods for the Analysis of Microplastics in the Marine Environment: Recommendations for quantifying synthetic particles in waters and sediments [Report]. National Oceanic and Atmospheric Administration Marine Debris Division. https://doi.org/10.25607/OBP-604
Napper, I. E., Davies, B. F. R., Clifford, H., Elvin, S., Koldewey, H. J., Mayewski, P. A., Miner, K. R., Potocki, M., Elmore, A. C., Gajurel, A. P., & Thompson, R. C. (2020). Reaching new heights in plastic pollution—Preliminary findings of microplastics on Mount Everest. One Earth, 3(5), 621–630. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.oneear.2020.10.020
Nava, V., Chandra, S., Aherne, J., Alfonso, M. B., Antão-Geraldes, A. M., Attermeyer, K., Bao, R., Bartrons, M., Berger, S. A., Biernaczyk, M., Bissen, R., Brookes, J. D., Brown, D., Cañedo-Argüelles, M., Canle, M., Capelli, C., Carballeira, R., Cereijo, J. L., Chawchai, S., . . . & Leoni, B. (2023). Plastic debris in lakes and reservoirs. Nature, 619(7969), 317–322. https://doi.org/10.1038/s41586-023-06168-4
Neelavannan, K., Sen, I. S., Lone, A. M., & Gopinath, K. (2022). Microplastics in the high-altitude Himalayas: Assessment of microplastic contamination in freshwater lake sediments, Northwest Himalaya (India). Chemosphere, 290, 133354. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.chemosphere.2021.133354
Negrete Velasco, A. D. J., Rard, L., Blois, W., Lebrun, D., Lebrun, F., Pothe, F., & Stoll, S. (2020). Microplastic and fibre contamination in a remote mountain lake in Switzerland. Water, 12(9), 2410. https://doi.org/10.3390/w12092410
Pandey, P., Dhiman, M., Chopra, P., & Adlakha, A. (2023). Investigating the role of tourists and impact of knowledge, behaviour, and attitude towards plastic waste generation. Circular Economy and Sustainability, 3, 1013–1027. https://doi.org/10.1007/s43615-022-00216-3
Pandita, A., & Pandita, D. (2020). Lotus (Nelumbo nucifera Gaertn). In: G.A. Nayik, A. Gull (Eds.), Antioxidants in vegetables and nuts - Properties and health benefits. Singapore: Springer. https://doi.org/10.1007/978-981-15-7470-2_2
Pedà, C., Romeo, T., Panti, C., Caliani, I., Casini, S., Marsili, L., Campani, T., Baini, M., Limonta, G., de Rysky, E., Caccamo, L., Perdichizzi, A., Gai, F., Maricchiolo, G., Consoli, P., & Fossi, M. C. (2022). Integrated biomarker responses in European seabass Dicentrarchus labrax (Linnaeus, 1758) chronically exposed to PVC microplastics. Journal of Hazardous Materials, 438, 129488. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jhazmat.2022.129488
Peng, X., Chen, M., Chen, S., Dasgupta, S., Xu, H., Ta, K., Du, M., Li, J., Guo, Z., & Bai, S. (2018). Microplastics contaminate the deepest part of the world’s ocean. Geochemical Perspectives Letters, 9, 1–5. https://doi.org/10.7185/geochemlet.1829
Qadir, J., & Singh, P. (2019). Land use/cover mapping and assessing the impact of solid waste on water quality of Dal Lake catchment using remote sensing and GIS (Srinagar, India). SN Applied Sciences, 1(1), 14. https://doi.org/10.1007/s42452-018-0027-6
Radhakrishnan, K., Sivapriya, V., Rajkumar, A., Akramkhan, N., Prakasheswar, P., Krishnakumar, S., & Hussain, S. M. (2021). Characterization and distribution of microplastics in estuarine surface sediments, Kayamkulam estuary, southwest coast of India. Marine Pollution Bulletin, 168, 112389. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.marpolbul.2021.112389
Ragusa, A., Notarstefano, V., Svelato, A., Belloni, A., Gioacchini, G., Blondeel, C., Zucchelli, E., De Luca, C., D’Avino, S., Gulotta, A., Carnevali, O., & Giorgini, E. (2022). Raman microspectroscopy detection and characterisation of microplastics in human breastmilk. Polymers, 14(13), 2700. https://doi.org/10.3390/polym14132700
Ranjani, M., Veerasingam, S., Venkatachalapathy, R., Mugilarasan, M., Bagaev, A., Mukhanov, V., & Vethamony, P. (2021). Assessment of potential ecological risk of microplastics in the coastal sediments of India: A meta-analysis. Marine Pollution Bulletin, 163, 111969. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.marpolbul.2021.111969
Ripken, C., Kotsifaki, D. G., & Nic Chormaic, S. (2021). Analysis of small microplastics in coastal surface water samples of the subtropical island of Okinawa, Japan. Science of the Total Environment, 760, 143927. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.scitotenv.2020.143927
Romeo, T., Pietro, B., Pedà, C., Consoli, P., Andaloro, F., & Fossi, M. C. (2015). First evidence of presence of plastic debris in stomach of large pelagic fish in the Mediterranean Sea. Marine Pollution Bulletin, 95(1), 358–361. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.marpolbul.2015.04.048
Sarkar, D. J., Das Sarkar, S., Das, B. K., Manna, R. K., Behera, B. K., & Samanta, S. (2019). Spatial distribution of meso and microplastics in the sediments of river Ganga at eastern India. Science of the Total Environment, 694, 133712. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.scitotenv.2019.133712
Sfriso, A. A., Tomio, Y., Juhmani, A., Sfriso, A., Munari, C., & Mistri, M. (2021). Macrophytes: A temporary sink for microplastics in transitional water systems. Water, 13(21). https://doi.org/10.3390/w13213032
Shah, R. A., Achyuthan, H., Krishnan, H., Lone, A. M., Saju, S., Ali, A., & . . . Dash, C. (2021). Heavy metal concentration and ecological risk assessment in surface sediments of Dal Lake, Kashmir Valley, Western Himalaya. Arabian Journal of Geosciences, 14, 1–13. https://doi.org/10.1007/s12517-021-06504-w
Shahul Hamid, F., Bhatti, M. S., Anuar, N., Anuar, N., Mohan, P., & Periathamby, A. (2018). Worldwide distribution and abundance of microplastic: How dire is the situation? Waste Management and Research, 36(10), 873–897. https://doi.org/10.1177/0734242X18785730
Smith, M., Love, D. C., Rochman, C. M., & Neff, R. A. (2018). Microplastics in seafood and the implications for human health. Current Environmental Health Reports, 5(3), 375–386. https://doi.org/10.1007/s40572-018-0206-z
Sruthy, S., & Ramasamy, E. V. (2017). Microplastic pollution in Vembanad Lake, Kerala, India: The first report of microplastics in lake and estuarine sediments in India. Environmental Pollution, 222, 315–322. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.envpol.2016.12.038
Sussarellu, R., Suquet, M., Thomas, Y., Lambert, C., Fabioux, C., Pernet, M. E. J., Le Goïc, N., Quillien, V., Mingant, C., Epelboin, Y., Corporeau, C., Guyomarch, J., Robbens, J., Paul-Pont, I., Soudant, P., & Huvet, A. (2016). Oyster reproduction is affected by exposure to polystyrene microplastics. Proceedings of the National Academy of Sciences of the United States of America, 113(9), 2430–2435. https://doi.org/10.1073/pnas.1519019113
Thompson, R. C., Moore, C. J., vom Saal, F. S., & Swan, S. H. (2009). Plastics, the environment and human health: Current consensus and future trends. Philosophical Transactions of the Royal Society of London. Series B, Biological Science, 364(1526), 2153–2166. https://doi.org/10.1098/rstb.2009.0053
Tsering, T., Sillanpää, M., Viitala, M., & Reinikainen, S. P. (2022). Variation of microplastics in the shore sediment of high-altitude lakes of the Indian Himalaya using different pretreatment methods. Science of the Total Environment, 849, 157870. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.scitotenv.2022.157870
van Emmerik, T., & Schwarz, A. (2020). Plastic debris in rivers. WIREs Water, 7(1), e1398. https://doi.org/10.1002/wat2.1398
Vidyasakar, A., Krishnakumar, S., Kasilingam, K., Neelavannan, K., Bharathi, V. A., Godson, P. S., Prabha, K., & Magesh, N. S. (2020). Characterization and distribution of microplastics and plastic debris along Silver Beach Southern India. Marine Pollution Bulletin, 158, 111421. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.marpolbul.2020.111421
Wright, S. L., Thompson, R. C., & Galloway, T. S. (2013). The physical impacts of microplastics on marine organisms: A review. Environmental Pollution, 178, 483–492. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.envpol.2013.02.031
Xiong, X., Zhang, K., Chen, X., Shi, H., Luo, Z., & Wu, C. (2018). Sources and distribution of microplastics in China’s largest inland lake—Qinghai Lake. Environmental Pollution, 235, 899–906. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.envpol.2017.12.081
Yang, J., Li, L., Li, R., Xu, L., Shen, Y., Li, S., Tu, C., Wu, L., Christie, P., & Luo, Y. (2021). Microplastics in an agricultural soil following repeated application of three types of sewage sludge: A field study. Environmental Pollution, 289, 117943. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.envpol.2021.117943
Yano, K. A., Geronimo, F. K., Reyes, N. J., & Kim, L. H. (2021). Characterization and comparison of microplastic occurrence in point and non-point pollution sources. Science of the Total Environment, 797, 148939. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.scitotenv.2021.148939
Zhang, K., Hamidian, A. H., Tubić, A., Zhang, Y., Fang, J. K. H., Wu, C., & Lam, P. K. S. (2021). Understanding plastic degradation and microplastic formation in the environment: A review. Environmental Pollution, 274, 116554. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.envpol.2021.116554
Zobkov, M., & Esiukova, E. (2017). Microplastics in Baltic bottom sediments: Quantification procedures and first results. Marine Pollution Bulletin, 114(2), 724–732. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.marpolbul.2016.10.060
Acknowledgements
The authors would like to express their gratitude to Head of the Department of Geology at the University of Madras, Guindy Campus, Chennai‐600025, India for generously providing laboratory facilities for conducting this study. The authors are grateful to the GNR Instrumentation Centre, Central Instrumentation Facility, University of Madras, Guindy Campus, Chennai for providing with the Raman spectroscopy.
Funding
This research did not receive any specific grant from funding agencies in the public, commercial, or not-for-profit sectors.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Conflict of Interest
The authors declare that they have no conflict of interest.
Additional information
Publisher's Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Supplementary Information
Below is the link to the electronic supplementary material.
Rights and permissions
Springer Nature or its licensor (e.g. a society or other partner) holds exclusive rights to this article under a publishing agreement with the author(s) or other rightsholder(s); author self-archiving of the accepted manuscript version of this article is solely governed by the terms of such publishing agreement and applicable law.
About this article
Cite this article
Nazir, A., Hussain, S.M., Riyaz, M. et al. Microplastic Pollution in Urban-Dal Lake, India: Uncovering Sources and Polymer Analysis for Effective Assessment. Water Air Soil Pollut 235, 89 (2024). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11270-024-06901-3
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11270-024-06901-3